Moving Apps to SD Card [Full Guide]
Feb 05, 2026 • Filed to: SD Card Solutions • Proven solutions
If your Android phone comes with inadequate internal storage space for your needs, we will show you how to move apps to the SD card and free up space.
The latest phone brands come with massive internal storage space. But if you have an older phone, extra capacity comes at a premium. A large amount of your phone's internal storage is already occupied by the operating system and bloat apps that come pre-installed. Once you start downloading your apps, you run out of space.
Thankfully, many Android devices have micro SD slots. This allows you to expand your capacity by investing a few dollars in a micro SD card. You can move applications to the SD card using Android's in-built features.
Important Information On How to Move Apps to SD card
But, before we get into the methods to move apps to the SD card, a bit of housekeeping.
First, not all devices support moving apps to an SD card or installing some of the elements of an installed application on an SD card. This feature is disabled on many high-end phones with large internal memories but remains available on most medium to low-end phones to allow users to extend the storage capacity.
Secondly, if your phone supports moving apps to an SD card, there is no guarantee that all apps can move. Many apps are hard-wired to store most of their data on the internal storage. That said, you can still save a lot of data by transferring movable apps to the memory card.
Part 1. How to Move Apps to SD card
There are two ways to move apps to an SD card using Android's in-built features.
Method 1. Using the Application Manager
Before we begin, it is important to note that there are several Android versions. So the actual route you take will differ slightly depending on your Android version. But, on all versions, the idea is to look for the Application folder in your phone's settings, tap the application and then look for an option to Change Storage or Move to an SD card. Below is an example of the steps to follow in Android Nougat.
- Navigate to Settings > Apps. Scroll down to identify the application you want to transfer to the micro SD card and tap on it.
- Select Storage. If the app is movable, you will see a section labeled Storage used. Tap the Change button.
- Select your SD card and then tap Move.
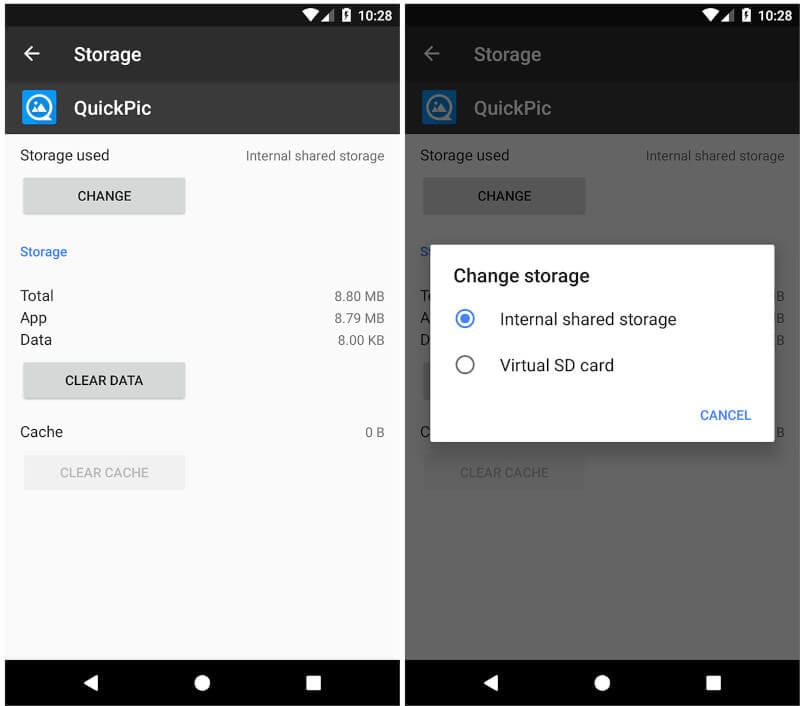
However, in later versions of Android and on some specific devices, moving apps to SD Card fully isn't supported. If this method doesn't work for you move on to the second method.
Method 2. Format SD Card as Internal Storage
Changes to the way phones handle SD Cards were first seen in the Android Marshmallow version. You can set the external storage to operate as the internal storage. This feature is referred to as Adoptable storage. Rather than having the operating system view these as two separate spaces, it views the external storage as an extension of the internal memory.
Applications and data can be written to either space as needed and seamlessly. Once set up, the user need not worry about the location of applications.
The setup process erases the SD card so you have to perform a backup before you begin. You can back up your data using a cloud application like Google. Simply open the Google Drive app and tap Backups to create a backup.
Next, follow the steps below to format the SD Card as internal storage.
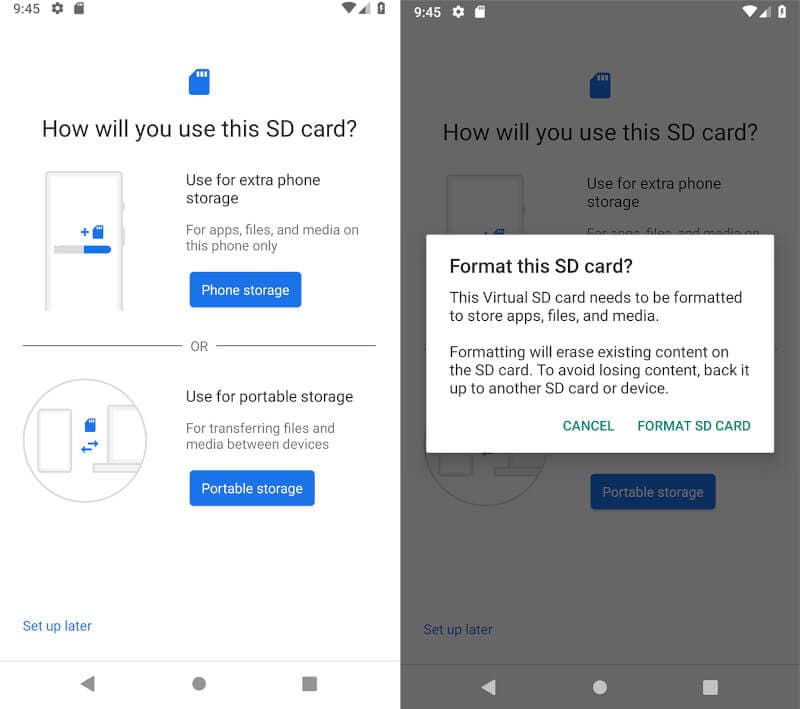
- Insert the card into the smartphone. A New SD Card notification will pop up, tap Set Up.
- Next, select how you want your phone to use the card. On Android Pie, select Phone Storage. On older versions, select Use as Internal Storage. You can also go to Settings > Storage, tap the SD card, then the menu button, select the Storage Settings, and then Tap Format as internal.
- Next, tap Format SD Card, or Erase & Format depending on your Android version. This creates a new partition and rewrites the file system. In the process, all contents are erased.
- If you using Android Pie, you will also have the opportunity to move your content and apps into the SD card. Tap Move Content to complete the process.
If you decide to use this method, you must keep your card on your phone at all times. The feature encrypts the SD card which means you can not use it on any other device. Unfortunately, not all manufacturers offer Adoptable storage.
Part 2. Problems of Moving Apps to SD Card
Have you encountered trouble moving apps to an SD card? For some apps, the option to move the app to the SD card may be greyed out or not available. If you have, then there are some reasons this could be happening.
Reason 1. Developer Choice
There are Android design elements that must be explicitly configured to enable the transfer of an app to the SD Card. If this isn't configured, then then the fix becomes more technical.
So why would a developer do this? Well, apps don't work on the external storage if it isn't mounted. So, if you happen to remove your SD card from a phone and are using it on another device, the app is unavailable. Developers want their products "always on" so they prefer to "switch off" the feature to move apps to an SD card. Also, no one wants to contend with 1-star reviews by non-technical users who claim an app isn't working.
Reason 2. Specified Functions
But, the second major reason apps can't be moved or installed on external storage is if the app is designed to use certain specified functions. These functions are:
- Account Managers
- Alarm Services
- App Widgets
- Broadcast Receivers listening for "boot completed"
- Device Administrators
- Input Method Engines
- Live Wallpapers
- Services
- Sync Adapters
Any app that uses any of the above features is by default configured not to install or transfer to external storage. This ensures it doesn't break and operates as expected.
How to Move Unmovable Apps to SD Card
So, does this then mean that you must use your phone and storage as developers want you to? On the contrary, if you have a good reason to move an app that is configured not to move, there are two methods you can use to force the app or elements of the app to move to the SD card.
Method 1. Copy or Move Files and Folders
This method involves using special free third-party apps to move some elements of apps to the SD card. This includes media folders, downloads, and other data.
One of these apps is known as Files To SD card and is available for free on the Google Play store.
1. Download and install the app, then tap to open it.
2. It will show you a list of apps and folders that you can transfer.
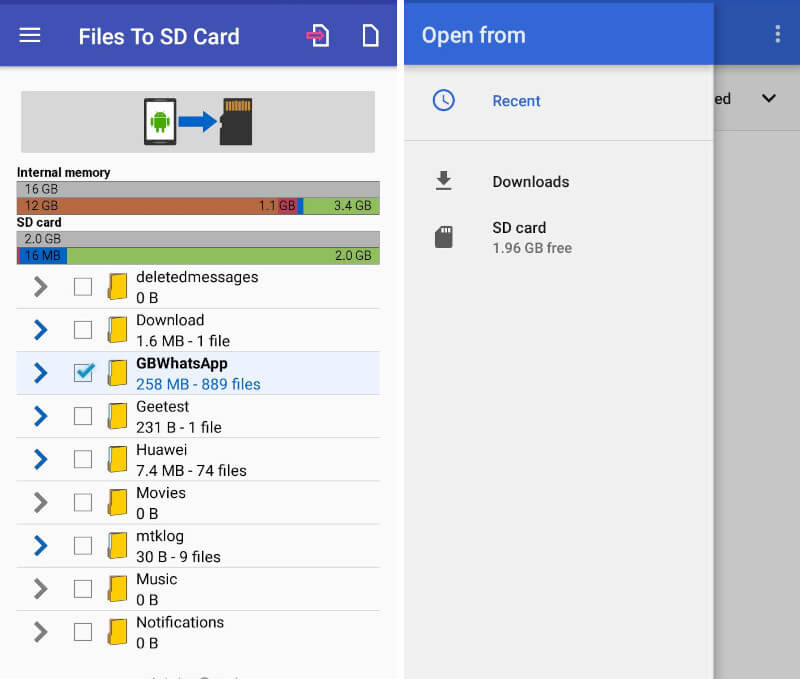
3. Select the app and/or folders you want to move then give the app permission to use the SD card by clicking select.
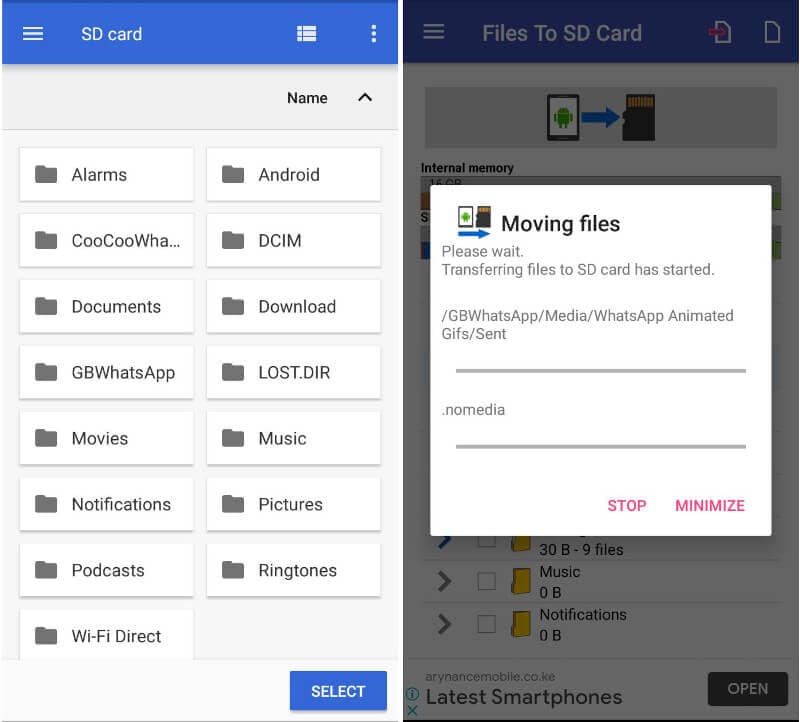
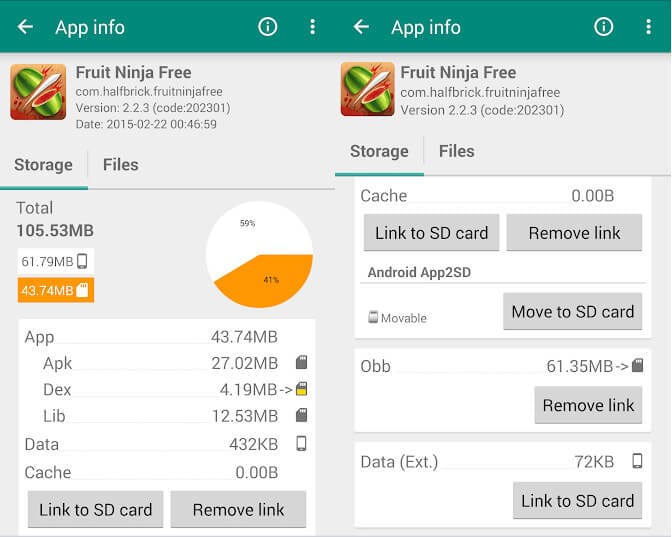
4. The app will start moving the files and notify you when done.
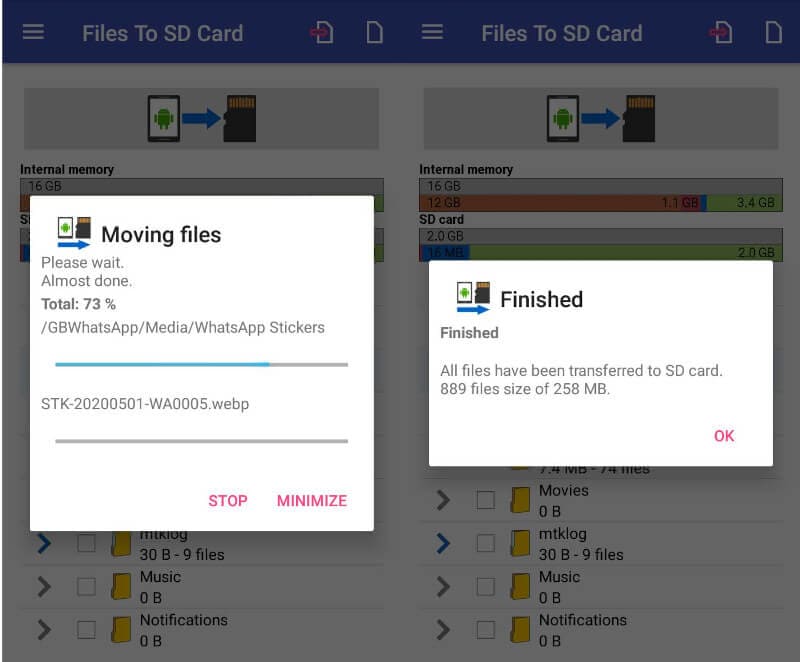
Note that this method will not move the apps system files but it does free up your internal storage.
Method 2. Rooted method
To move an entire application you must root your phone. Rooting the phone means getting administrator privileges. This allows you to modify the phone's system applications and settings.
As an administrator, you can overcome limitations placed by developers, device manufacturers, and mobile phone carriers. You can also run special apps that require administrator-level permissions - to transfer unmovable apps, you can root the phone and then install such an app.
A word of caution before we begin. Rooting a phone is a technical issue and you must take the time to learn about the risks before you start. One of the disadvantages is that you void your phone's warranty. Also, one wrong move and you could brick your phone.
There are different ways to root your phone depending on your device. The easiest way is to use a free rooting app. Some popular free apps include KingoRoot, iRoot, King Root, FramaRoot, and Towel root. To install these apps, you have to download them from the respective developer websites and follow the instructions provided.
Assuming you have successfully rooted the phone, head to the Google Play Store and download the Link2SD, a free app. The app has root permissions that enable it to use a secondary partition on your SD card as internal storage. To create this secondary partition, you will need to use another free app known as AParted which also needs root access.
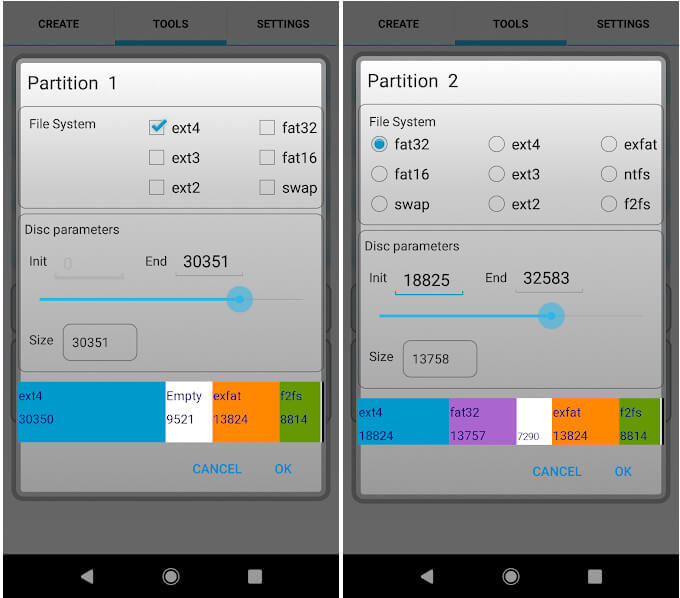
Perform a backup of your SD card and then use AParted and create two partitions on your SD card. One of the partitions should be formatted in the FAT32 file system which is where you will store your regular data. The other partition should use the ext2, ext3, ext4, or f2fs file system to link the application's private data files.
After that, reboot the phone, open Link2SD again, and move the applications to the SD card.
Let’s now examine what to do if you lose files while using transferring applications.
Part 3. How to Recover Lost Files from SD Card?
Formatting as internal storage, rooting the phone, and formatting partitions can lead to accidental file deletion. This is why we recommend backing up your SD card before attempting any of the solutions and methods we have described above.
However, mistakes do happen. In the event you have inadvertently formatted your SD card before making a backup, it is possible to recover your data.
The first thing you should do once you realize the mistake is to avoid any further data being written to the SD card. Take it out of the phone.
After that, get your PC and download Wondershare Recoverit data recovery software. This is a powerful tool that uses advanced algorithms to scan storage devices and recover deleted data.
Wondershare Recoverit is compatible with Windows and Mac. The tool can recover data in over 1,000 types and formats. It also comes with a video repair tool which is great if you accidentally erased your prized personal videos.
Once you have downloaded the tool, double click the download file and follow the instructions to install it. After this, you can launch the application by clicking the shortcut icon on the desktop. If you can't find a shortcut icon, go to the Windows search box and type "Recoverit". Click the app or choose to "Open" it and connect the SD card to the PC.
After that, it is a mere three steps as follows.
Step 1. Select the SD Card
In the window, identify your SD card in the SD Card section. Select the SD Card and then click Scan to begin the data recovery process.
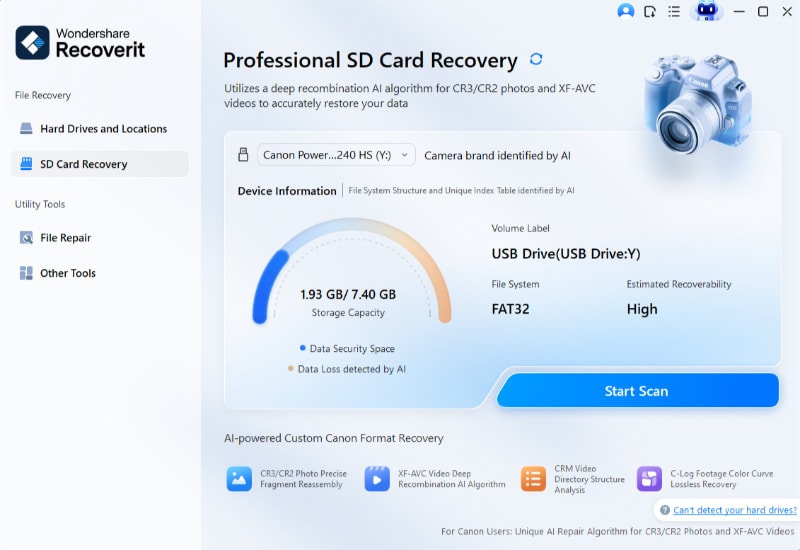
Step 2. Scan the SD Card
In the next window, all-around scan launches. A progress bar lets you see the progression of the process. This process can be paused and restarted.
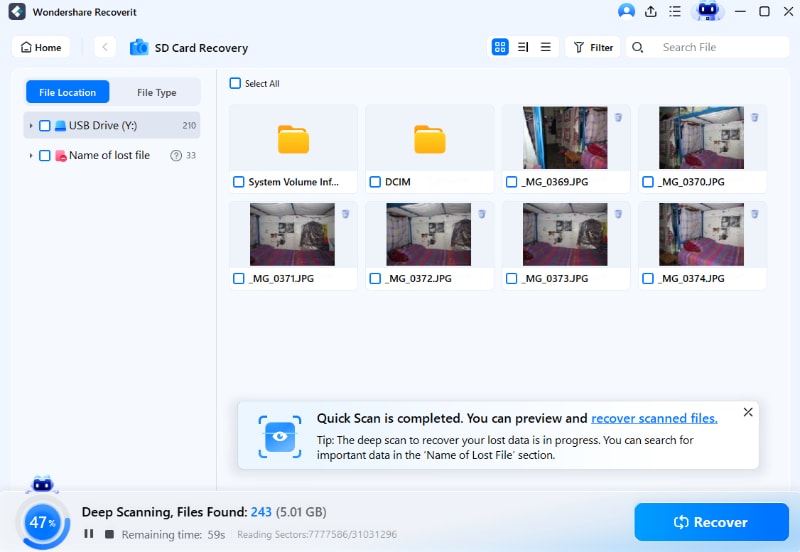
Step 3. Preview and recover files from the SD Card
The next window is an interface that allows you to select the files you want to recover and save them in a different location on your computer.
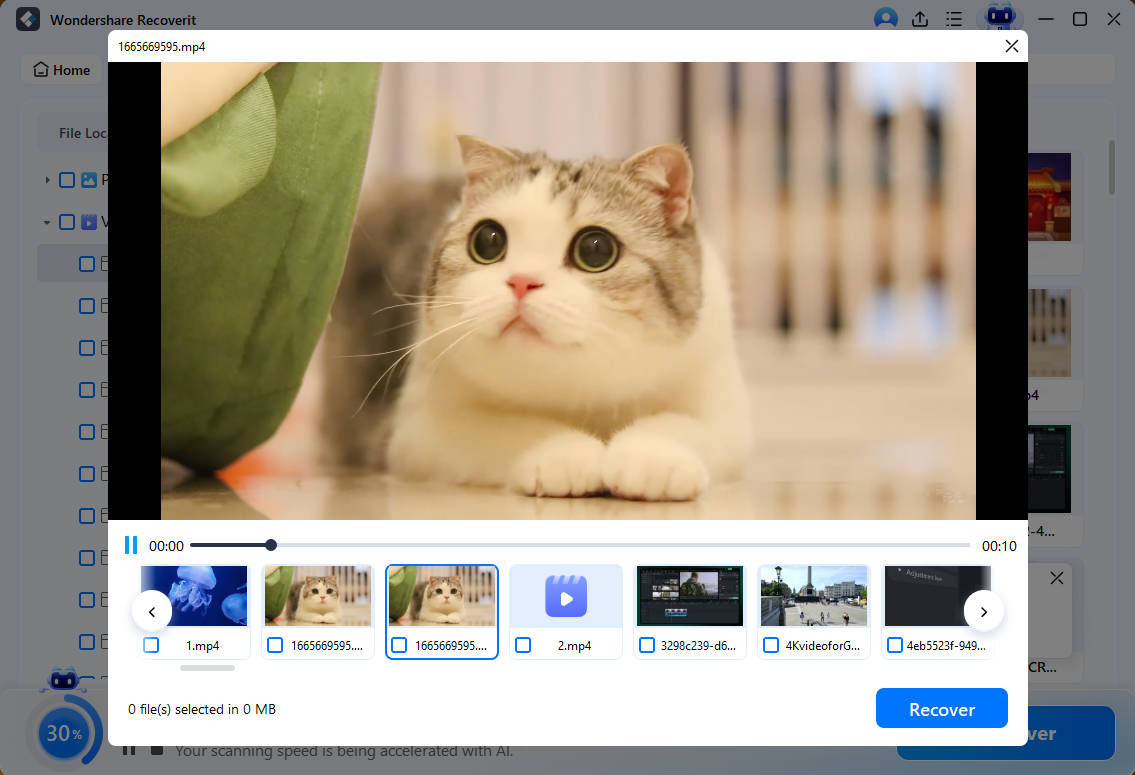
Let’s now examine the conventional wisdom on transferring applications to external storage.
Part 4. Pros and Cons of Moving Apps to SD Card
Moving apps to SD cards isn't generally recommended unless you are using a low-end phone with a small internal memory or you have exhausted your phone's internal memory.
Some of the issues you may want to consider before you move an app are explained below.
1. Speed: Most SD cards on the market are slower than phone processors. So, the first thing you notice when you move your apps is a drop in performance. Depending on the specifications of your SD card, the speed could be severely compromised. If you plan on using the SD card to store app media, consider using a premium card with a UHS-I or class 10 rating. If you plan moving entire apps, then use a card with a high bus interface app performance rating of A2.
2. Disappearing Shortcuts and Forgotten Passwords: When you completely move apps to an SD card, you are likely to encounter some instances of vanished shortcuts, widgets, and passwords anytime your device powers down.
3. Finding files becomes difficult: Even though formatting an SD card as adoptable internal storage turns it into part of the internal storage, there is no guarantee that your phone model will view them as a single entity. Finding files may become problematic as your storage becomes more fragmented. In some scenarios, you may even end up with duplicates.
4. Failure: SD cards have a finite number of read/write cycles when they roll off the production line. According to the SD Card Association, normal card usage guarantees you at least 10 years of usage. But, when you use an SD card as internal storage, the read and write instances are dramatically increased. The card may end up going through its lifespan in a short time.
5. Migration to a New Phone is difficult: When you use an SD card as adoptable storage, it is encrypted and "locked" to that device. So don't expect to eject it and use it on a new device seamlessly. You have to format it first and doing so erases all the data.
6. Gaming Performance: If you are an avid gamer, don't expect to get the same performance you get from an SD card as you do from the internal storage. Even the high-performance cards aren't able to keep up with the demands of some modern Android games.
7. App updates: During app updates, the device will move the apps back to the internal storage for the update to take place. So, you will find yourself having to move apps back after each update.
More Related:
Transfer Files from C Drive to D Drive
3 Methods to Transfer Files from PC to SD
Conclusion
Transferring or moving applications to your external storage depends a great deal on your Android version, whether your device manufacturer has implemented the features and the specific application you want to move.
Moving Apps to SD Card FAQ
-
1. Why can't I move some apps to SD Card?
Some applications are hardwired by developers to reside on the internal storage. Also, some phone manufacturers and mobile carriers choose to "switch off" this functionality. -
2. How do I get apps to download directly to the SD Card?
On your phone, go to Settings>Storage and change the default storage location to the SD Card. -
3. Which apps can I move to the SD card?
Applications configured to move by the developer can be transferred. But apps that are configured to reside on the internal storage cannot be moved without rooting the device. -
4. Why do my apps keep moving from my SD card?
Before you can move an app to the external storage, it must first be installed in the internal storage. During app updates, the app is moved back to internal storage for the update. You have to move it back manually. -
5. Should I use my SD card as internal storage?
This is generally not a good idea if you intend to use the external storage on other devices. If you choose to do so, the external storage can only be used on the device.



 ChatGPT
ChatGPT
 Perplexity
Perplexity
 Google AI Mode
Google AI Mode
 Grok
Grok























Eleanor Reed
staff Editor