What should you do in the Linux terminal if you wish to delete files? Most people use the rm command. But there's another method. You can use the unlink Linux command instead. It deleted files or links from the system. You may read more about how to use this command in this article.
But what if you accidentally unlinked the wrong file? Can you recover it? The answer to this question is also provided below.
How To Use Unlink Command on Linux
unlink sounds like it only removes links from the system. You probably never thought of using this command to delete files. But it works.
Why is that? Deleting processes in Linux is essentially unlinking. Here's what happens when you delete a file. The Linux kernel finds that the file corresponds to inode number X. Then, it will remove the file entry from its directory's listing. On top of that, the kernel will subtract 1 from the inode's link count, making it 0.
Because the inode's link count is now 0, the kernel knows that nothing is linking to it. It learns that removing the inode and the associated data block is safe. And that's how the unlink command works.
The syntax for the unlink command is: unlink filename
Here are the ways how to use this command:
Example 1: Remove a Particular File on Linux
Suppose you want to delete a particular file on Linux. You can use the unlink command for that. To do this, select the name of the file you want to delete. In this example, let's assume you have a file named "file2delete.txt."
Type the following command: unlink file2delete.txt
And that's it. The command will remove the file from the system.
Example 2: Using the Unlink Command to Remove an Actual Link
Of course, the unlink command works for removing soft links in the system. A soft link is a specific file that acts as a reference. To perform this, locate the directory where the soft link is stored. Suppose you want to delete the "file2delete.txt" file in the "Office" directory.
Access the directory and type this command: unlink /home/yourusername/Office/file2delete.txt
This command will remove the file from the directory.
Example 3: Delete the Soft Link of the Directory
Aside from removing files and soft links, the unlink command also helps remove the directory link from the system. Suppose there is a "Soft_dir" directory link in the "Home" directory.
Enter the following command: unlink Soft_Dir
Confirm that the directory soft link has been removed by typing the command that follows: ls
You can't remove an actual directory using the unlink command. It will output the message: cannot unlink 'directory name': Is a directory.
You may also be interested in: Remove Symbolic Link in Linux
Tips/Notes When Using the unlink Command
Here are some notes that you should keep in mind.
1. Unrecoverable Data
Please be careful. Know the correct file name or soft link you want to remove. Also, ensure that you type it on the terminal window correctly. Why? Because once you delete it, you can't fully recover it without a professional Linux data recovery software.
2. Files or Links Cannot be Deleted at Once
The unlink command and rm commands are different. unlink uses the unlink system command. On the other hand, the more powerful rm command uses an unlink at system call. One of the most glaring differences is that unlink can only handle one argument at a time. Because of how it works, you can only delete one file in one go. Meanwhile, the rm command does not have this limitation as it can remove multiple files at once.
If you try this, it throws an error and does not delete any files. For example:
unlink *.txt
unlink: extra operand ‘file2.txt’
Try 'unlink --help' for more information.
The same is true for deleting multiple links at the same time.
3. You Can’t Delete Directories With Unlink
Another difference between the unlink and rm commands is the ability to delete directories. As discussed above, the unlink command can't do this.
If you execute the following command: unlink new_dir
It will show this output:unlink: cannot unlink 'new_dir': Is a directory
How To Recover Files Accidentally Deleted by unlink in Linux?
Mistakes take time to avoid. Thus, you may accidentally delete the wrong files using unlink command on your Linux computer. What do you do when this happens? Don't panic. There's a reliable solution to that. You can use Wondershare Recoverit, a software designed for data recovery. It has a Linux File Recovery feature, allowing you to bring back your deleted files from Linux devices.
The following are some of the key attributes of Wondershare Recoverit Linux Recovery:

Wondershare Recoverit - Your Safe and Reliable Linux Recovery Software
5,481,435 people have downloaded it.
Recovers lost or deleted documents, photos, videos, music, emails, and other 1000+ file types effectively, safely, and completely.
Compatible with all mainstream Linux distros, including Ubuntu, Linux Mint, Debian, Fedora, Solus, Opensuse, Manjaro, etc.
Assists in 500+ data loss scenarios, such as deletion, disk formatting, OS crash, power outage, virus attack, lost partition, and many more.
The simple point-and-click interface allows you to recover data from Linux hard drives in just a few clicks.
Works through a remote connection. You can recover lost data even when your Linux device is crashed.
Wondershare Recoverit provides a straightforward and effortless solution for recovering Linux data in only three simple steps.
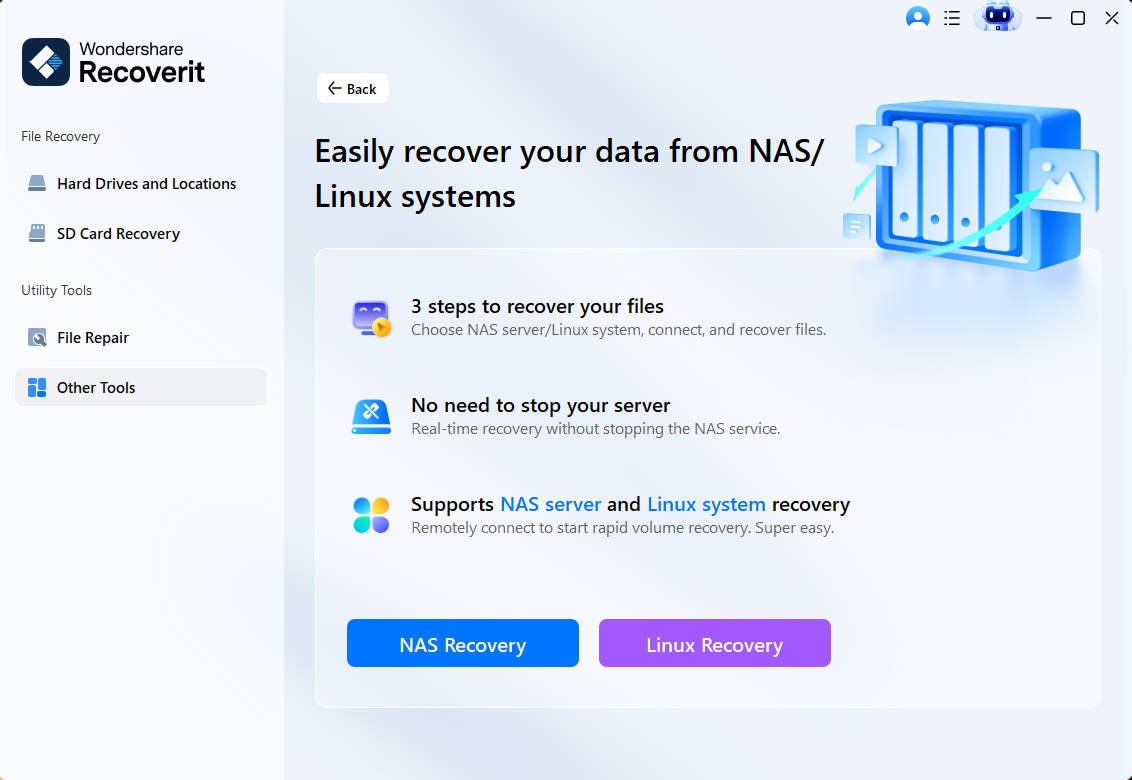
Step 1Click Linux Recovery
Launch the software once you have installed Wondershare Recoverit on your computer. Select the NAS and Linux options, and then opt for the Linux Recovery option.
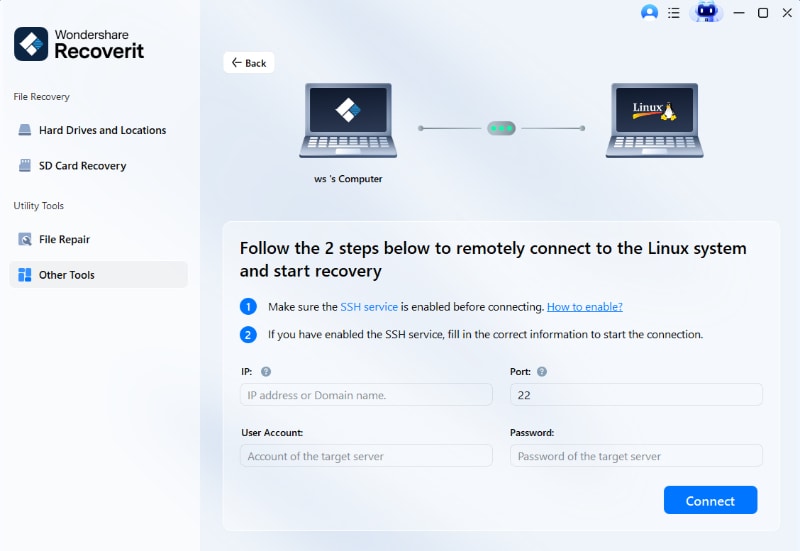
Step 2Create a Remote Connection
Upon selecting Linux Recovery, a new window will emerge on your screen. Fill in the necessary details to establish a remote connection and click the Connect button.
After establishing the remote connection, Recoverit will automatically scan your Linux computer to locate missing files.
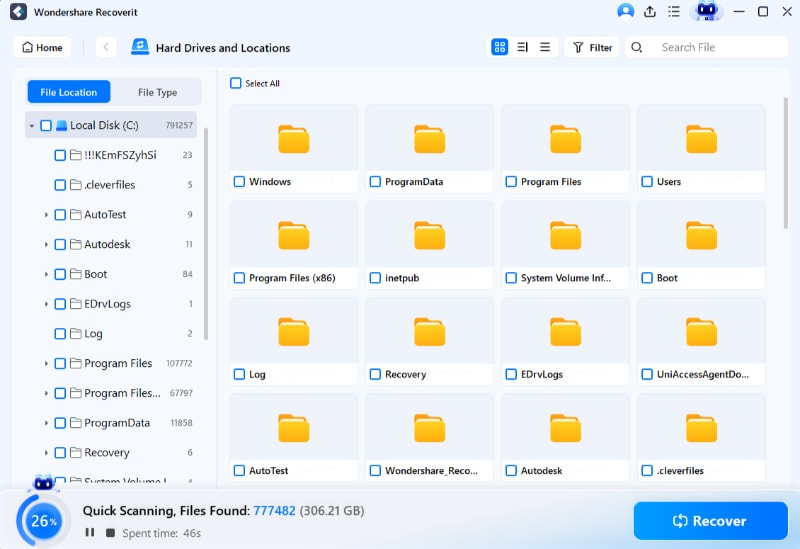
Step 3Preview and Restore Deleted Files
Recoverit offers the convenience of stopping the scanning process at any point once you have found the file you want to recover. After scanning, you can preview the files to verify that they are the ones you want to recover. Finally, select all desired files or folders and click Recover to save them.
For Windows Vista/7/8/10/11
For macOS X 10.10 or later
Conclusion
The unlink command allows you to remove files and links from the Linux system. It's a great alternative to the rm command, especially if you want to delete only one file or link. Suppose you removed the wrong files; you can use Wondershare Recoverit to find and recover them.