
You must carry out Linux disk partition Formatting beforehand if you're a Linux user. Additionally, the Linux Format Disk procedure can be helpful for other purposes, such as changing the file system, rectifying errors, or deleting all data. Linux disk partition formatting is actionable through two techniques: using GUI or CLI.
Part 1. Check Hard Drive Disk Partition Before Formatting
Check the hard drive partition you want to format before you do anything else. This step is necessary to determine how many partitions of hard disks you have and which file system they operate. Run the lsblk command, which lists block devices, to perform this. Block devices are files that represent several types of hardware, including CD/ROM drives, USB drives, RAM disks, and hard disks.
lsblk
The terminal outputs a list of all block devices along with details about each one:
- NAME: Device names
- MAJ: MIN: Major or minor device numbers
- SIZE: The size of the device
- TYPE: The type of the device
- RM: Whether the device is removable (1 if yes, 0 if no)
- RO: Whether the device is read-only
- MOUNTPOINT: Device's mount point
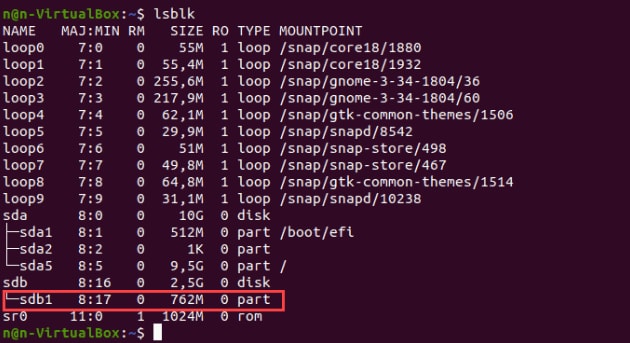
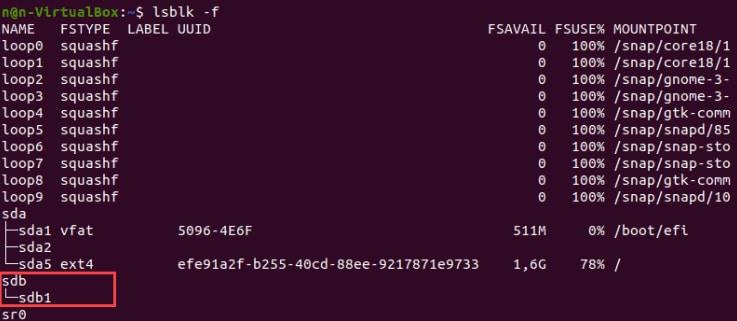
Add the -f option to display a list with information about the file system.
The terminal will show the list of all block devices. Non-formatted partitions do not hold data on the active file system.
Part 2. How to Format a Hard Drive Disk Partition in Linux?
For Win 7 or later (64-bit)
For macOS 10.12 or later
Depending on the tools utilized, there are two ways to format drive Linux. The one is carried out using GUI through GParted, which is more convenient for users with a less technical background. The other method is partitioning the disk using CLI, a complex process used by tech-savvies.
Depending on the kind of file system, there are three ways to format disk partitions with the mkfs command:
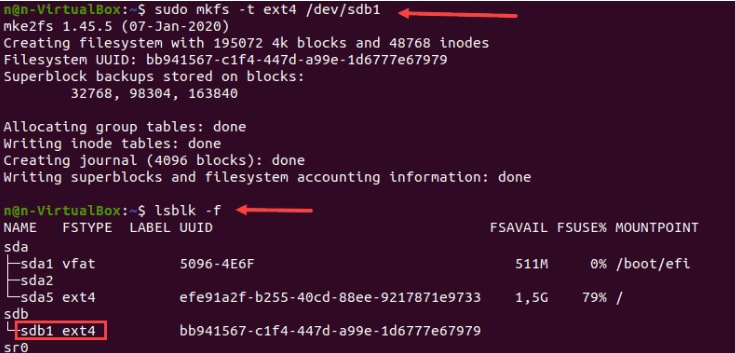
1. Format Hard Drive Disk Partition with ext4 File System
Step 1: Use the following command to format a disk partition with the ext4 file system:
sudo mkfs -t ext4 /dev/sdb1
Step 2: Next, use the following command to confirm the file system change:
lsblk –f
The terminal will list all the block devices.
Step 3: Locate the preferred partition and ensure it uses the ext4 file system.
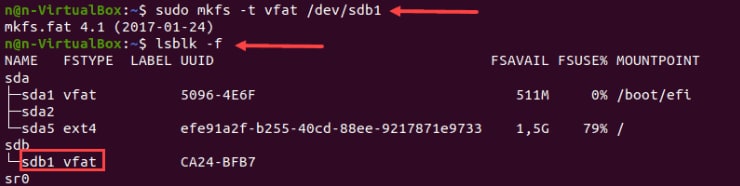
2. Format Disk Hard Drive Partition with FAT32 File System
Step 1: For a FAT32 file system disk format, use the following command
sudo mkfs -t vfat /dev/sdb1
Step 2: To find the selected partition from the list and confirm the file system change, reissue the lsblk command.
Step 3: The output will be:
3. Format Hard Drive Disk Partition with NTFS File System
Step 1: To format a drive partition, use the mkfs command for the NTFS file system:
sudo mkfs -t ntfs /dev/sdb1
When the formatting process is finished, the terminal prints a confirmation message.
Step 2: After that, confirm the file system change by using the following:
lsblk –f
Step 3: Identify the desired partition and make sure the NFTS file system is being used.

Part 3. How to Mount Disk or Partition in Linux?
Make a mount point and mount the partition before utilizing the disk. A directory known as a mount point is used to access data on disks.
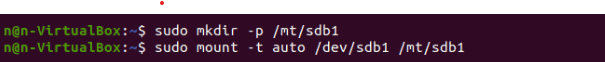
Step 1: To make a mount point, type:
sudo mkdir -p [mountpoint]
Step 2: Next, mount the partition by executing the command below:
sudo mount -t auto /dev/sdb1 [mountpoint]
If the operation is successful, there isn't any output.
Step 3: Use the below command to see if the partition is mounted:
lsblk –f
The output will be:

Part 4. How to Recover Data from a Formatted Hard Drive?
Although it always remains an excellent option to keep an additional backup of your important files and data; but, suppose you have formatted your disk accidentally or thoughtlessly and lost your valuable data without prior backup; what to do in such a situation? In that case, it is recommended to use reliable recovery software that might help your recover lost files. Recoverit is the top-notch hard drive recovery solution to retrieve your essential data.
Operational steps:
Step 1: Locate the Ext4 Data by Scanning It
Install the software, scan, choose where the Ext4 data is stored on the hard disk, and initiate Scanning.
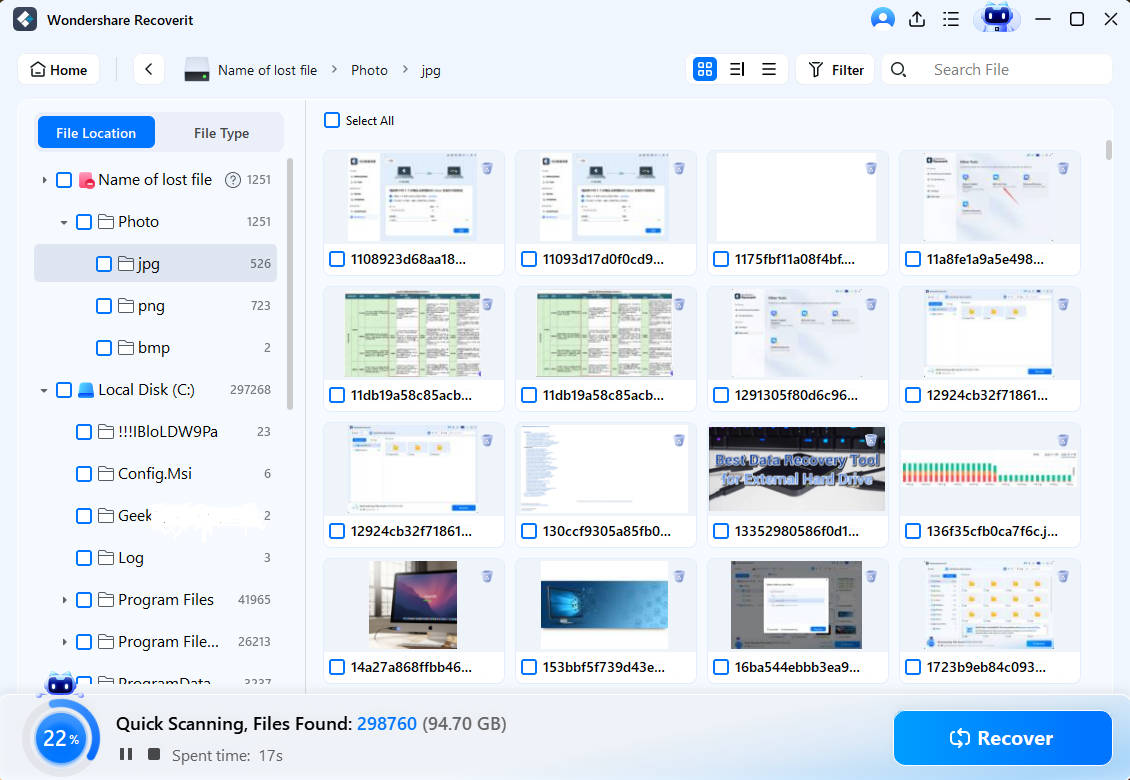
Step 2: Displaying Retrieved Ext4 Data on Your Linux OS
Your Ext4 Linux partition's whole retrievable data will be displayed immediately after the scanning procedure is finished.
Step 3: Preview the Scanned Files
View and locate the recoverable files once the Scanning gets completed.
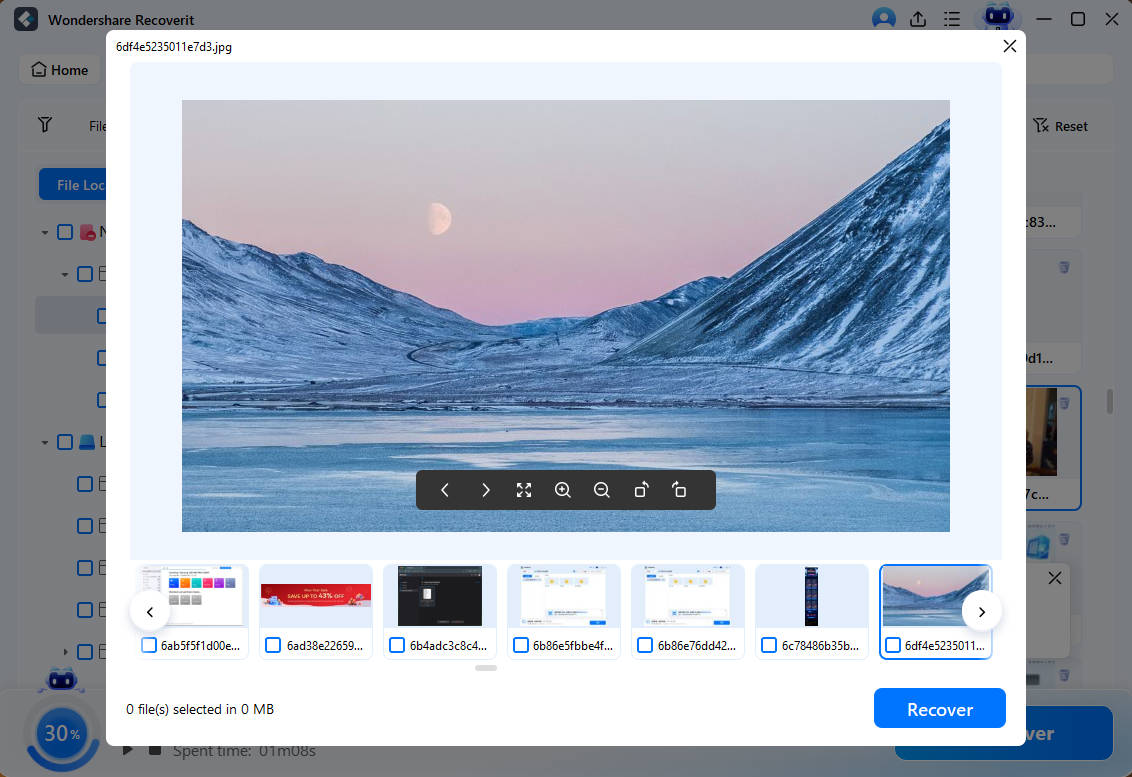
Step 4: Recovering Desired Files
Now, you can select the particular files you need to recover and instantly click on the Recover button.
Conclusion
Linux is one of the most popular open-source Unix operating systems. On Linux, formatting a drive disk partition is a simple procedure. You must concentrate on a few things and complete Linux Format Disk effectively. You have a comprehensive method for formatting the ext4 file system, the FAT32, and the NTFS file system perfectly.
For Windows XP/Vista/7/8/10/11
For macOS X 10.10 or later
FAQs
What does Linux format partition mean?
Formatting prepares the Linux operating system for use for the first time. The storage space on a device can be made available through formatting. Usually, when Linux is formatted, one or more file systems are formed.
Why is it necessary to format the hard disk partition?
Hard disk partition formatting allows you to prepare your hard drive for its first use. Moreover, it makes your space allocable for OS installation, data storage, and other purposes.
What to do before a format drive Linux?
Formatting a hard disk removes all your data from the hard drive. To prevent this, we suggest backing up your data if you decide to format a hard disk in Linux.
How do I format a disk in Linux?
On Linux, wiping off a drive is not a difficult task. You have three easy-to-use methods to make the process mentioned above possible.
How to recover accidentally lost data during a hard drive disk partition formatting?
An endless array of software is available to retrieve data lost during formatting; however, we recommend using Recoverit, a one-stop solution for all your recovery-related worries.
What is the mkfs command in Linux OS?
The mkfs command stands for "make file system," usually used to create a file system on a formatted storage media, typically a partition on a hard disk drive (HDD). A file system is a system for organizing a hierarchy of directories, subdirectories, and files.
For what purpose Sudo command is used?
It is one of the most well-known fundamental Linux commands that enables you to carry out various operations requiring administrative or root permissions. Usually, the command runs for fifteen minutes.
Why is the mkdir command used?
This command is typically used to create one or more folders at once. Additionally, we may use this command to specify permissions for each guide.

 ChatGPT
ChatGPT
 Perplexity
Perplexity
 Google AI Mode
Google AI Mode
 Grok
Grok






















