How do I recover permanently deleted files from Ubuntu? – Quora
Every PC user has to deal with losing data at some point. We have all experienced circumstances where we wished we could recover the erased data, whether due to a hard drive crash or an accidentally deleted file. Fortunately, unlike other operating systems, Linux makes it easier to restore deleted files. By reading this article, you can learn how to recover deleted files in Linux.
Here is an overview of the solutions to perform Linux deleted file recovery.
Solution |
Solution Type |
| Recover Deleted Files From Linux Trash | Only for Soft Deletion |
| Recover Deleted Files/Folders/Partitions on Linux Using Wondershare Recoverit | GUI Tool |
| Recover Deleted Files on Linux Using R-Linux | GUI Tool |
| Recover Deleted Files on Linux Using R-Studio | GUI Tool |
| Recover Deleted Files on Linux Using TestDisk | Command Line Tool |
| Recover Deleted Files on Linux Using PhotoRec | Command Line Tool |
| Recover Deleted Files on Linux Using Extundelete | Command Line Tool |
| Recover Deleted Files on Linux Using Foremost | Command Line Tool |
Method 1: Recover Deleted Files From Linux Trash (For Soft Deletion)
Like Windows and Mac operating systems, Linux also has the Trash feature for storing softly deleted files. Therefore, if you've deleted some important files using the Delete button on your keyboard, you can find them in the Trash and restore them instantly.
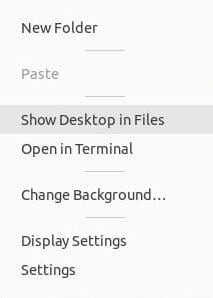
Step 1. Open your file manager by right-clicking on a blank space on your Desktop and selecting Show Desktop in Files from the context menu.
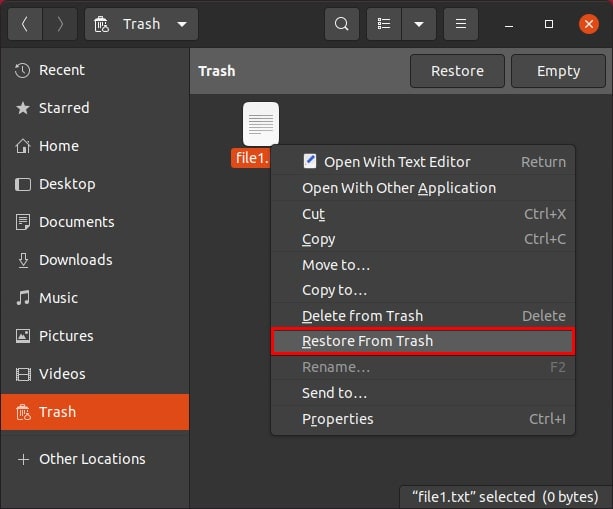
Step 2. Select Trash from the left sidebar. Right-click the file you want to recover to its original location and select Restore From Trash.
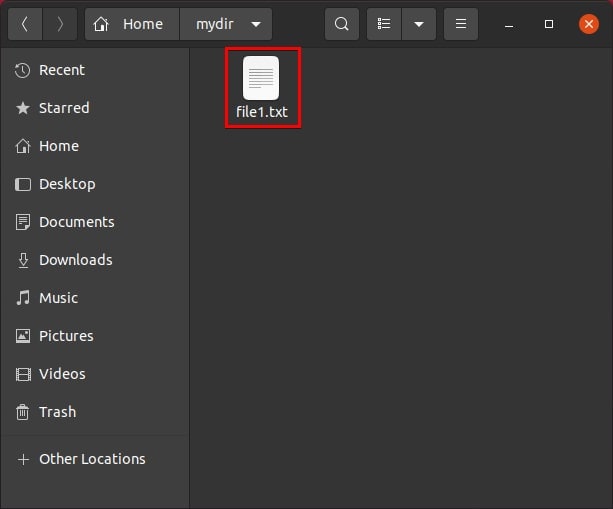
Step 3. Explore the original location of your deleted file to verify that it has been successfully restored.
However, if you delete your files permanently using Shift + Del, you must go for the following solutions.
Method 2: Recover Deleted Files/Folders/Partitions on Linux Using Wondershare Recoverit (GUI Tool)
Several methods and software tools are available to recover a deleted file in Linux. However, you should select the best of the best! It is why Wondershare Recoverit Linux Recovery is a top recovery tool recommendation for all users. Wondershare Recoverit can recover deleted files/folders/partitions in Linux. It was created with the primary goal of recovering all types of data loss.

Wondershare Recoverit – Almighty Linux Data Recovery Tool
5,481,435 people have downloaded it.
Compatible with all mainstream Linux distros, including Ubuntu, Linux Mint, Debian, Fedora, Solus, Opensuse, Manjaro, etc.
Assists in 500+ data loss scenarios, such as deletion, disk formatting, OS crash, power outage, virus attack, lost partition, and many more.
Recovers lost or deleted documents, photos, videos, music, emails, and other 1000+ file types effectively, safely, and completely.
The simple point-and-click interface allows you to recover data from Linux hard drives in just a few clicks.
To restore your deleted files on Linux using this Linux file recovery software, follow the instructions below:
Step 1. Choose Linux Recovery
Download and install Wondershare Recoverit on a Windows or Mac PC. Start the program and select NAS and Linux. Then, click Linux Recovery.
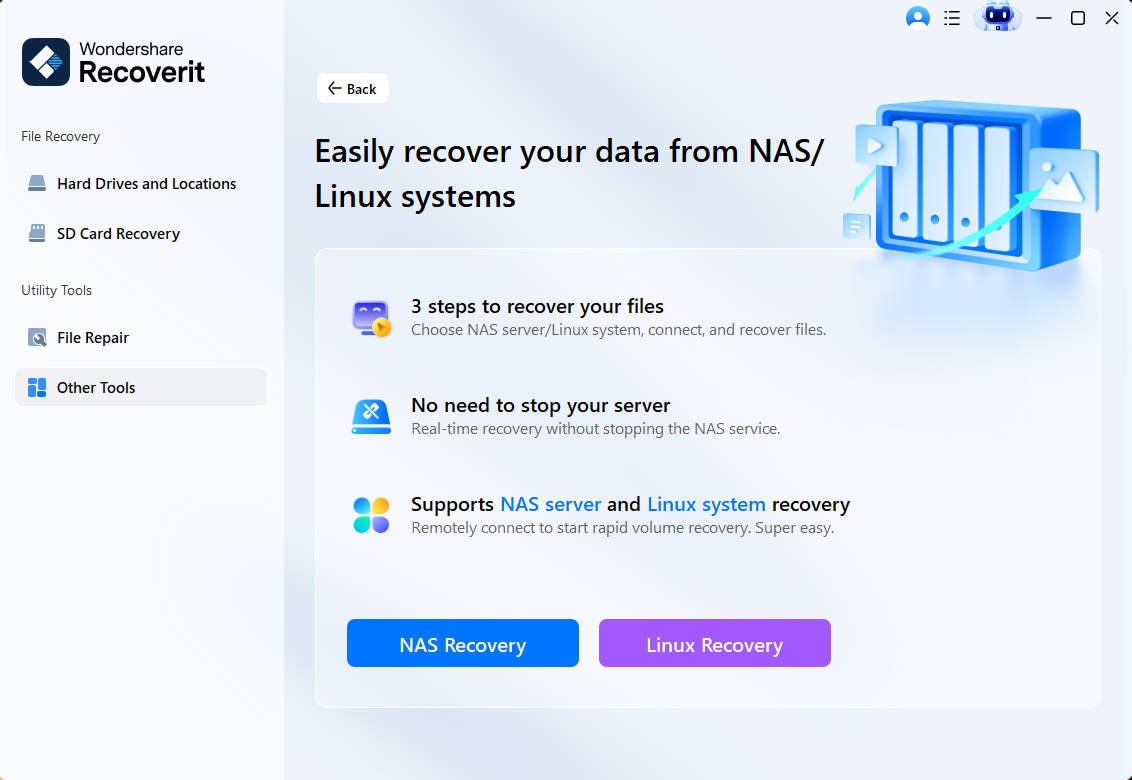
Step 2. Connect the Linux Computer
Enter the required information to establish a remote connection between the Linux file recovery software and your Linux device. When finished, click Connect.
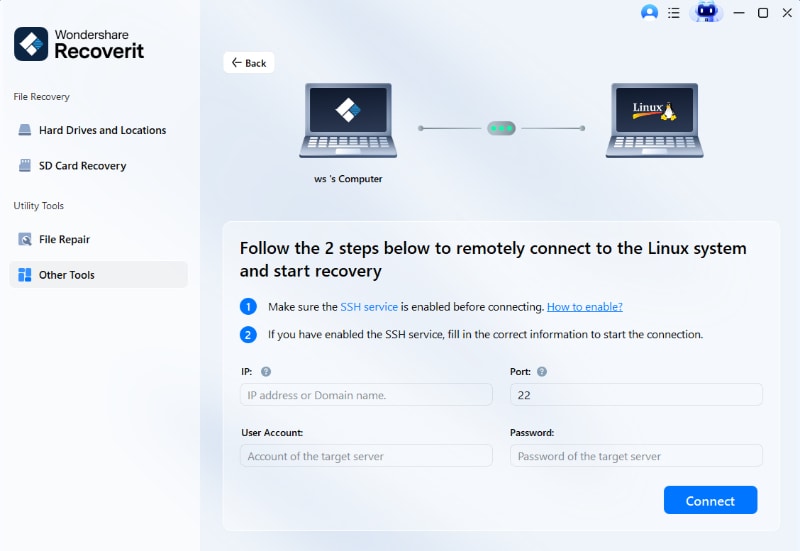
Wait for the connection to be established; Recoverit will run an automatic scan to look for your lost files on a Linux computer.
For Windows Vista/7/8/10/11
For macOS X 10.10 or later
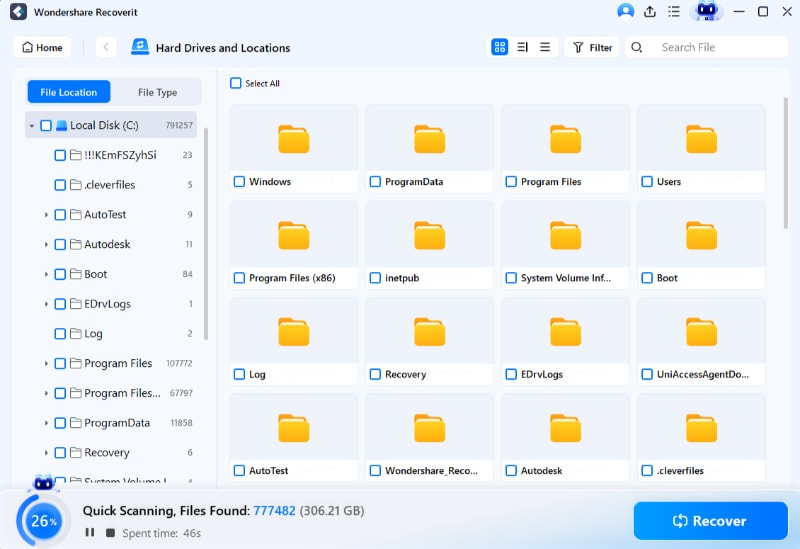
Step 3. Preview and Recover Deleted Files
Depending on the amount of data being scanned, the scanning process can take some time. On the bottom bar, the scanning progress is displayed. The best part about Recoverit is that you can stop scanning whenever you want once you've found the file you want to restore.
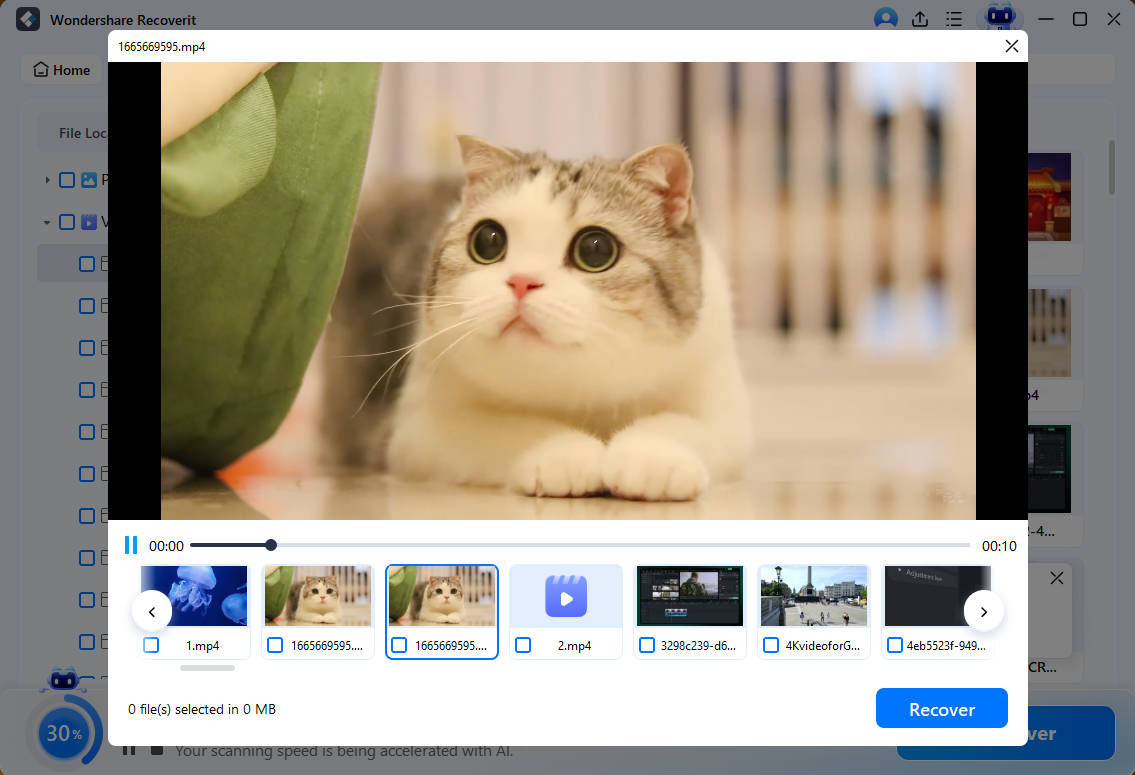
Recoverit also lets you preview the files to ensure they are the ones you want to recover. Click Recover to save the file to a safe location.
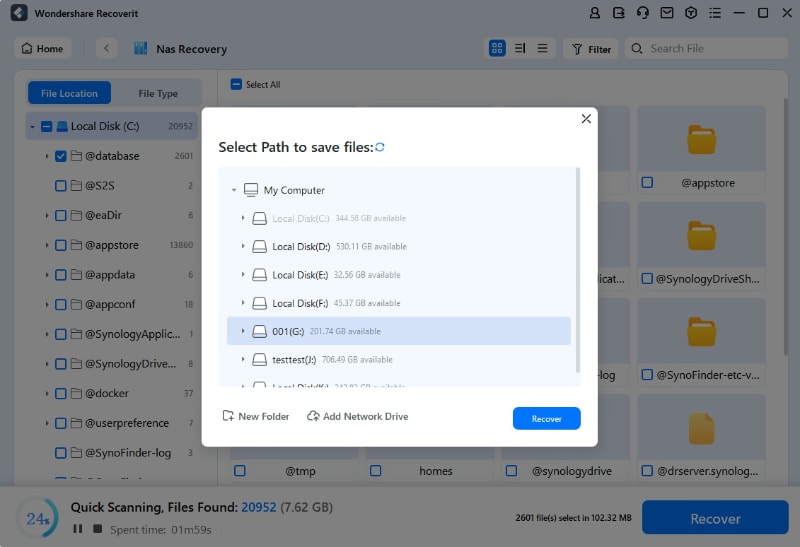
The software will ask you to select a location on your computer to save the restored files. Make sure you take a different place than where you lost your files.
Video Tutorial on How to Recover Files on Linux
For Windows Vista/7/8/10/11
For macOS X 10.10 or later
You may also like: How To Recover Data From Linux-based RAID Using mdadm
Method 3: Recover Deleted Files on Linux Using R-Linux (GUI Tool)
R-Linux is a file recovery tool for the Ext2/3/4FS file system used by the Linux operating system and several Unixes. Thanks to R-usage Linux's innovative IntelligentScan technology and adaptable parameter settings, you have complete control over the quickest data recovery ever. Even when file records are lost, it retrieves files from existing Linux partitions. It uses the traditional "Windows Explorer" interface and visualizes the process in detail.
Simple file recovery can be performed for deleted files that had previously been on a partition that was visible to the operating system. Advanced-Data Recovery is necessary for all other circumstances.
To restore deleted files from a recognized or existing Linux partition with R-Linux, follow the steps below:
Step 1. To list all the files on the disk, double-click a partition in the Drives panel of R-Linux.
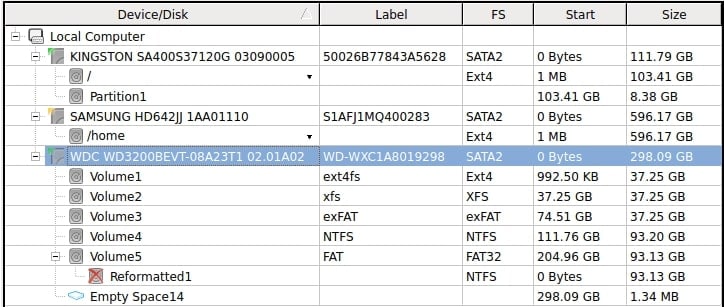
Step 2. Choose a file or folder to restore. You can pick multiple items by simultaneously clicking on various files or folders within the same parent folder while holding down the Shift key.
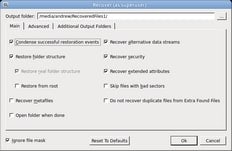
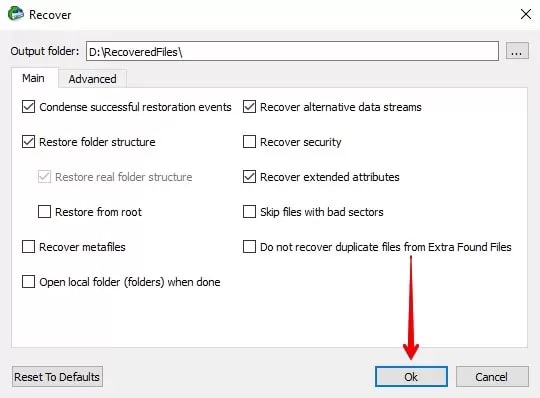
Step 3. Select Recover or Recover Marked from the menu. Enter your recovery preferences and the output folder on the Recover dialog box, then click OK.
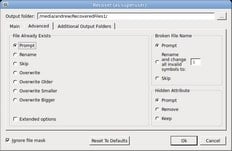
Note: Do not try to save restored files or folders to the same partition where they reside! Alternatively, you can get unexpected outcomes and lose all of your data.
Method 4: Recover Deleted Files on Linux Using R-Studio (GUI Tool)
Thanks to R-Studio, the suite of robust and reasonably priced data recovery programs from R-TT is now available for the Linux operating system. Users have complete control over their data recovery efforts with R-Studio for Linux's adjustable parameters and adjustable settings.
Data can be recovered from logical drives, partitions, and disks and partitions that have been destroyed, damaged, or re-formatted using R-Studio for Linux. Additionally, raw file recovery can be employed for severely damaged or unidentified file systems.
Adhere to the following instructions to recover deleted files on Linux using R-Studio:
Step 1. Download and install R-Studio. Choose the drive or partition containing the missing or deleted files and select Scan.
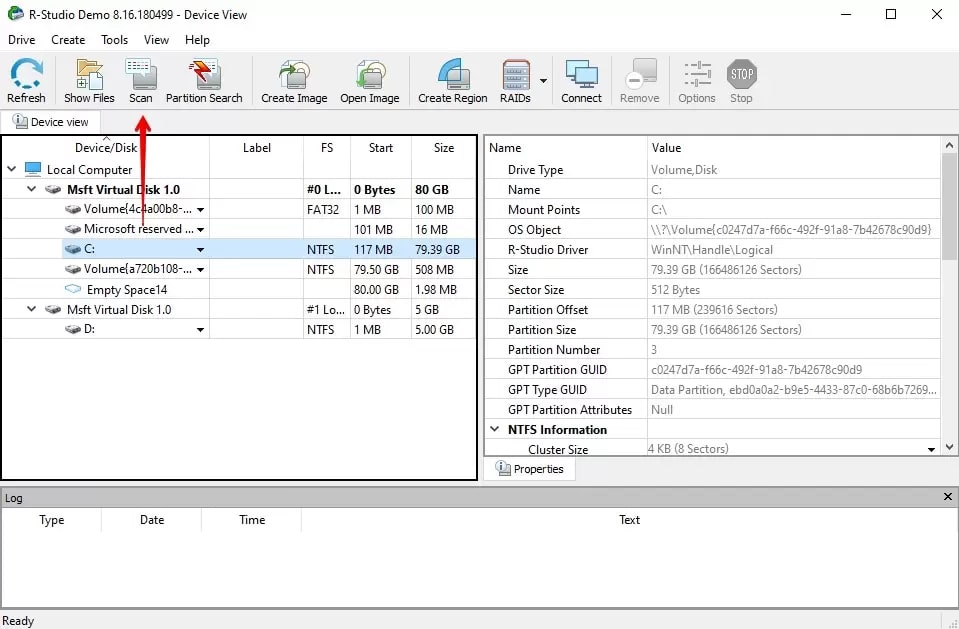
Step 2. If you're a techie and prefer to tweak the scan parameters, this is where you can change which parts of the drive are scanned.
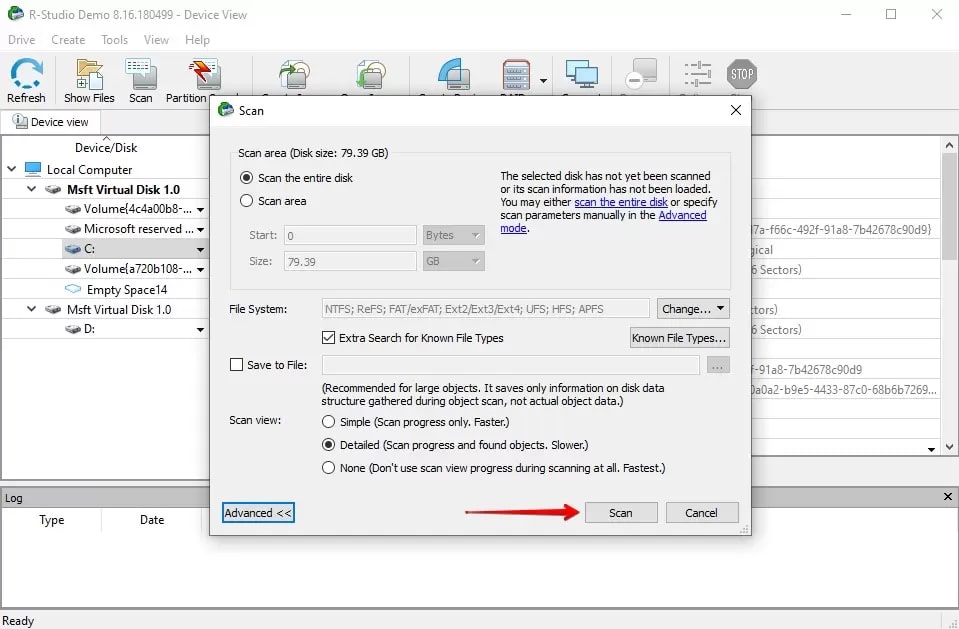
Step 3. Select Show Files.
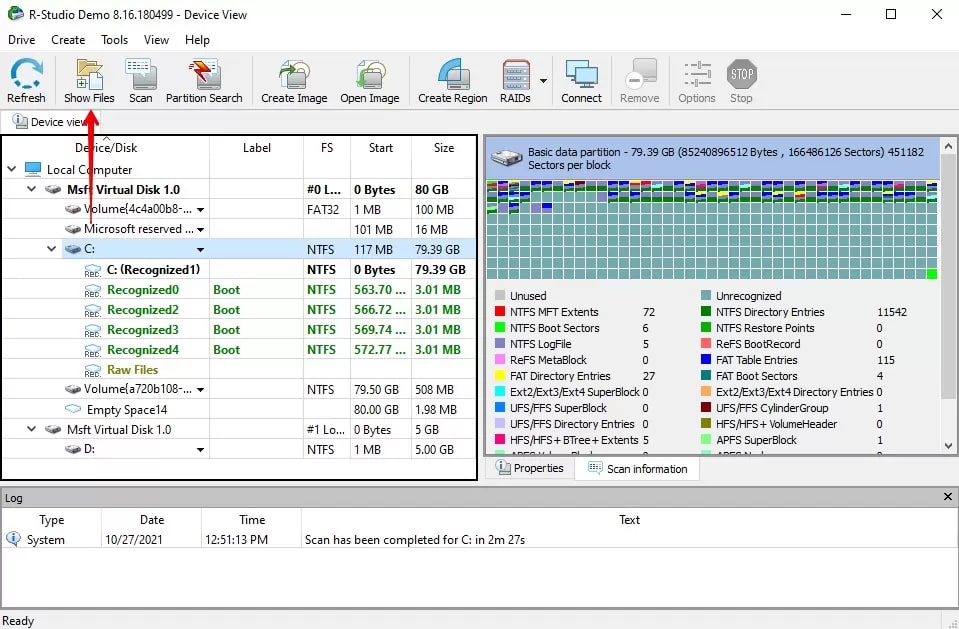
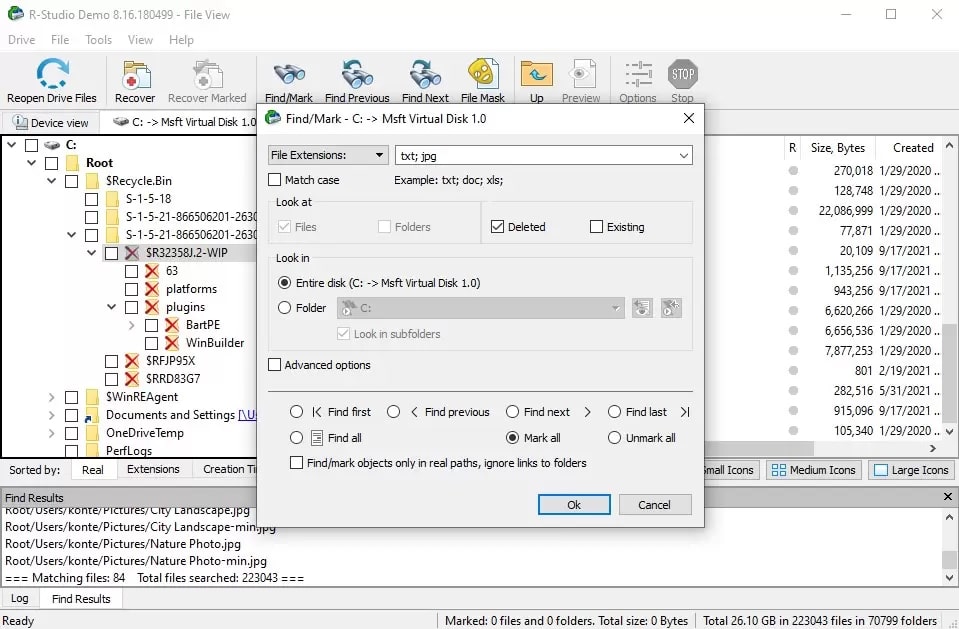
Step 4. Use the Find/Mark function to find automatically and mark files for recovery based on their file type.
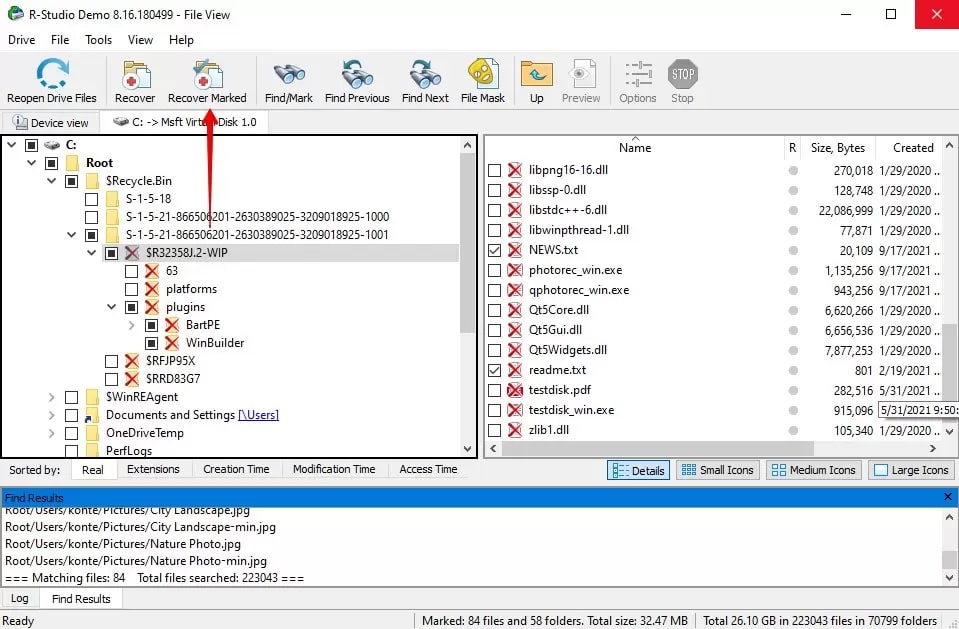
Step 5. When you're finished, click Recover Marked.
Step 6. Indicate the output location and click OK.
Method 5: Recover Deleted Files on Linux Using TestDisk (Command Line)
TestDisk is a free, open-source data recovery program that can restore deleted files and partitions on Windows, Mac, and Linux. It has several beneficial features and a simple interface.
Using TestDisk, follow the steps outlined below to recover deleted files on Linux.
Step 1. TestDisk can be installed on Linux using the following commands:
# Ubuntu and Debian
sudo apt install testdisk
# RHEL and CentOS
sudo yum install epel-release
sudo yum install testdisk
# Arch Linux
sudo pacman -S testdisk
Start TestDisk by opening a Terminal and entering the test disk command.
sudo testdisk
Step 2. To create a log file, use the arrow keys to navigate to the TestDisk's initial page and press Enter. The log file contains a record of all actions taken in TestDisk.
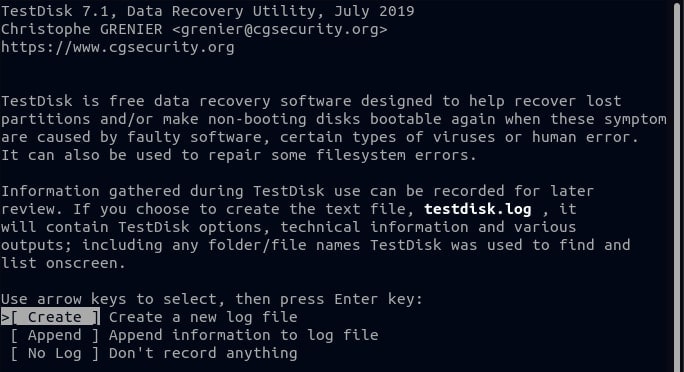
Step 3. Then, using the Up and Down arrow keys, navigate the list and select the disk from which you want to recover your deleted files. After you've highlighted the disk, press the Right arrow key to highlight the Proceed option, then press Enter to select it.
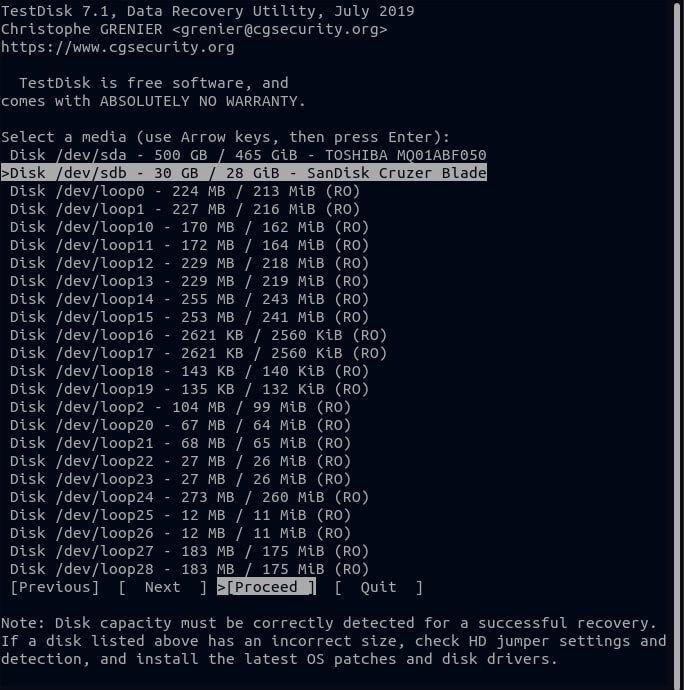
Step 4. Select the partition type for your disk and press Enter. Identifying the correct partition table type can be difficult, but don't worry because TestDisk predicts and highlights the right partition.
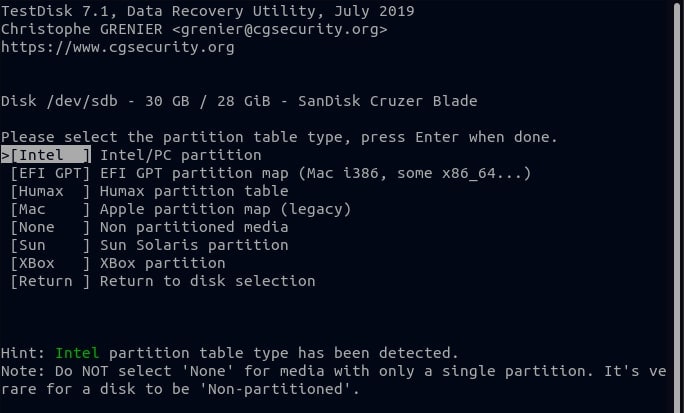
Step 5. Because you're recovering a deleted file, select the Advanced option on the next screen and press Enter.
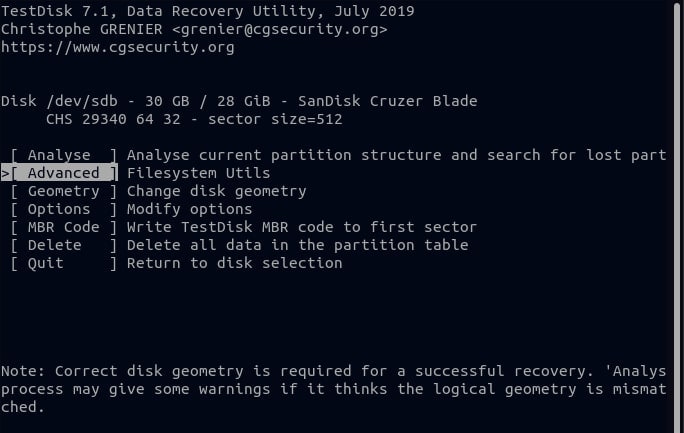
Step 6. Highlight the partition on your disk, press the Right arrow key, select Undelete, and press Enter.
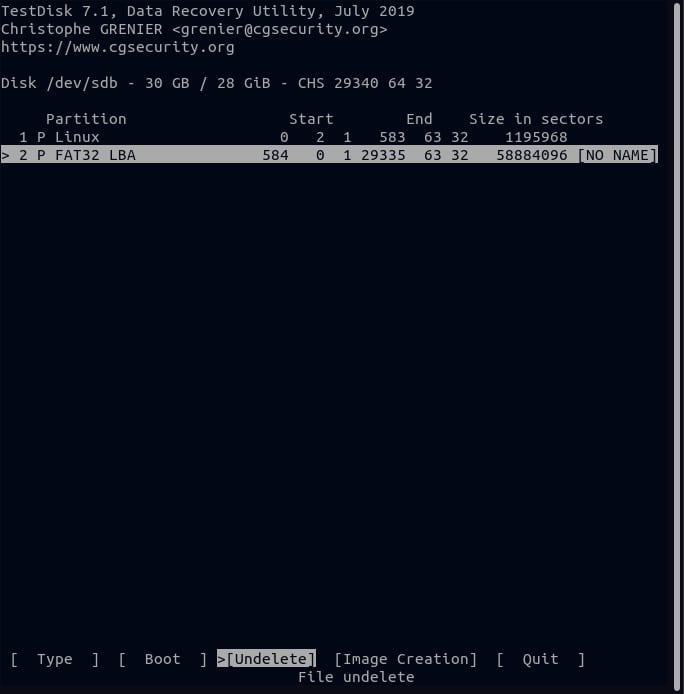
Step 7. From the list of files, select the file you want to restore. If you need to restore multiple files, navigate to each one and press the colon (:) key to select the file. Once you've chosen all the files to be restored, press C to copy them to memory.
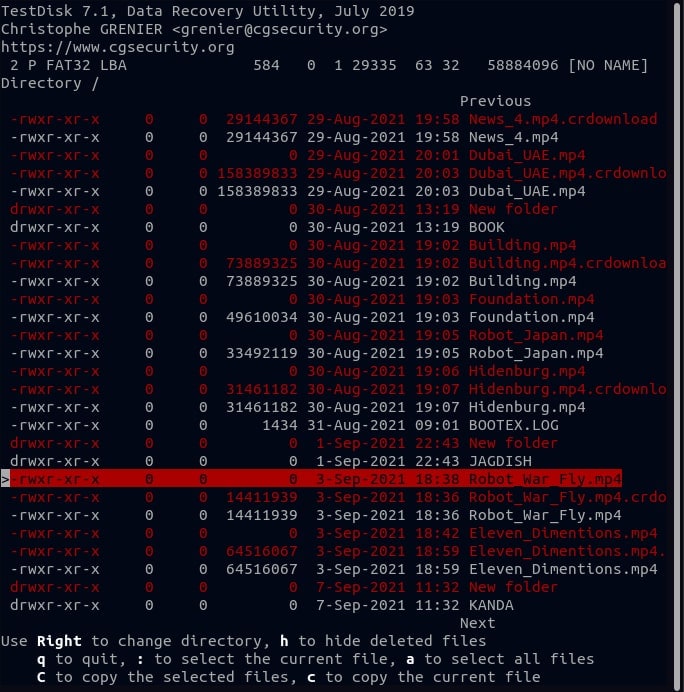
Step 8. Choose where you want to save the recovered file and press Enter.
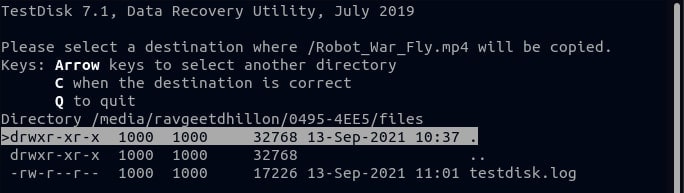
Step 9. Navigate to the location where you copied the file and confirm that you successfully restored your deleted file.
Method 6: Recover Deleted Files on Linux Using PhotoRec (Command Line)
PhotoRec is another free data recovery tool created by the same developers of TestDisk. It was initially developed to recover deleted photos. But now, it can get back all types of deleted files.
To recover deleted files on Linux using PhotoRec, adhere to the specific guidelines below.
Step 1. Linux installation of PhotoRec
Run the following command to install PhotoRec:
sudo apt -y install testdisk
Following setup, use the following command to download and launch the Photorec utility:
sudo photorec
Step 2. Start PhotoRec and begin searching for deleted files
For this demonstration, I created and deleted a random image file. Let us proceed to recover this file.
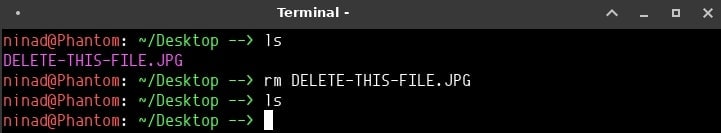
To make things easier, navigate to the Directory where you want to run the recovery before running the command.
sudo photorec
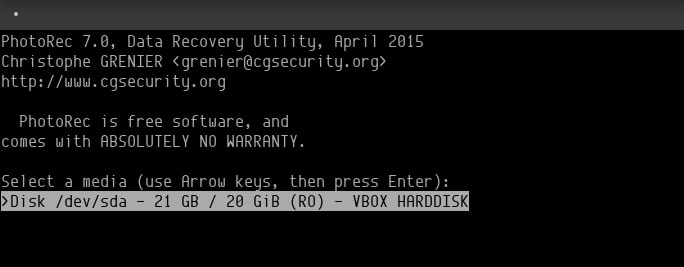
After you've launched PhotoRec, navigate to the hard drive you want to restore and press Enter. You will be asked to choose which partition you want to run the recovery process on.
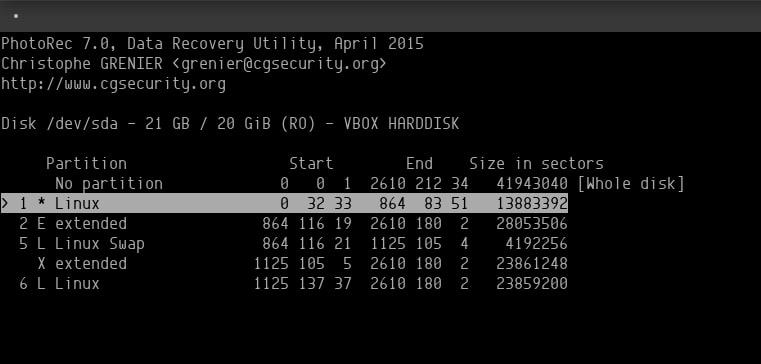
Before you continue, select the file type from the file options menu on the partition selection screen. Because we're only looking for our JPG file, I've chosen that extension.
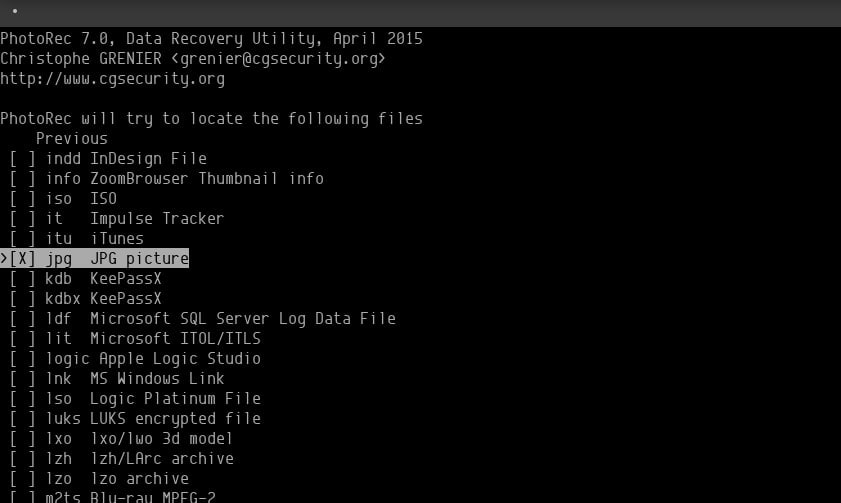
Choose the partition type, which in our case is ext4.
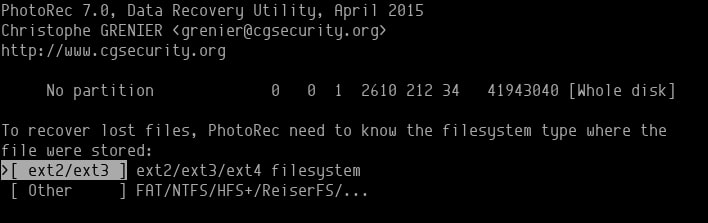
Choose whether you want the utility to examine only free sectors or the entire drive.
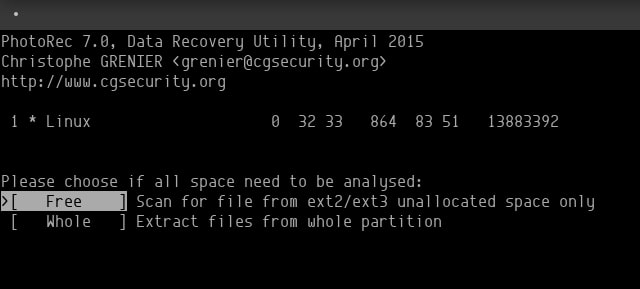
In the /Desktop Directory, this is where the command will start looking by default. Once you've decided which folder to search, press the letter C, and the program will begin searching for files.

Step 3. Recover Files with PhotoRec
Depending on how many file types you've selected, it may take some time.
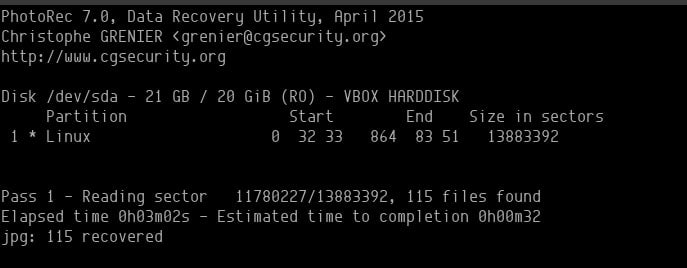
All recovered files will be restored in a folder called recup_dir. Even while the recovery is taking place, you can access the files.
Method 7: Recover Deleted Files on Linux Using Extundelete (Command Line)
Extundelete is a data recovery program that recovers deleted files from the ext3 and ext4 filesystems. These are the filesystems that are used by popular Linux distributions such as Ubuntu.
Step 1. Extundelete can be installed with one of the following commands:
# Ubuntu and Debian
sudo apt install extundelete
# RHEL and CentOS
sudo yum install extundelete
# Arch Linux
sudo yay -S extundelete
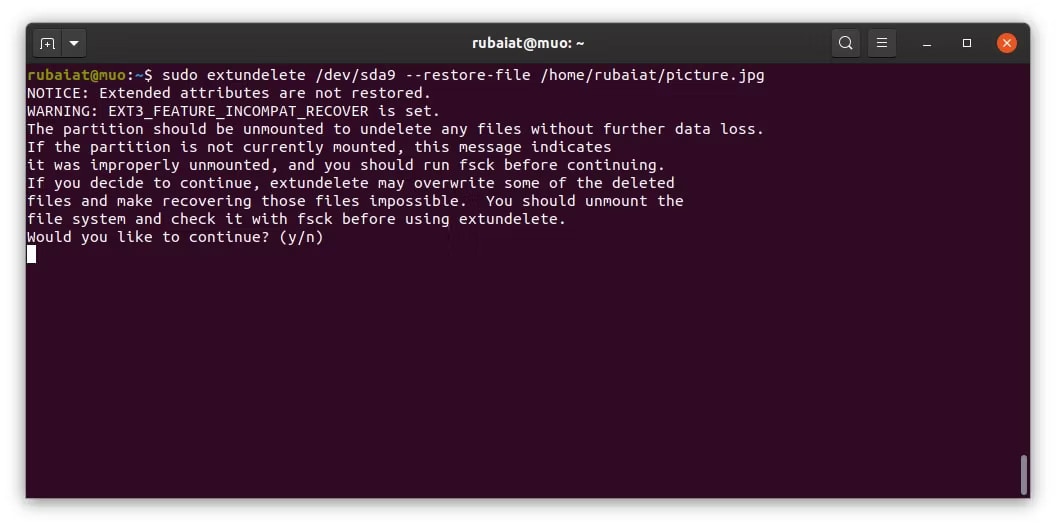
Step 2. Once installed, you can use Extundelete to recover deleted files from your Linux system. To quickly restore a specific file, use the command below. It should be noted that the file path is relative to the partition's root.
sudo extundelete --restore-file picture.jpg /dev/sdb1
Step 3. The following command reclaims all files from the /dev/sdb1 partition. Modify the partition name to match the name of your source.
sudo extundelete --restore-all /dev/sdb1
Step 4. If you want to save the restored files to a specific directory, use the -o option to specify it. Extundelete saves the recovered files in the RECOVERED_FILES/ sub-directory by default.
sudo extundelete -o ~/recovery --restore-all /dev/sdb1
Method 8: Recover Deleted Files on Linux Using Foremost (Command Line)
Foremost is a free data recovery tool for Linux. It includes a straightforward CLI interface. Although the software is less interactive than TestDisk or PhotoRec, it is still useful in some situations.
Step 1. Foremost can be installed on Linux by running the following commands:
# Ubuntu and Debian
sudo apt install foremost
# Fedora
sudo dnf install foremost
# Arch Linux
sudo pacman -S foremost
Step 2. The software is relatively simple to use once it has been installed. Using the following command, you can list all possible options for foremost:
foremost -h
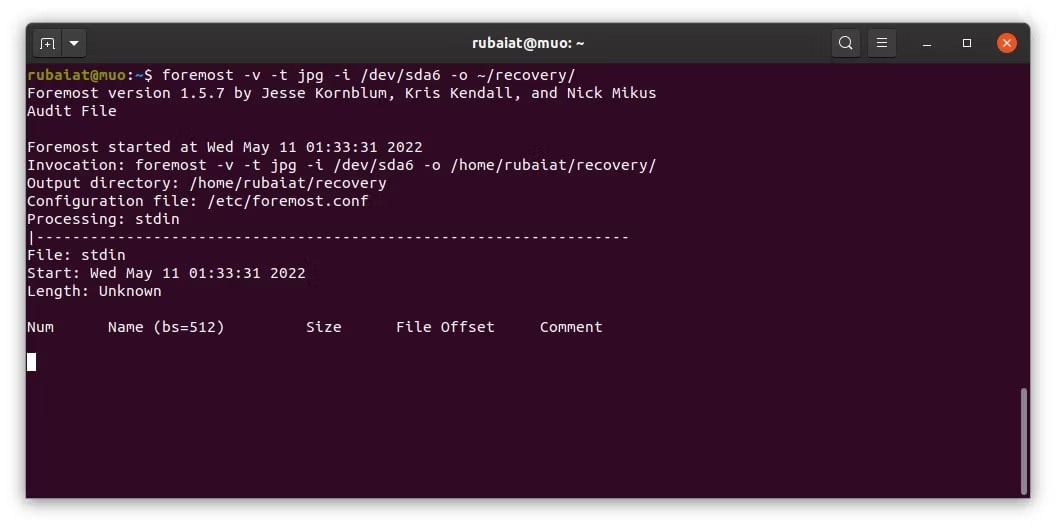
Step 3. Using the first command, we can recover the deleted file picture.jpg:
foremost -v -t jpg -i /dev/sdb1 -o ~/recovery/
Step 4. This command will search /dev/sdb1 for all lost JPG images and restore them to ~/recovery. The -v option enables verbose logging, while -i specifies the source partition and -o the output directory.
Users can specify which files to search for using the -t option. Foremost can locate images, videos, text, and executables, among other file types. A comma-separated list can be used to search for multiple extensions.
More Related: How To Recover Deleted Files/Folders in Ubuntu
Conclusion
Recovering deleted files on Linux is surprisingly simple because many excellent data recovery tools are available. Depending on the type of the deleted file and the partitioning setup of your Linux computer, you can choose any of the methods mentioned above: by using a built-in tool on Linux for soft deletion, GUI tools, and command line tools.
However, as this software offers a clear and straightforward interactive user interface, we suggest Wondershare Recoverit Linux Recovery to restore your lost or deleted data easily and safely in Linux.
For Windows Vista/7/8/10/11
For macOS X 10.10 or later

 ChatGPT
ChatGPT
 Perplexity
Perplexity
 Google AI Mode
Google AI Mode
 Grok
Grok






















