Accidentally deleting important files can be a frustrating experience, especially if you don't know how to undo the action. The rm command is employed to delete files or directories in Linux, and once a file is deleted, it is typically not recoverable from the trash or the recycle bin.
However, a few methods can be used to recover deleted files in Linux, depending on the circumstances. In this guide, we will discuss ways to undo the effects of the rm command and recover deleted files in Linux.
Part 1: What Is the RM Command?
The rm command in Linux and other Unix-based operating systems removes or deletes files and directories. It stands for "remove." The rm command is typically used to delete files and directories that are no longer needed. It is a powerful command and should be used with caution, as it can permanently delete files, and there is no trash bin or recycle bin to recover them from.

When using the rm command, you can use flags such as “-r” to remove the directory and its content, “-f” to force removal without prompt, or -v to show what was removed.
Part 2: Is It Possible To Undo RM in Linux?
It is typically impossible to undo the rm command after it has been executed, as the file or directory is permanently deleted. However, some methods can recover deleted files by rm in Linux, but it depends on certain circumstances. Some methods include using a file recovery or command line tool.
However, the chances of recovery depend on many factors, such as file system, storage medium, time passed since the deletion, and whether any new data has been written to the storage medium.
Part 3: How To Undo RM in Linux
Here are the 3 different ways to undo rm in Linux.
Method 1: Undo the Effects of RM Using Recoverit Linux Recovery (GUI Tool)
When recovering deleted files by rm in Linux, using a graphical user interface (GUI) recovery tool can be a convenient option for users who are not comfortable working with command-line utilities. One of the best GUI data recovery tools is Wondershare Recoverit Linux Recovery. Recoverit is a comprehensive data recovery solution for Linux that provides high-caliber features.

Wondershare Recoverit - Your Safe and Reliable Linux Recovery Software
5,481,435 people have downloaded it.
Recovers lost or deleted documents, photos, videos, music, emails, and other 1000+ file types effectively, safely, and completely.
Compatible with all mainstream Linux distros, including Ubuntu, Linux Mint, Debian, Fedora, Solus, Opensuse, Manjaro, etc.
Assists in 500+ data loss scenarios, such as deletion, disk formatting, OS crash, power outage, virus attack, lost partition, and many more.
The simple point-and-click interface allows you to recover data from Linux hard drives in just a few clicks.
You can easily undo rm in Linux using Recoverit Linux Recovery in three simple steps:
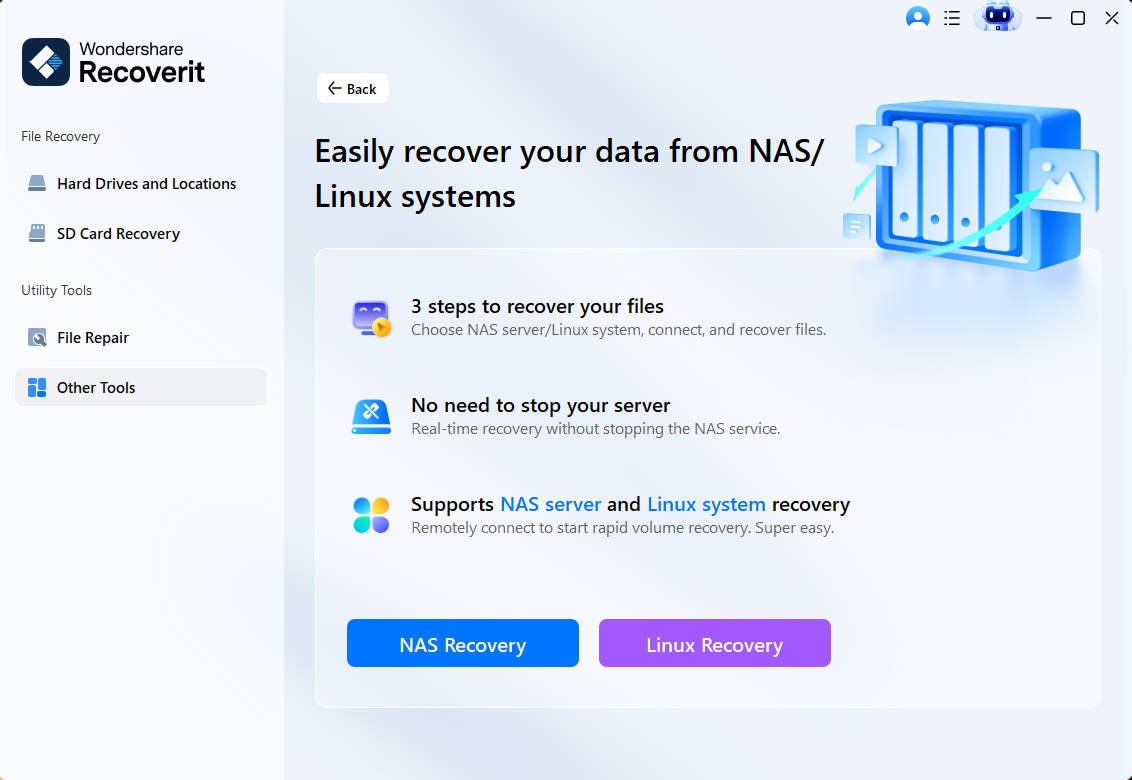
Step 1Choose Linux Recovery Option
After downloading and installing the Linux data recovery software on your computer, navigate to NAS and Linux and select the Linux Recovery feature.
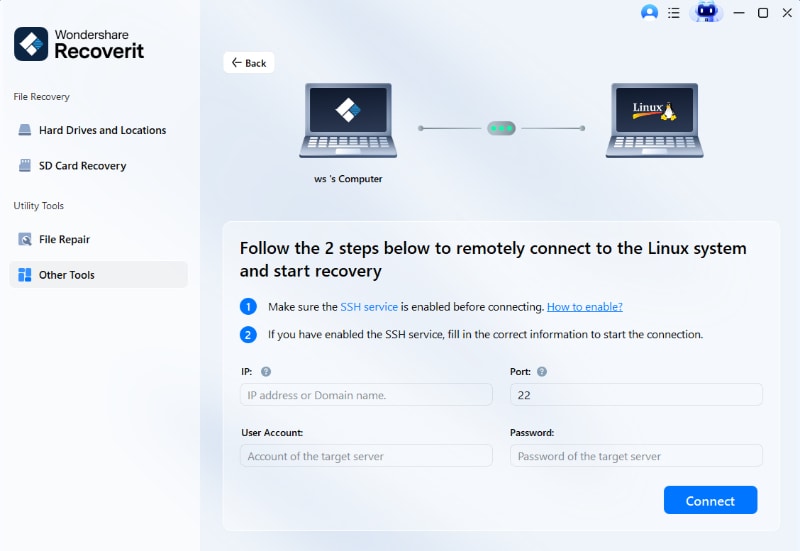
Step 2Connect to the Linux system
Before starting the recovery process, you need to remotely connect Wondershare Recoverit to your Linux computer system by providing the IP address, port number, username, and password.
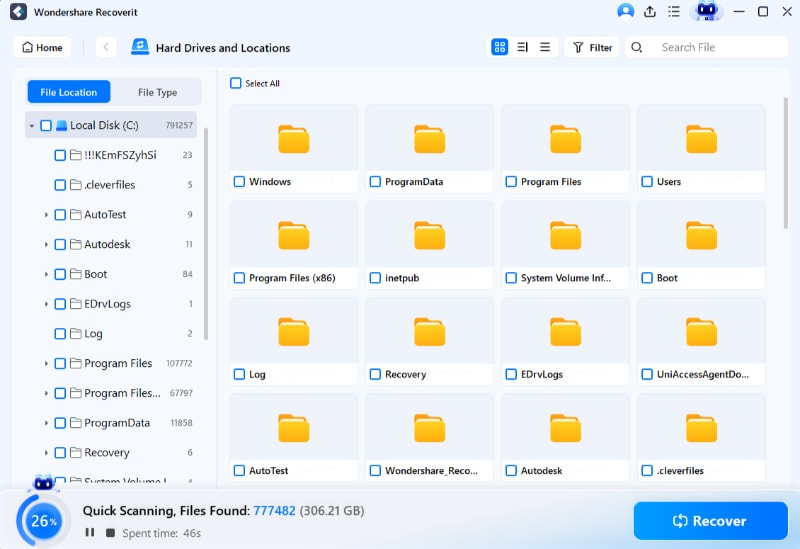
Step 3Scan and Recovery
Recoverit will begin searching for missing data on your Linux device as soon as the connection is completed. You can preview the files to ensure that the file you want to recover is the one you want.
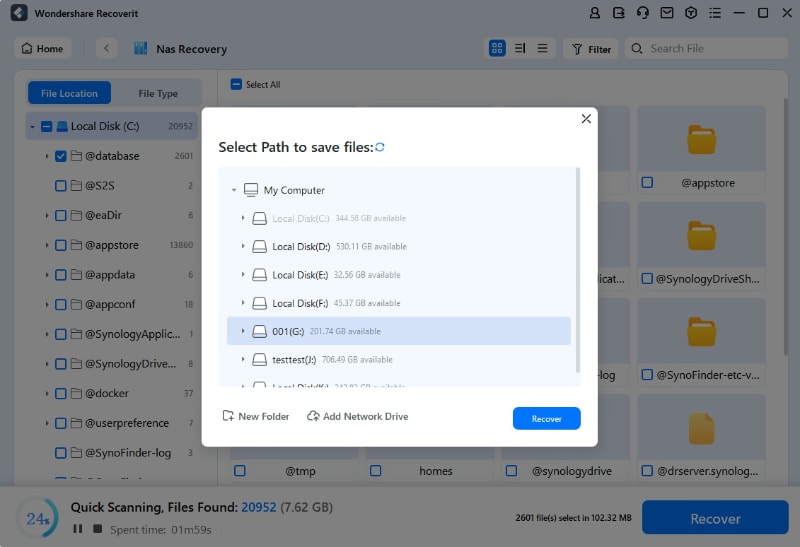
Finally, select your desired files and click Recover to undo rm in Linux.
For Windows Vista/7/8/10/11
For macOS X 10.10 or later
Video Tutorial on How to Undo RM?
For Windows Vista/7/8/10/11
For macOS X 10.10 or later
Method 2: Undo the Effects of RM Using Foremost (Command Line Tool)
For advanced Linux users comfortable working with command-line utilities, using a command-line tool to undo the rm command can be a powerful way to recover deleted files. One popular command-line tool for recovering deleted files in Linux is Foremost. This tool offers advanced options for scanning and recovering files and can be run through the Terminal.
Foremost is a Linux data recovery program that uses file carving to restore data using its headers, footers, and data structures. Foremost can quickly recover files from hard disks, memory cards, pen drives, and other devices. It can also work with image files generated by any other application.
Suppose you accidentally deleted files in an external storage device using rm; you can follow the steps below to undo an rm command in Linux.
- Step 1:Install Foremost.
Use the APT package manager to install Foremost in any Ubuntu and Debian Linux: sudo apt install foremost
Run the DNF package manager to install Foremost in Fedora Linux: sudo dnf install foremost
Use pacman to install Foremost in ArchLinux: sudo pacman -S foremost
- Step 2: Please execute the following command to view the available options and their functions.
foremost [options]

- Step 3: Connect the Linux system to the external memory storage. First, you must determine the path of your external memory device using the command below and copy the disk path from here.
fdisk -l

- Step 4: You can recover the files from the device after copying the device path. Use the
foremost -hcommand's available options.

- Step 5: Following the execution of this command, all files will be saved in the specified folder. You can see the folder recovered on the desktop; all files will be saved here.

Method 3: Undo the Effects of RM Using Scalpel (Command Line Tool)
Another highly recommended command-line tool is Scalpel. This tool recovers files by analyzing the file system and looking for files marked as deleted. The Scalpel was created with a Foremost improvement of 0.69. We've already discussed Foremost.
Scalpel, like Foremost, can quickly recover permanently deleted data. Scalpel is an excellent forensics tool that comes with Kali Linux. It can change the configuration file to specify which types of files we want to recover.
The instructions below explain how to use Scalpel to undo an rm command in Linux:
- Step 1: To use the Scalpel, enter the following command:
scalpel -h

- Step 2: Run the following command to undo
rm:scalpel -o recovered/ KaliLinuxIn.dd

The recovery process has been completed. We specified the output folder by using the -o flag. As a result, a new folder called "recovered" is created on our desktop.
- Step 3: On our desktop, we can see the recovered output folder.

Part 4: How To Protect Linux Data From Accidental Running of RM Command?
Tips #1: Using Trash Command
The Trash command is a command line utility for moving files and directories to the trash or recycle bin. It is a convenient alternative to permanently deleting files using the rm command, as it allows the recovery of accidentally deleted files. We will use CLI trash in this part.
- Step 1: Let's look at how to add the "trash-cli" application to your Linux distro:
sudo apt install trash-cli -y # For Debian Based OS(Ubuntu, Mint, Pardus etc)
sudo apt-get install trash-cli -y # For Debian-based old version operating systems (Ubuntu, Mint, Pardus etc.)
sudo pacman -S trash-cli # For Arch Based OS(Archman Linux, Arch Linux, Manjaro etc)
sudo dnf install trash-cli # For Redhat-based OS(Centos, Fedora, AlmaLinux, Rocky Linux etc)
sudo yum install trash-cli -y # For Redhat-based old version operating systems(Centos, Fedora, AlmaLinux, Rocky Linux etc)
sudo zypper install trash-cli # For openSUSE - Step 2: After installation, use the
trashcommand to delete files:foc@ubuntu22:~$ ls
text-1.txt text-2.txt text-3.txt text-4.txt
foc@ubuntu22:~$ trash text-1.txt
foc@ubuntu22:~$ ls text-2.txt text-3.txt text-4.txt - Step 3: The
trashcommand deleted the file; for the directory, use the-dparameter:foc@ubuntu22:~$ trash -d folder - Step 4: The
trash-listcommand can be used to list the deleted files and directories:foc@ubuntu22:~$ trash-list
2022-11-09 18:44:37
/home/foc/folder 2022-11-09 18:41:11
/home/foc/text-1.txt 2022-11-09 18:42:46
/home/foc/text-1.txt - Step 5: For retrieving a deleted file or folder from the trash, use the
trash-restorecommand:foc@ubuntu22:~$ trash-list
2022-11-09 18:44:37 /home/foc/folder
2022-11-09 18:49:45 /home/foc/text-1.txt
foc@ubuntu22:~$ trash-restore /home/foc/text-1.txt
0 2022-11-09 18:49:45 /home/foc/text-1.txt
What file to restore [0..0]: 0
foc@ubuntu22:~$ ls
text-1.txt text-2.txt text-3.txt text-4.txt - Step 6: The
trash-emptycommand removes all trash:foc@ubuntu22:~$ trash-empty - Step 7: Now, open a text editor and add the line below to the user's ".bashrc" file:
foc@ubuntu22:~$ nano ~/.bashrc
alias rm='trash' - Step 8: Then communicate this change to the user:
foc@ubuntu22:~$ source ~/.bashrc - Step 9: When you use the
rmcommand, thetrashcommand now works:foc@ubuntu22:~$ rm -h
Usage: trash [OPTION]... FILE...
Put files in trash
...
Tips # 2: Sort of Hack Solution for Undo RM
This hack solution is a technique you can perform to protect files from being deleted, but it will not assist you in recovering deleted files.
- Step 1: The "
mv" command can now be used as an alias for thermcommand. The ".Trash" directory is created in the user's home directory for this purpose:[foc@rocky9 ~]$ mkdir ~/.trash - Step 2:The
mvcommand Alias is then defined:[foc@rocky9 ~]$ vi ~/.bashrc
alias rm='mv --target-directory="$HOME/.trash"' - Step 3: Then communicate this change to the user:
[foc@rocky9 ~]$ source ~/.bashrc - Step 4: Then execute the
rmcommand:[foc@rocky9 ~]$ rm text-1
[foc@rocky9 ~]$ ls ~/.trash/
arch text-1
You will have a restricted "undo rm" feature if you use rm in this manner.
Tips #3: Using Interactive RM Command
Once again, an alias is required. This time, we'll give the rm command its parameter. This method is done by default in some Linux distributions. They made the "-i" parameter the default for the rm command. In this manner, the user requests approval before proceeding with the deletion process.
- Step 1: Edit the "
.bashrc" file as follows:[manjaro manjaro]# nano ~/.bashrc
alias rm="rm -i" - Step 2:Then communicate this change to the user:
[manjaro manjaro]# source ~/.bashrc - Step 3: Additionally, try deleting files:
[manjaro manjaro]# rm text-1
rm: remove regular empty file 'text-1'? y
Before deleting, you will now be warned. There is no undo function, but you will have some time before the deletion begins.
More Related: Recover Deleted Files by RM Command on Linux (Ubuntu)
Final Words
This article helps you learn the different methods to undo rm in Linux (by GUI or command-line tool). It's dangerous to delete data from servers. When granting users permission, caution should be used. However, the system can be protected against using the undo techniques and measures listed above.
For Windows Vista/7/8/10/11
For macOS X 10.10 or later

 ChatGPT
ChatGPT
 Perplexity
Perplexity
 Google AI Mode
Google AI Mode
 Grok
Grok






















