
Do you have Windows and Linux distributions installed on your computer? In that case, you will not face any issues when accessing Windows hard drives. This is because NTFS drives are easily mounted by most Linux distros. But this is not true if you are a Windows user.
The reason behind this fact is that Linux file systems, e.g., Ext4, are not supported. This isn’t something to be worried about, as you can access Linux partitions from Windows with an additional tool. This article presents the top ways to read files from Windows on your Linux computer. Let’s get deeper into the discussion.
Part 1. What Is a Linux File System?
Linux operating systems come with a built-in layer that is used to manage the storage data. This built-in layer is commonly called a Linux file system. One of the major responsibilities of this layer is the file arrangement on the disk storage. It covers managing the creation date, size, and name of the files.
Linux File System Structure
The hierarchical file structure of a Linux file system consists of a root directory connected to its sub-directories. A root directory can help you access all sub-directories. As far as the partition is concerned, mostly, it contains a single file system. However, it can have more file systems. The design of a file system offers significant support for non-volatile storage data by managing and providing an appropriate space.
The namespace of a file system describes characters used to create a file name or the length of the name. The use of directories to organize particular files is also associated with the namespace. As soon as you define the namespace, the next step is to define the metadata description of that specific file.
The hierarchical directory structure needs the support of the data structure. The data structure helps you determine the available and used space on the disk for a specific block. Other details the data structure holds include file modification, file update, file creation time, etc. It also stores detailed information about the disk’s volumes and partitions.
The advanced data does not depend on the metadata of the file system. The Linux file system structure is shown below. The Application Programming Interface (API) is required for the file system. It performs a variety of tasks, including but not limited to creating, copying, and deleting files.

Common Linux File Systems
Installing Linux operating systems gives you access to the most common file systems, e.g., Ext2, Ext3, and Ext4. The Ext2 file system enables you to manage data of up to 2TB. On the other hand, Ext3 is the advanced version of the Ext2 file system, and it does not offer support for disk snapshots and file recovery.
As far as the Ext4 file system is concerned, it is the default and faster file system that is highly compatible with Solid-State Drives (SSDs).
Part 2. Can I Access Linux Files from Windows?
Ext4 is the most common file system, as stated earlier. If you want to access Linux files, you should read Ext4 from Windows. At the same time, Windows does not support the Ext4 file system.
As soon as you click on the Ext4 partition, a couple of options will become disabled, as shown below. It is a fact that you can’t use Windows to access or read Ubuntu or Linux files directly. So, what to do if you need to read or access Linux files on Windows? To get an answer to this query, keep reading.

Part 3. How to Access Linux Partitions from Windows?
You can’t directly access Ext4 from Windows until you use a credible tool to do this job. This section presents 6 different methods to access Linux partitions from Windows 10. Let’s look at how each method makes the assignment easier for you.
Method 1: Access Linux Partitions from Windows Using DiskInternals Linux Reader
When it comes to reading or accessing Linux partitions or files from Windows 10, Diskinternals Linux Reader plays a key role. The best thing about this tool is that it is free to use. You can also read Linux drives on Windows with this program.
Supported File Systems |
Supported OS |
| Ext4 | Windows 7 (32bit/64bit) |
| ReFS | Windows 8 (32bit/64bit) |
| HFS | Windows 10 (32bit/64bit) |
| HFS+ | - - |
Steps to Use Diskinternals Linux Reader
Within 7 steps; you can access the Linux partition from Windows with this tool.
Step 1: Download and install the program on your laptop or personal computer.
Step 2: The Linux Reader will start detecting all partitions on your disk. Once done, go to the Ext4 partition from the drives list.
Step 3: Now, open the Ext4 partition by double-clicking on it. It will allow you to preview the drive’s data. You can save it as well.
Step 4: Transfer Linux files from the Ext4 partition to the other location if you want complete access to Linux files on Windows.
Step 5: This step is about saving the file. For this, press right-click and tap on the “Save” option, as shown below.

Step 6: It is time to choose “Save Files” and hit “Next,”

Step 7: Tap on “Browse,” choose the desired path and hit “OK.”

Method 2: Access Linux Partition from Windows Using Ext2explore
It helps you efficiently access the Ext2, Ext3, and Ext4 files on Windows. The working principle of Ext2explore and Diskinternals Linux Reader is pretty similar. The only thing that creates the difference is that you can’t preview files with Ext2explore. You can easily run a .exe file without installing any utility.
Supported File Systems |
Supported OS |
| Ext2 | Windows XP |
| Ext3 | Windows 7 (32bit/64bit) |
| Ext4 | Windows 8 (32bit/64bit) |
| - - | Windows 10 (32bit/64bit) |
Steps to Use Ext2explore
You just need to follow 2 convenient steps, as given below.
Step 1: Open the program as “Run as administrator.” For this, you can also click on the downloaded file and go to its properties. Then, navigate to the “Compatibility” tab, and click on the checkbox “Run this program as an administrator.” Now, hit the “OK” button.

Step 2: You will now be able to access Linux files and the Ext4 partition. Make sure you save the files to the Windows partition if you want to open them on your Windows computer. Now, right-click on the file you want to access and tap on “Save,” as shown below. Go to a different path to save these files on your Windows PC.

Method 3: Access Linux Partition from Windows Using Linux File Systems for Windows
This is a relatively newer approach to access Linux partitions from Windows. Remember, it is not a free utility. However, it charges you a few dollars only. It offers support for reading and writing a variety of file systems, as listed below.
Supported File Systems |
Supported OS |
| Ext2 | Windows 7 |
| Ext3 | Windows 8/8.1 (32bit/64bit) |
| Ext4 | Windows 10 (32bit/64bit) |
| - - | Windows 11 |
| - - | Windows Server 8/12/16 |
Steps to Use Linux File Systems for Windows
All you have to do is to follow the below-listed steps.
Step 1: Once you install it on your computer, it will automatically detect the Linux partitions attached to your Windows PC. They will be mounted too. You have the option to disable the feature of automatic mounting. If you are worried about losing your important data, you can disable “Mount in Read/Write Mode” as well.

Step 2: In case the tool is unable to detect the disk, tap on the three dots and select the “Restart the service” option, as shown below.

Step 3: Linux File Systems for Windows, introduced by Paragon, mounts the Linux partitions in the File Explorer. It indicates that you are free to interact or communicate with everything on the Linux partitions. You will be able to use all Windows shortcuts and controls.

Method 4: Access Linux Partition from Windows Using ext2fsd
This Windows file system driver offers great support for the Ext2, Ext3, and Ext4 file systems. You can read Linux partitions Windows 10 with this efficient tool. Moreover, if you mount the Ext4 partition and assign the drive letter, this program enables you to access Ubuntu files too.
Supported File Systems |
Supported OS |
| Ext2 | Windows 2000, XP, Server 2003, Server 2008, Vista |
| Ext3 | Windows 7 (32bit/64bit) |
| Ext4 | Windows 8 (32bit/64bit) |
| - - | Windows 10 (32bit/64bit) |
Steps to Use est2fsd
It helps you follow 4 easy steps to get through.
Step 1: Download and install the utility on your Windows computer. Uncheck the box (as shown below) if you don’t want the software to launch automatically on every boot.

Step 2: Now, go to “Tools” from the main interface and choose the “Service Management” option.

Step 3: It is time to check the boxes shown below and hit the “Apply” button.

Step 4: Now, open the “File Explorer” by pressing the “Windows + E” keys from the keyboard.
After following the above steps, you will be able to access or read Linux partitions on Windows.
Method 5: Access Linux Partition from Windows Using Explore2fs
It performs well for older hardware, e.g., Jazz Disk, CD-ROM, and Floppy disks. If you intend to access or read Linux partitions on Windows, try Explore2fs. The supported file systems and operating systems are presented in the below table.
Supported File Systems |
Supported OS |
| Ext2 | All Windows versions |
| Ext3 |
Steps to Use Explore2fs
This tool does its job in 3 steps only.
Step 1: Download the latest version of Explore2fs.
Step 2: Now, double-click on the executable file. You will find it in the new folder.

Step 3: Now, you can browse the Linux partitions. Copying and pasting the files to the Windows partition also becomes possible.

Method 6: Access Linux Partition from Windows Using Ext2 IFS
With this utility, you get access to reading, writing, moving, deleting, and renaming directories or files. While installing Ext2 IFS, you can select the drive letter. Once it is installed, you will be able to see the Linux file system in File Explorer.
Supported File Systems |
Supported OS |
| Ext2 | Windows Server 2003/2008/2012 |
| - - | Windows XP/Vista |
| - - | Windows 7/8 |
Steps to Use Ext2 IFS
Follow the below steps to get over the line.
Step 1: This utility provides you with complete read and writes access for Linux file systems and volumes. Download the program and install it on your Windows computer.
Step 2: Now reboot your system to allow changes to apply.
Following the above steps will enable you to access Linux partitions from Windows.

Part 4. How to Recover Lost or Deleted Data in Linux?
Formatting, accidental deletion, virus attacks, and hardware problems, all lead to data loss in the end. It has become one of the most severe challenges for thousands of companies around the globe. These days, the market holds different third-party software to recover lost data in Linux, but finding a reliable one is another big challenge.
If you are on the hunt for a program you can trust, you must try Wondershare Recoverit. It is an unbelievable tool that helps you get your lost or deleted data back. The biggest reason why you should download and try this utility is that it offers more than a 95% recovery rate. In addition, it offers superb support for thousands of file formats and storage media.
Steps to Use Recoverit to Recover Deleted/Lost Data in Linux
It simply asks you to follow 3 steps only, as given below.
Video Tutorial on How to Recover Files on Linux?
For Windows Vista/7/8/10/11
For macOS X 10.10 or later
Step 1: After installing Recoverit on your device, look for the “NAS and Linux” option. You will see it on the left side of the main interface, as shown below. Press “Linux Recovery” later.
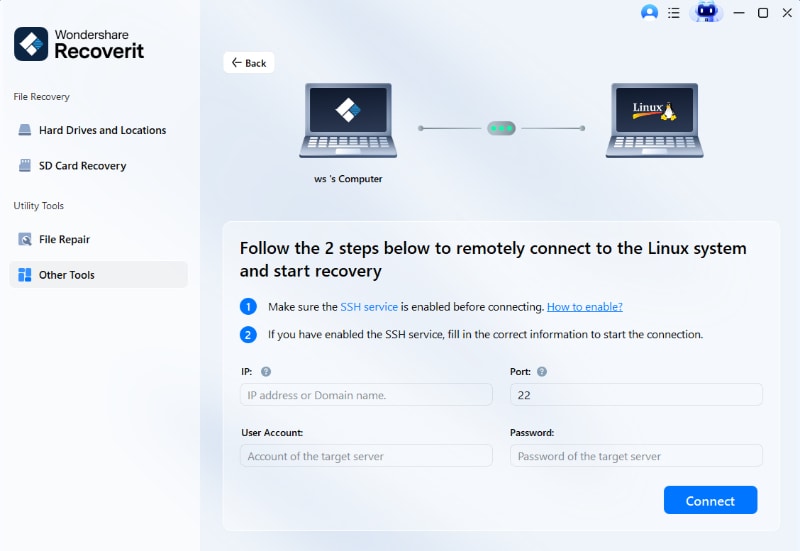
Step 2: Now, the tool will ask you to put some information. After that, hit the “Connect” button to create a remote connection to connect your Linux computer.
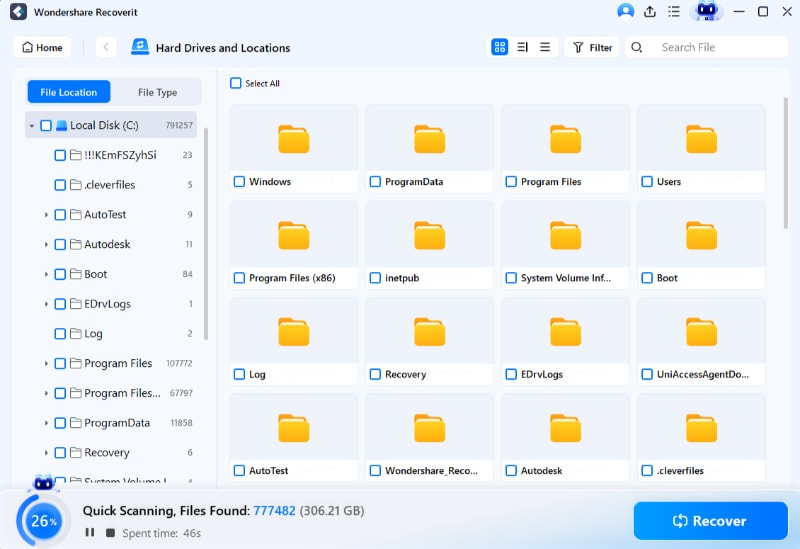
Step 3: Once you establish a successful remote connection, this software will start auto scanning. Observe the scanning progress at the bottom of the program’s screen.
If you find the right file before a full scan is completed, you can pause it at any time. This is something that sets Recoverit apart from traditional tools. You have the option to preview the files before recovering them. For this, you have to tap on “Preview.”
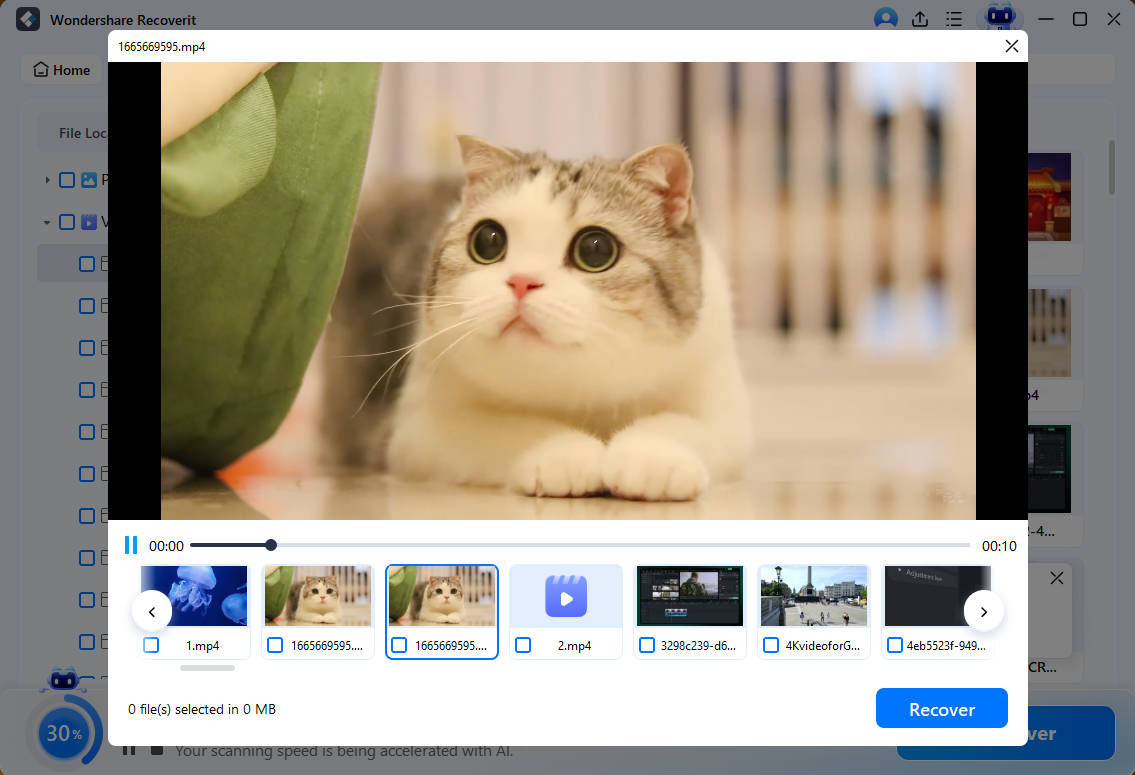
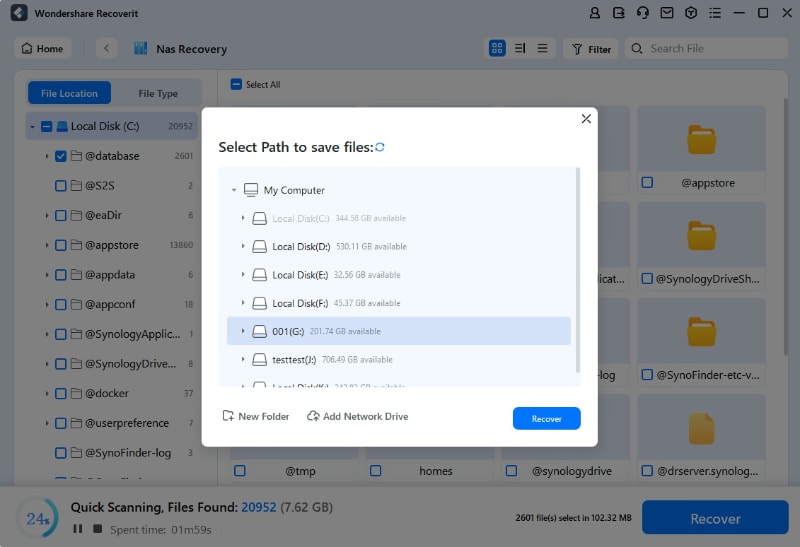
Has Recoverit shown you the data you want to get back? If yes, hit the “Recover” button, choose the right path, and save it on your system. For security reasons, the new path should not be the same as the one where you lost the files.
Part 5. Access Linux Partition from Windows FAQs
How can I access a Linux shared folder?
Press “Alt + F2” from the keyboard. It will open a “Run” dialog box. Now type “smb://” and write the IP address of your Linux server after it. Don’t forget to put the folder name along with the IP address. Now, hit the “Run” button to proceed.
What are the popular ways to view disk partitions in Linux?
The top 3 ways to view partitions in Linux include the hwinfo command, Isblk command, and Fdisk command.
Does Windows has a Linux terminal?
Yes. Go to the search menu of your Windows and write “Turn Windows features on and off,” and open it. Now, look for “Windows Subsystem for Linux,” and check this box. It is time to click “OK,” and you are done.
Parted or Fdisk? Which one is better?
Well, Parted is a great alternative utility to Fdisk. It has the ability to perform all Fdisk operations. Moreover, it comes with an additional feature of creating file systems and copying and resizing Linux partitions.
How can I list directories and files in Linux?
The “Is” command enables you to list directories and files in Linux and all Unix-based OS. After listing them all, this command interacts through the command line.
Final Words
This article has presented the top 6 methods to effectively deal with the problem of accessing Linux partitions from Windows. You can try any of the above-listed approaches to read Linux partitions on Windows.
If you are worried about losing your important data or have lost it already during mounting, give Wondershare Recoverit a try to get out of the chaos. This program is known for its highest data recovery rate, amazing customer support, and a 7-day money-back guarantee. Furthermore, millions of happy and satisfied users worldwide have helped this tool gain more and more customers' trust in the last couple of years.
For Windows Vista/7/8/10/11
For macOS X 10.10 or later

 ChatGPT
ChatGPT
 Perplexity
Perplexity
 Google AI Mode
Google AI Mode
 Grok
Grok






















