
You may have accidentally deleted important files on your Kali Linux system. The unfortunate event of accidentally deleting critical files can happen to anyone and cause significant workflow disruptions. The need for Kali linux data recovery is crucial as it is a popular operating system among information security professionals and enthusiasts.
This article will cover various methods to recover deleted files on Kali Linux, including graphical interface and command-line tools.
Overview of Kali Linux
Previously known as BackTrack Linux, Kali Linux is a Debian-based open-source Linux distribution designed for advanced penetration testing and security auditing. It offers a comprehensive set of tools, configurations, and automation features to enhance efficiency and allow users to focus on the target task at hand.
The distribution comes with over several hundred tools pre-installed and configured to work together, making it easy for users to perform a wide range of tasks without manually setting up and configuring individual tools. Some of the most popular tools included are Nmap for network scanning, Wireshark for packet analysis, Metasploit for exploitation, and many others.
It is available as a free resource.
How To Recover Deleted Files on Kali Linux?
Make sure you sign in with the Root user before moving forward.
Way 1: Kali Linux Data Recovery With Foremost (CLI Tool)
Foremost is a command line tool included in Kali Linux and is used for data recovery. It scans a given disk or partition to identify and recover the deleted files based on their headers, footers, and data structures. It can recover many file types, including JPEG, GIF, PDF, DOC, XLSX, and many other formats. This Kali Linux data recovery tool is efficient, lightweight, and easy to use.
Follow the steps below to recover deleted files on Kali Linux using Foremost.
Case 1. Recovering Files From a USB drive
- Press "Ctrl + Alt + T" to open the Terminal.
- Determine the path of your USB drive by using the command "sudo fdisk -l" in the Terminal to list all connected storage drives on the system.
You will receive the following output.
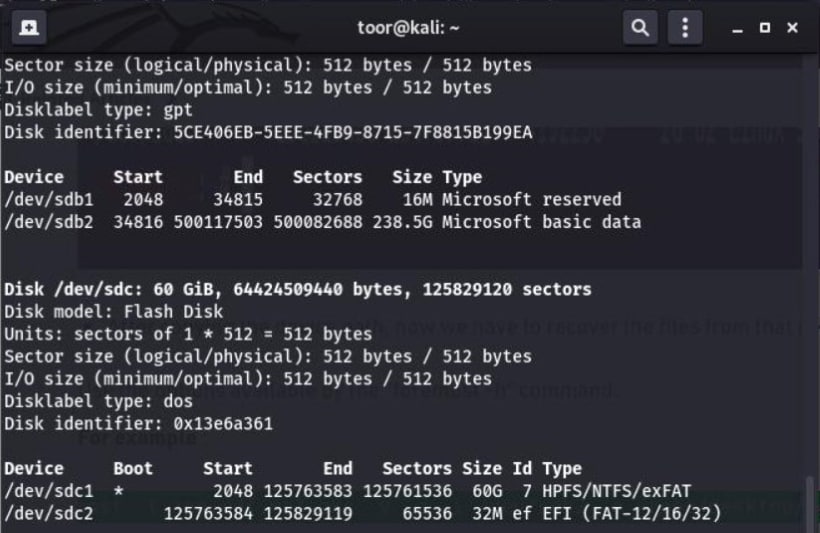
- Locate the path of your USB drive by using the command "sudo foremost -v -t jpg,pdf,mp4,exe -q -i /dev/sdc -o /home/Desktop/recover -T" and use that path as an input for the Kali Linux data recovery process.
- Use the "-t" flag when running the recovery process to specify the types of files to be recovered per the requirement.
- Use the "-o" flag during the recovery process to specify the desired output file path where the recovered files will be saved.
- Use the "-i" flag to specify the drive you wish to recover files during the recovery process.
The above command will give you the following output:
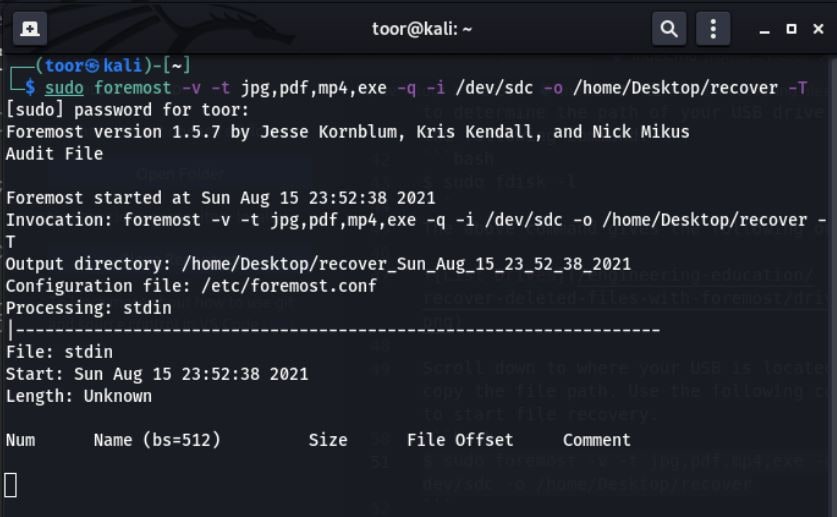
- As the recovery process runs, it displays the files being recovered in real-time, which are subsequently saved in the specified output file path.
- Upon completion of the recovery process, the recovered files will be saved in the designated output file path. Note that the duration of the process may vary depending on the size of the drive. You can find the recovered files in the specified output file path.
Case 2. Recover Files From a Hard Disk
- Utilize the command "sudo fdisk -l" in the Terminal to list all the storage devices connected to the system and identify the specific device for data recovery
- The command "sudo fdisk -l" provides an overview of all the storage devices connected to your machine, along with their partitions, as demonstrated in the output illustrated below.
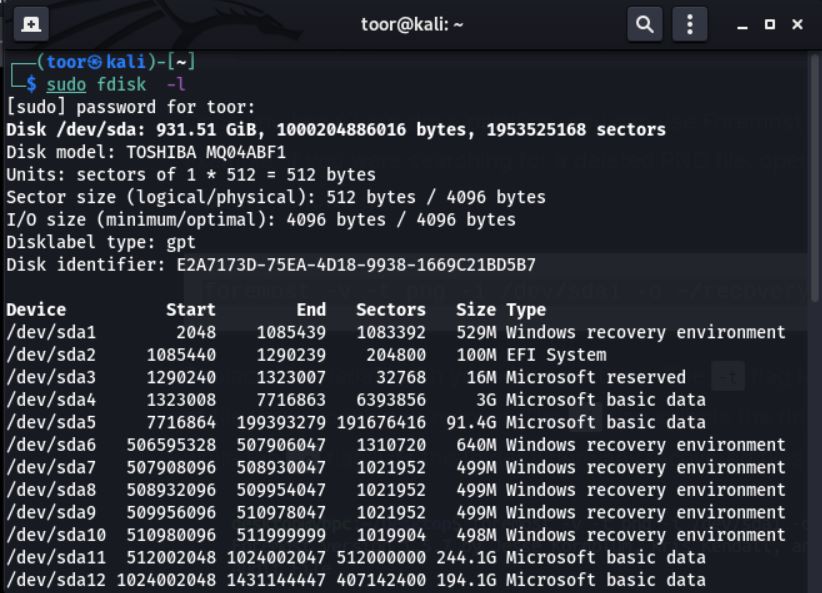
- There are two main methods to recover lost or deleted files from a hard drive:
- Foremost can recover files from all partitions on the Linux hard drive, but it takes more time.
- When you know the partition containing the deleted files, you can use Foremost to recover files only from that specific partition. This allows for a more targeted and efficient recovery process.
- To recover files from an entire hard drive, use the command "sudo foremost -v -t png,mp4,pdf -i /dev/sda -o /home/Desktop/recover -T".
- Use the appropriate hard drive path when running the recovery process. Additionally, the output of the above recovery command is illustrated below.
- Type the following command to recover files from a single partition: "sudo foremost -v -t png,mp4,pdf -i /dev/sda1 -o /home/Desktop/recover -T".
When recovering files from a specific partition, be sure to replace the partition path with the appropriate path for your system.
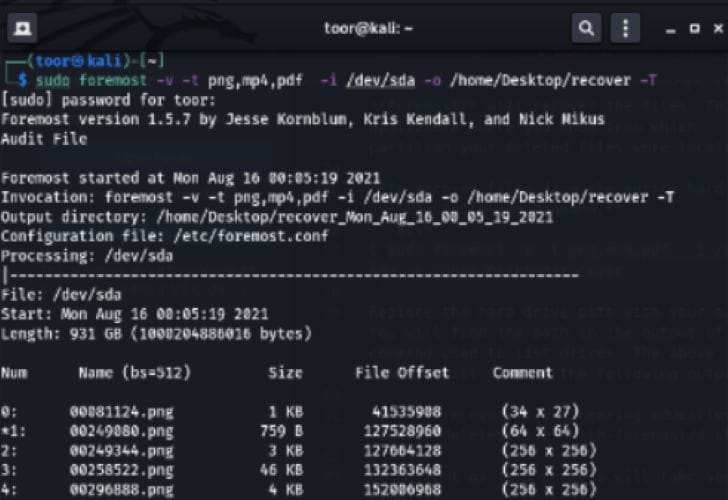
The Kali Linux data recovery process may take varying duration depending on the size of the partition.
Case 3. Recovering Files of All Types
- Type the command "sudo foremost -v -q -i /dev/sdc".
- When running the file recovery process, make sure to replace the drive path in the command with the appropriate path for the specific device you wish to recover files from. This process will automatically generate an output folder named "output" in the home directory that contains the recovered files.
Way 2: Kali Linux Data Recovery With Wondershare Recoverit (GUI Tool)
Wondershare Recoverit is a Kali Linux data recovery tool with a GUI interface. It is a powerful and easy-to-use Linux data recovery software that can help you to recover lost or deleted files from a wide range of devices, including NAS servers, computers/laptops, hard drives, USB drives, and memory cards. Besides, it supports various file systems, including NTFS, FAT16/32, exFAT, ext2/3/4, and btrfs.

Wondershare Recoverit - Your Safe and Reliable Linux Recovery Software
5,481,435 people have downloaded it.
Recovers lost or deleted documents, photos, videos, music, emails, and other 1000+ file types effectively, safely, and completely.
Compatible with all mainstream Linux distros, including Ubuntu, Linux Mint, Debian, Fedora, Solus, Opensuse, Manjaro, etc.
Assists in 500+ data loss scenarios, such as deletion, disk formatting, OS crash, power outage, virus attack, lost partition, and many more.
The simple point-and-click interface allows you to recover data from Linux hard drives in just a few clicks.
To recover deleted files from a Kali Linux device using this Kali Linux data recovery tool, you can take the following four simple steps:
- Download and install Wondershare Recoverit on a Windows or Mac computer.
- Navigate to the sidebar, select the 'NAS and Linux' option, then click 'Linux Recovery' to proceed with the Kali Linux data recovery process.
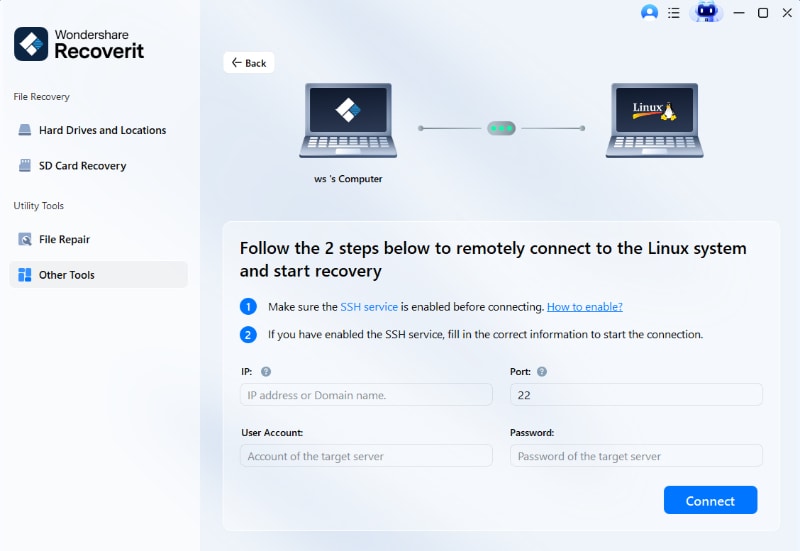
- Recoverit requires information about the Linux device from which files have been lost in order to establish a remote connection. Provide the necessary information and select 'Connect' to grant Recoverit access to the Kali Linux device.
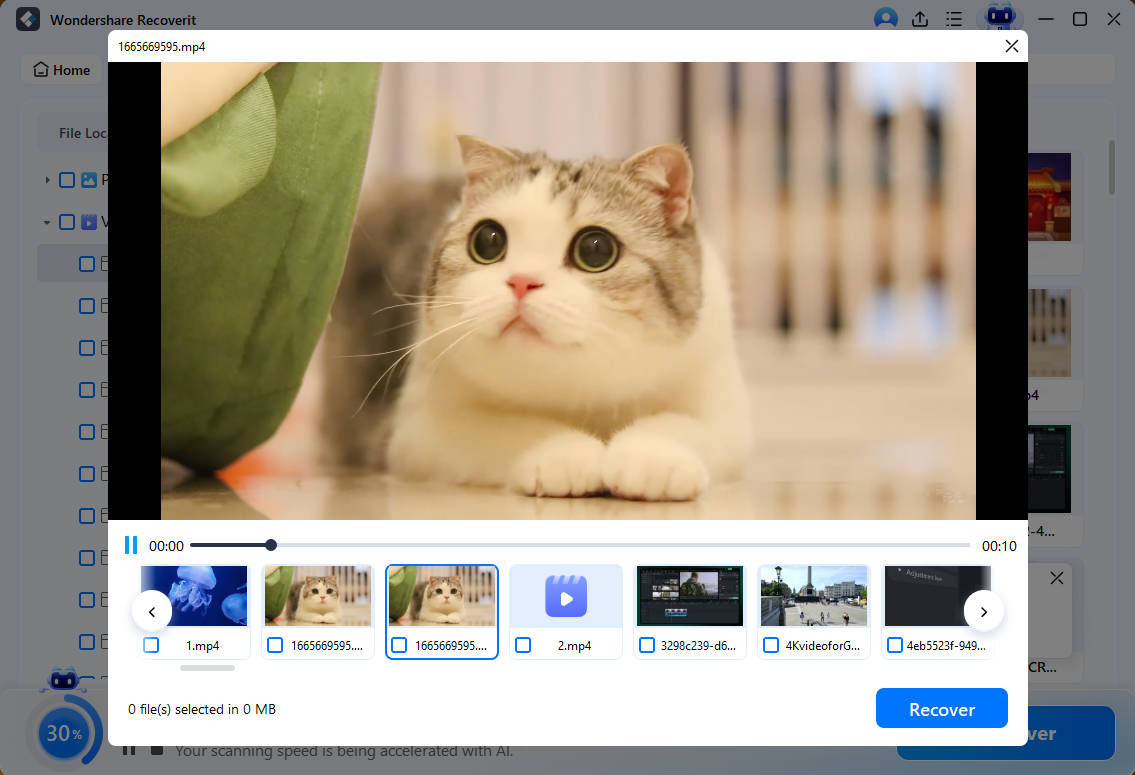
- Once the connection is established, the data recovery software will automatically start scanning for deleted files in your Kali Linux device.
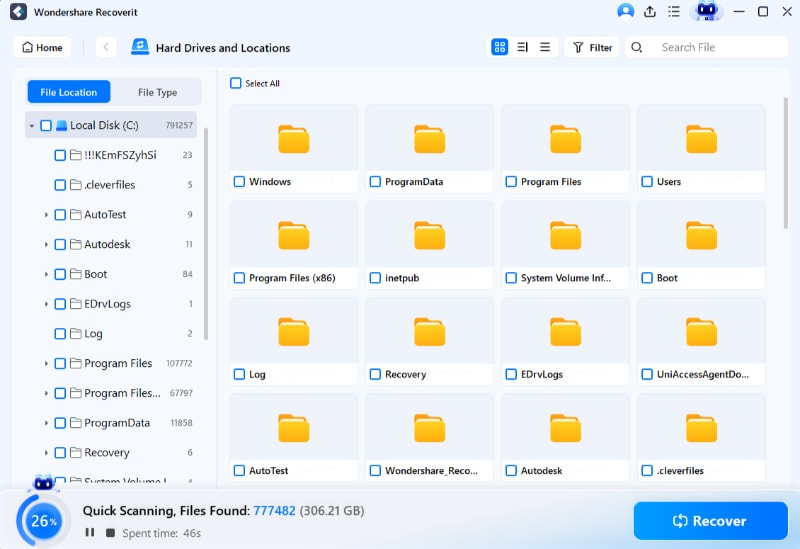
- Preview files during the scanning process; you can interrupt the scanning at any time. Once you have identified the desired files, select them and click the 'Recover' button. The files will be successfully restored and saved.
For Windows Vista/7/8/10/11
For macOS X 10.10 or later
Video Tutorial on How to Recover Files from NAS Server?
For Windows Vista/7/8/10/11
For macOS X 10.10 or later
Conclusion
Recovering deleted files on Kali Linux is a task that can be accomplished by using specialized data recovery software. Foremost and Wondershare Recoverit are two excellent Kali Linux data recovery tools that aid in the recovery of data lost due to a variety of reasons, such as accidental deletion, power failure, and disk formatting. They are truly efficient and effective solutions for data recovery on Kali Linux.


 ChatGPT
ChatGPT
 Perplexity
Perplexity
 Google AI Mode
Google AI Mode
 Grok
Grok






















