No matter what kind of system you're operating, there's always a chance that your data can get erased. That is why it's a good idea to have data recovery software installed and ready at all times.
However, that can be a bit of a snag for those who use Linux. Several developers often overlook the OS and attribute the small market size to saving the effort for more common systems. Yet, Scalpel for Linux can help you out of it. Throughout this piece, you’ll learn all about Scalpel and its related versions, how effective they are at recovering deleted files in Linux, and what alternative you can adopt for it.
Part 1. What Is Scalpel?
An improvement over its predecessor, Foremost, Scalpel is an open source, fast and lightweight command line-based file carver that reads a media (e.g., hard disk or CD-ROM) and extracts the content by carving it into blocks of data. It is designed specifically for Linux but also runs on other platforms such as Windows and Mac OS X.
It comes pre-installed with Kali Linux. You can also avail of it on other kernels, such as Chimera and Ubuntu. Unlike Foremost, which puts plenty of strain on the CPU, Scalpel can work in the background while you perform more urgent tasks on your PC.

Features of Scalpel
Scalpel has several valuable features that make it more efficient than some other Linux data recovery tools. With a Scalpel Ubuntu or Kali Linux version, you get access to the following.
- Ability to carve files from a wide range of image types, including RAW images from camera memory cards, dd images, and advanced forensic formats like SmartForensic ISO 9660;
- Can be used to recover known file types (such as documents) even if the filesystem has been corrupted;
- Built-in support for popular compression algorithms such as ZIP and RAR;
- Flexibility in specifying what types of data should be carved – users can define their own signatures to search for specific files/types;
- Supports more than 100 file systems out-of-the box, including FAT16, FAT32, exFAT, EXT2, EXT3, EXT4, NTFS, etc. Users don’t have to write custom scripts to extract data from different drive types.
- Easy to configure with a few command lines. So, you can create backups for specific drives instead of drawing resources for the entire system.
- You can use Scalpel to recover files on external media devices, like USB drives, SD cards, and digital cameras, provided it’s suitably configured.
- Doesn’t occupy too much space on your system. You can install Scalpel for less than 300 MB on your Linux PC and even have it active in a dedicated flash drive.
Part 2. How To Download Scalpel?
If you’re operating Kali Linux, you might already have Scalpel pre-installed. In case it’s not, you can download a suitable version from PKGS. It’s a secure website that stores the relevant installer packages for all known versions of Linux. Moreover, it has mirror servers for different architectures, just in case you’re using Linux to run virtual machines by sharing the same hardware for multiple operating systems.
Part 3. How To Install Scalpel on Kali Linux?
Depending on the specific kernel of Linux, you have to execute different commands for installing Scalpel onto your system. Here, we’ll focus on the most popular kernels, as listed below.
● Install on Debian/Ubuntu and Linux Mint:
Press Ctrl+Alt+T to access the terminal on your system. Then, you need to enter the following command and press Enter.
$ sudo apt-get install scalpel
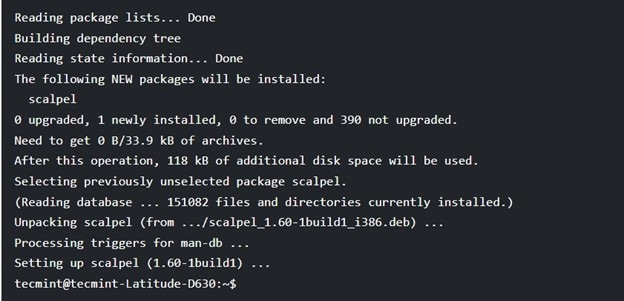
Once the setup completes, you can configure the software for your system and proceed with recovering any deleted files. Ubuntu also lets you use the graphical interface to change the location of the installed files.
● Install on RHEL/CentOS and Fedora:
For CentOS and Fedora, you need to enter the following command from the terminal.
# yum install scalpel
The setup shall install Scalpel within the default drive. Yet, you can configure the precise location on the system by accessing the file ‘/etc/scalpel/scalpel.conf’ or ‘etc/scalpel.conf’ from the terminal.
Part 4. How To Recover Files on Linux Using Scalpel?
Before you recover files using Scalpel, you have to configure it so that the program can access the deleted files' relevant images. For Scalpel on Kali Linux, you can do it through the following procedure.
- Open the configurations file using the command:
sudo mousepad /etc/scalpel/scalpel/conf
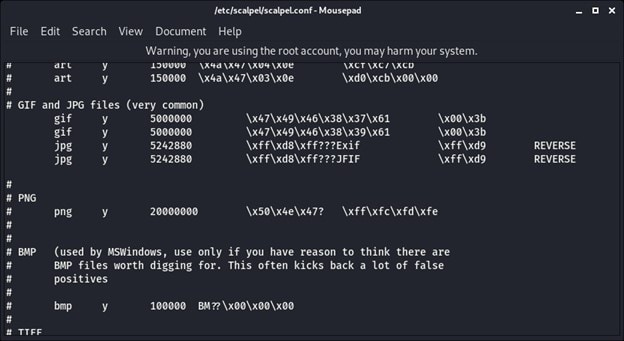
- Your screen will now display the file types with a “#” next to them. In order to locate the deleted files, remove the hashtag from the file types you wish to recover.
- Once comfortable with the file types, press Ctrl+S to save the configuration and close the mousepad.
Now, you can recover the required files from your drive of choice. Just follow the below-mentioned procedure for the same.
- Press Ctrl+Alt+T to access the terminal on your PC.
- Run Scalpel using the command:
$ scalpel -h
- Locate the required file images by typing:
$ scalpel -o recovered/ Linuxdrive.dd
You can replace “Linuxdrive.dd” with the adequate drive or device directory.
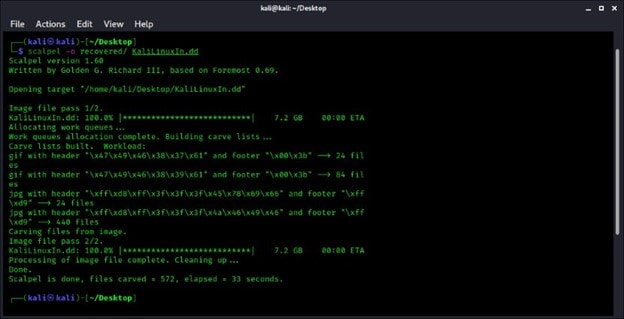
- Wait for the process to complete. Once the process concludes, you can find all the files in the folder named ‘recovered’ on Desktop or where you specified it using the Scalpel configuration.
Part 5. The Best Alternative to Scalpel for Linux Data Recovery
While Scalpel is quite convenient to use, it is only partially practical. Wiped drives that no longer contain the file images can’t be detected by Scalpel. In addition, you don’t have a choice on select files. You can only define the file types and have to wait until it scans the entire drive.
Both these issues and more can be addressed by using a graphics-based alternative to Scalpel. That’s where Recoverit Linux Recovery can prove invaluable. It’s compatible with all NAS and Linux systems, and you can conveniently install it from the official website. It also comes loaded with several useful features for recovering deleted files from Linux.

Wondershare Recoverit - Your Safe and Reliable Linux Recovery Software
5,481,435 people have downloaded it.
Recovers lost or deleted documents, photos, videos, music, emails, and other 1000+ file types effectively, safely, and completely.
Compatible with all mainstream Linux distros, including Ubuntu, Linux Mint, Debian, Fedora, Solus, Opensuse, Manjaro, etc.
Assists in 500+ data loss scenarios, such as deletion, disk formatting, OS crash, power outage, virus attack, lost partition, and many more.
The simple point-and-click interface allows you to recover data from Linux hard drives in just a few clicks.
Works through a remote connection. You can recover lost data even when your Linux device is crashed.
To recover data using Recoverit Linux Recovery, you can follow the steps mentioned below.
For Windows Vista/7/8/10/11
For macOS X 10.10 or later
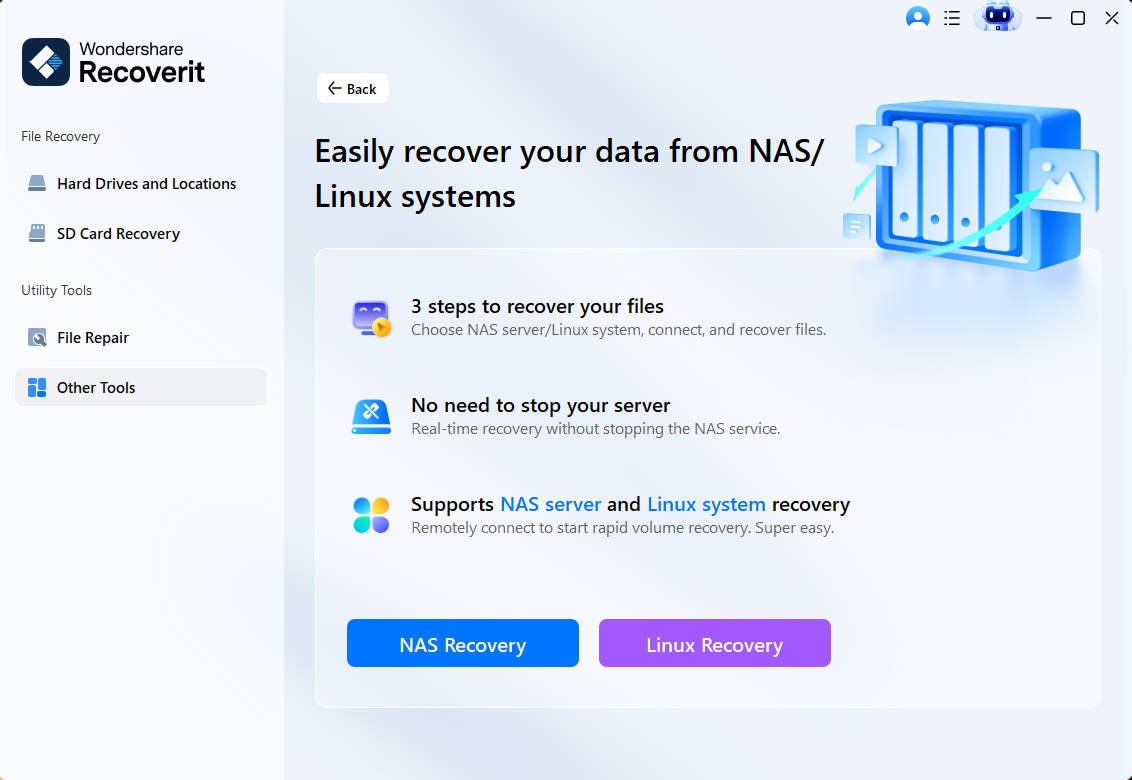
Step 1. Choose Linux Recovery Option
Download and install the Scalpel alternative software on your Windows or Mac PC. Then, launch it and select the Linux Recovery under the NAS and Linux tab to proceed with the data recovery process.
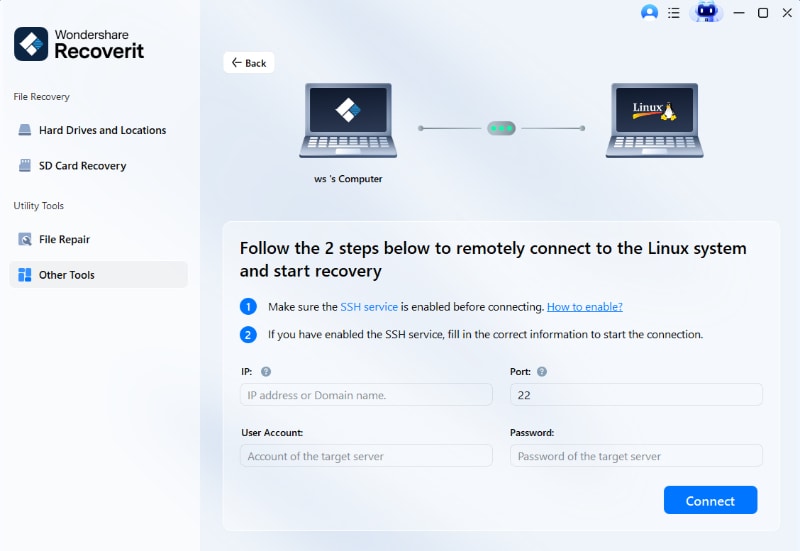
Step 2. Create a Remote Connection
Input the necessary information about the Linux device from which files have been lost to establish a remote connection. Then, click Connect to grant Recoverit access to your Linux device.
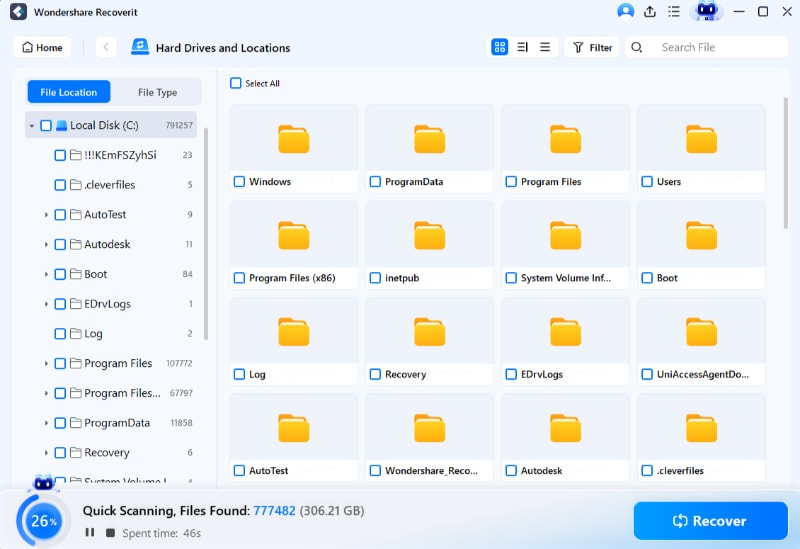
Step 3. Scan for Lost Linux Files
Once the connection is established, the software will commence the scanning process automatically. You can search and preview files during the scanning process to quickly locate your desired files.
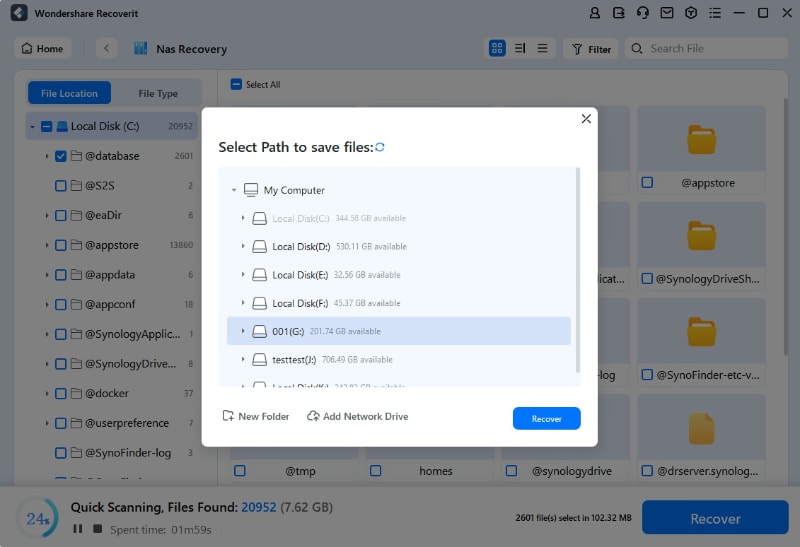
Step 4. Recover and Save Files
Once the desired files have been identified, select them and click the Recover button to retrieve them to a safe location.
For Windows Vista/7/8/10/11
For macOS X 10.10 or later
Summing Up
Scalpel is a powerful tool for recovering deleted files in Linux. It's easy to use and offers many features like custom file signatures and recovery of fragmented files. The ability to search multiple drives at once and dynamically adjust the data blocks size makes it highly suitable for many kinds of file recovery scenario.
While Scalpel is an excellent open-source data retrieval tool, its limitations can get in the way of you recovering the desired files quickly. So, you can also use a Scalpel alternative like Wondershare Recoverit to save yourself time and effort.

 ChatGPT
ChatGPT
 Perplexity
Perplexity
 Google AI Mode
Google AI Mode
 Grok
Grok






















