“I accidentally deleted the USR/share directory on Ubuntu 16. How do I recover the files within that folder?” – Quora
We've all experienced the frustration of losing a file, searching the trash for it, and not even find it there. Fortunately, the distress is only momentary, and you have access to several techniques to retrieve your lost file. This article will review the different processes for recovering deleted files/folders in Ubuntu.
In this article
Part 1. How Does File Undeletion Work in Ubuntu
Ubuntu uses journaling file systems like EXT4, like most Ubuntu-based operating systems. Because it maintains a "journal" of which files are kept in which locations on your drives, a journaling file system gets its name. For more detailed information about journaling file system, watch the video below:
For Windows XP/Vista/7/8/10/11
For macOS X 10.10 or later
On Ubuntu, the disk isn't truly deleted when deleting a file. Until new data replaces it, the existing data remains in place. That is how Ubuntu's undelete tools operate: they scour your file system for indications of material that has been deleted from the file system journal but is still there on the disk.
The amount of data that will likely remain after deletion is very difficult to determine. After you delete data, it can be overwritten in a matter of moments or remain there for days. The likelihood of recovering a deleted file on Ubuntu mostly depends on luck and the number of open programs and processes on your system. The more things you have running, the more likely it is that anything will decide to write data to the location where your deleted file is stored.
Undeleted files have a better chance of surviving if they are located on a partition that is not a part of your main system since system partitions experience more data activity from background activities. On the other hand, the partition where your operating system stores all of its constantly changing logs and application data is less likely to have your erased data intact. Instead, an external disk drive that you use to store videos and images is more likely to have your deleted data intact.
Part 2. 4 Ways to Recover Deleted Files and Folders on Ubuntu
Way 1: Recovering Deleted Files on Ubuntu From Trash
When you delete a file with the file manager on your Ubuntu device, it is normally placed in the Trash and should be recoverable. To recover a file from the Trash, follow these steps:
Step 1. Start typing Files in the Activities overview.
Step 2. To open the file manager, click Files.
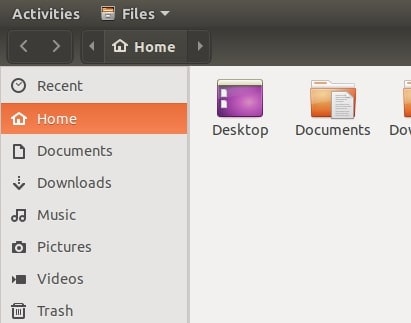
Step 3. In the sidebar, select Trash. If the sidebar is not visible, click the Menu button in the window's upper-right corner and select Sidebar.
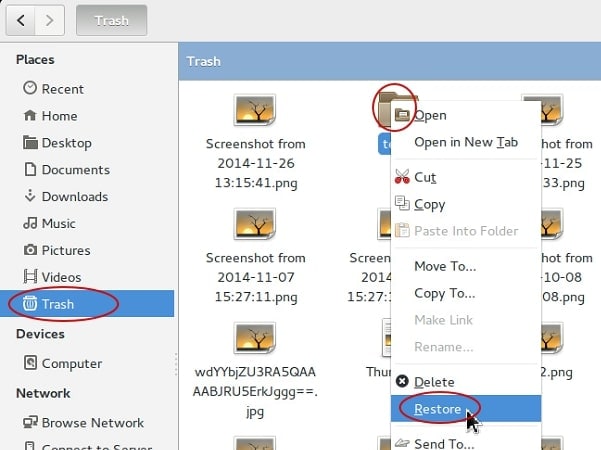
Step 4. If your deleted file is still there, right-click it and choose Restore. It will be restored to the folder from which it was deleted.
The file has been permanently deleted if you deleted it by pressing Shift+Delete or by using the command line. Permanently deleted files cannot be recovered from the Trash. You need to utilize the following methods to restore permanently deleted files on Ubuntu.
Way 2: Recovering Deleted Files on Ubuntu From Backup
Have you previously backed up your data to a safe location? If yes, you can also recover deleted files on Ubuntu from your backup.
Step 1. Open Terminal.
Step 2. Enter the following command.
sudo mount -o rw,remount/
Step 3. When prompted, enter your user account password.
Step 4. Execute the following command:
sudo cp <filename> /media/<backup_location>
Repeat step 3, and the deleted file will be restored to its original location.
Way 3: Deleted File Recovery on Ubuntu Using Wondershare Recoverit (GUI Tool)
If the above two methods don’t work for you, you will need a professional data recovery tool. That's where Wondershare Recoverit Linux Recovery can be valuable. It is a powerful and user-friendly software solution that can recover lost or deleted files from different storage devices, including Ubuntu Linux devices. Take a glance at some of Recoverit Linux Recovery features:

Wondershare Recoverit – Your Safe and Reliable Linux Recovery Software
5,481,435 people have downloaded it.
Recovers lost or deleted documents, photos, videos, music, emails, and other 1000+ file types effectively, safely, and completely.
Compatible with all mainstream Linux distros, including Ubuntu, Linux Mint, Debian, Fedora, Solus, Opensuse, Manjaro, etc.
Assists in 500+ data loss scenarios, such as deletion, disk formatting, OS crash, power outage, virus attack, lost partition, and many more.
The simple point-and-click interface allows you to recover data from Linux hard drives in just a few clicks.
You can recover deleted files on Ubuntu using Wondershare Recoverit Linux Recovery with the following 3 steps.
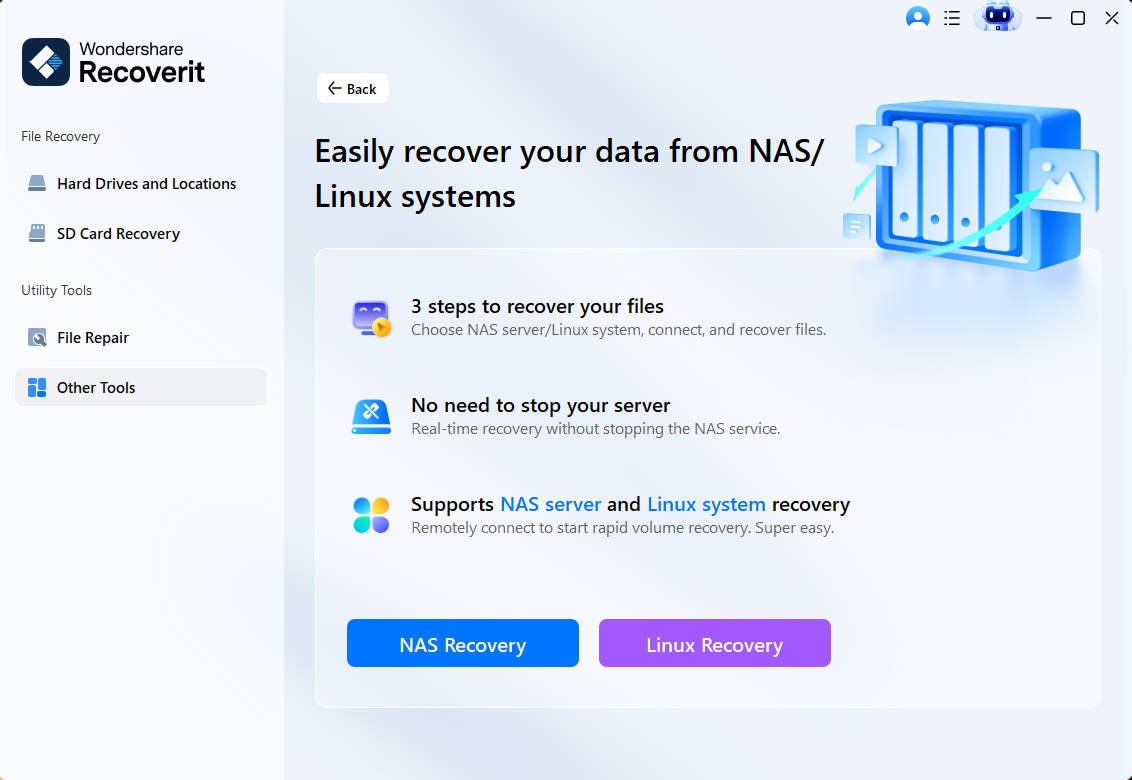
Step 1. Choose the Linux Recovery Option
After downloading and installing Recoverit on a Windows or Linux computer, go to the NAS and Linux section and select Linux Recovery.
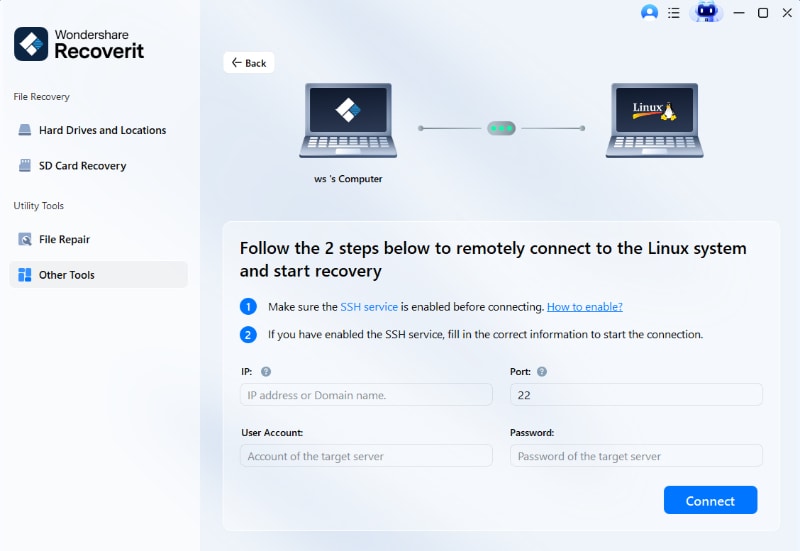
Step 2. Connect to the Ubuntu device
Now, connect the Linux File Recovery program to your Ubuntu computer by entering the IP address, port number, user name, and password.
Step 3. Scan and Recover
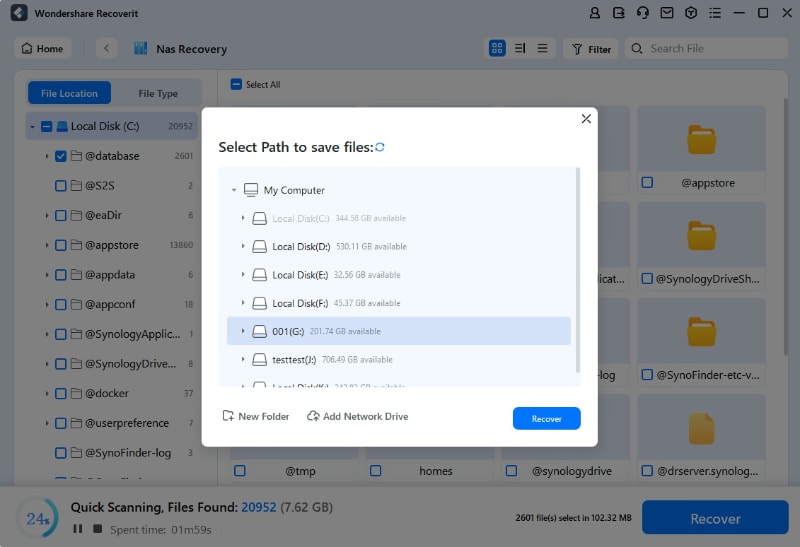
Recoverit will begin searching for lost data in your Linux system as soon as the connection is successful. The scanning process takes some time, depending on the amount of data stored on your Ubuntu device.
The scanned files and folders will display on the screen, and you can preview them to make sure they are recoverable. Finally, click Recover to restore the deleted files or folders from your Ubuntu device.
For Windows Vista/7/8/10/11
For macOS X 10.10 or later
Video Tutorial on How to Recover Linux Files on Windows?
For Windows Vista/7/8/10/11
For macOS X 10.10 or later
Way 4: Deleted File Recovery on Ubuntu Using TestDisk (Command Line)
TestDisk, a tried-and-true program recovering deleted Ubuntu files for over a decade, is another free and useful tool for undeleting data in Ubuntu. You can follow the detailed steps below or watch this video for a more comprehensive explanation.
For Windows Vista/7/8/10/11
For macOS X 10.10 or later
Step 1. You must first install the TestDisk tool. To install TestDisk, run the following command:
sudo apt install testdisk
Step 2. Use the following command to launch TestDisk in the terminal:
testdisk
Step 3. To navigate, use the arrow keys and press Enter to select.
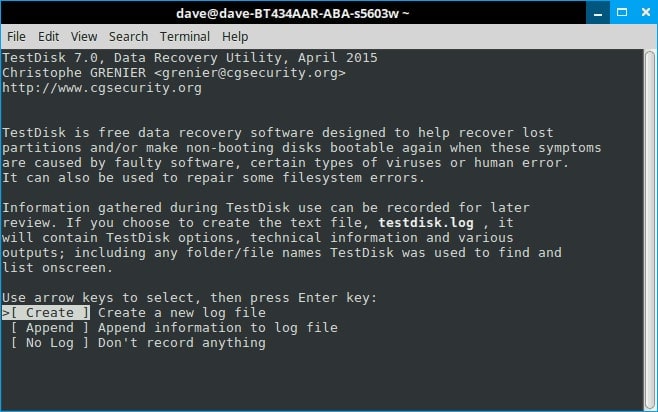
Step 4. Testdisk requires your permission to open them. Choose sudo and enter your password. On the next screen, press Enter twice more to create another log file.
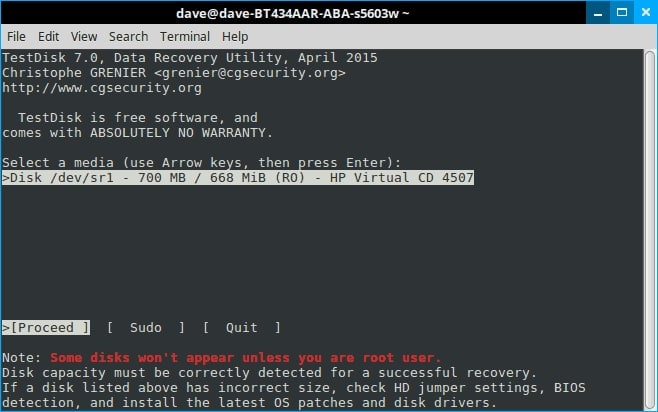
Step 5. Testdisk shows you all of your drives. Enter by arrowing to the drive.

Step 6. Testdisk has chosen the correct setting. Enter once more.
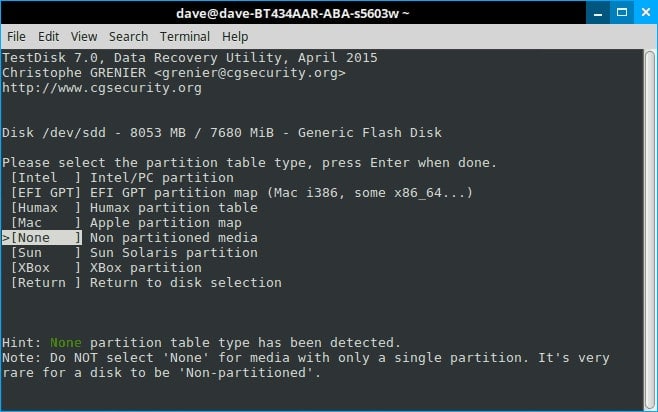
Step 7. Enter Advanced.
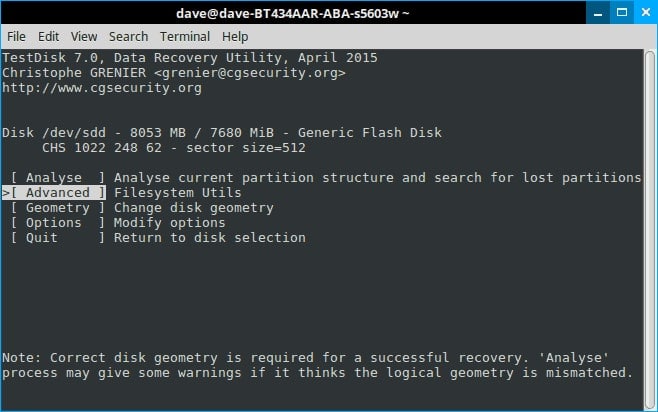
Step 8. Select Undelete at the bottom of the page.
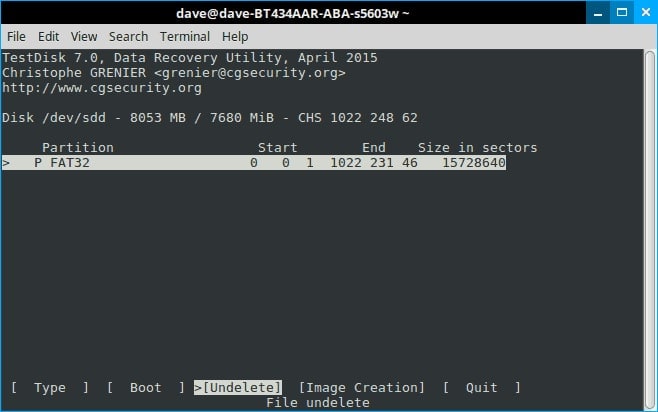
Step 9. Testdisk will scan your files and display a list of deleted files in red. Arrow down to it and read the options at the bottom carefully.
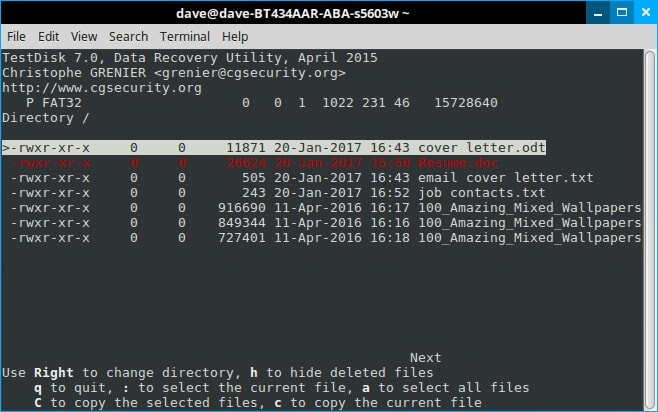
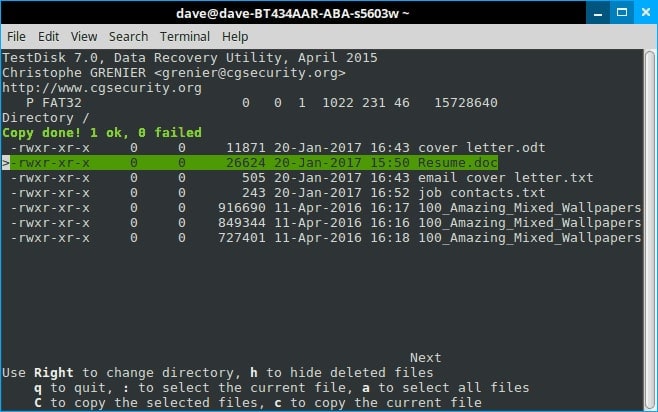
Step 10. Remember that Testdisk is a multi-functional tool. The majority of these options deal with groups of files. So press the c key.
FAQs
Where do delete files go to Ubuntu?
A deleted file on Ubuntu is transferred to the Trash, which remains until the Trash is emptied. If you need something from the Trash or unintentionally removed something, you can return it to its original location.
Can deleted files be recovered from Ubuntu?
Yes, you can recover the deleted files on Ubuntu. You can do it by the abovementioned steps:
● Restoring it from the Trash
● Using a reliable GUI data recovery tool like Wondershare Recoverit
● Using the open-source command line tool TestDisk
How do I restore permanently deleted files in Linux?
When a file is deleted permanently from the Recycle Bin/Trash, it remains on the hard drive until it is overwritten with new data. As a result, some or all of the data can be restored using a Linux data recovery tool.
Conclusion
That’s all there to it! This article provided information on recovering deleted files or folders in Ubuntu. The 4 ways are mentioned, wherein you can recover the deleted files from the Trash, from the Ubuntu backup, using a GUI tool and a command line app. Choose what’s the best for you, but we highly recommend using Wondershare Recoverit as it can easily and safely recover your data!
For Windows Vista/7/8/10/11
For macOS X 10.10 or later

 ChatGPT
ChatGPT
 Perplexity
Perplexity
 Google AI Mode
Google AI Mode
 Grok
Grok






















