How do I restore an overwritten file on Linux?
Accidentally overwriting a file can happen to anyone, and it can be a frustrating and potentially disastrous situation. The best part is that there are ways to recover overwritten files on Linux.
In this article, we'll discuss the various methods and tools used on Linux to recover an overwritten file step-by-step. We will also explain why this type of data loss occurs and provide tips on how to prevent it in the future.
Part 1. Is It Possible to Recover Overwritten Files?
Yes, it is possible to recover overwritten files. Still, the success rate depends on various factors, such as the file system type, the amount of new data written over the file, and whether the file has been physically deleted.

When a file is overwritten, the new data writes over the top of the old data on the hard drive, potentially rendering the old data unrecoverable. However, some remnants of the original file may still be present on the hard drive and can be retrieved using specialized data recovery software.
Additionally, specific techniques can be used to recover overwritten files, such as File Carving, which attempts to reconstruct the original file by analyzing the disk and identifying the file's unique headers and footers.
It is worth noting that the chance of successful recovery decreases as more data is written over the file. Therefore, it is advisable to stop using the affected storage device immediately after the file is lost and seek professional help in recovery.
Part 2. Cautions When You Want to Keep an Overwritten File
When attempting to recover an overwritten file, taking certain precautions is essential to increase the chances of successful recovery. One of the most important precautions is to stop or limit writes to the disk containing the overwritten file. Writing new data to the disk can overwrite the original data, making it more difficult or impossible to recover.
Other cautions to consider when attempting to recover an overwritten file include the following:
- Do not attempt to recover the file using the exact location that contains the overwritten file.
- Do not install any software or run any commands on the affected device, as this can overwrite the original data.
- Use specialized data recovery software that is specifically designed to recover overwritten files.
- Seek professional help in case of need.
Part 3. How To Recover an Overwritten File on Linux?
Due to the complicated nature of data recovery on Linux, it is crucial to maintain regular backups of important files to ensure minimal data loss in case of accidental deletion or overwriting. You can employ specialized commands and GUI tools to restore your overwritten file if such incidents occur.
Way 1: Recover Overwritten Files on Linux Without any Special Programs
It is possible to recover overwritten files on Linux even if you do not have any special programs.
Step 1: Try the following command if you remember some unique string in your .txt file:
$ sudo grep -i -a -B100 -A100 'string' /dev/sda1 > file.txt.
Note: It will search for the string in the partition /dev/sda1 and write the 100 lines before and after the match to a file named 'file.txt'.
Step 2: If you're trying to recover a large file that may be in multiple non-contiguous blocks, you can use the following process:
Use the grep command to search for specific text within the deleted file. For example:
grep -a -b "text in the deleted file"/dev/sda1
Step 3: Once you have the offset, use the dd command to extract the data. For example:
dd if=/dev/sda1 count=1 skip=$(expr 13813610612 / 512)
Way 2: Recover Overwritten Files on Linux Using TestDisk
TestDisk is a command-line-based data recovery tool. It can recover lost partitions and make non-booting disks bootable again. The tool is designed for both novice and expert users, and it can be used to recover data from a wide variety of file systems, including NTFS, FAT, EXT2/3/4, and more.
The process of recovering overwritten files on Linux using TestDisk can be broken down into several steps:
Step 1. Install TestDisk on your Linux computer using the “apt” utility (for Ubuntu).
$ sudo apt install testdisk
Step 2. Run the following command to start TestDisk.
testdisk
Step 3. Before initiating the recovery process for overwritten files, create a "testdisk.log" file. This log data serves as crucial documentation as it contains valuable information that will be instrumental in recovering lost files.
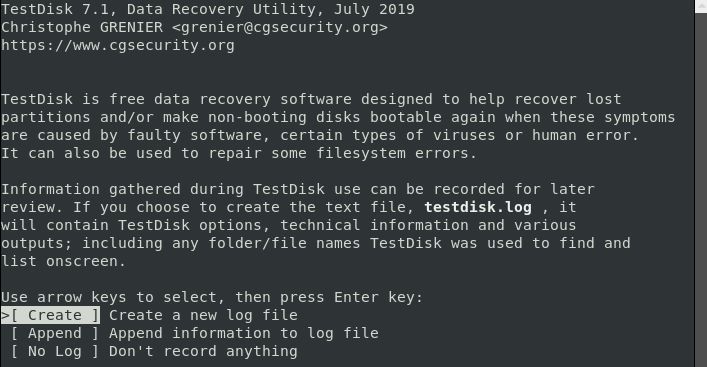
The utility description screen presents three options, each designed to cater to different needs and requirements. These options are described in detail as follows:
- The "Create" option allows the user to generate a new log file.
- The "Append" option enables the user to append additional information to previous sessions' reports.
- The "No log" option is available for users who do not intend to retain log data for future reference.
Note: Each option serves a specific purpose and can be selected based on the user's requirements and preferences.
Choose 'Create' to make a new log file. Depending on system security, the computer may ask for a sudo password before proceeding with the recovery.
Step 4. You will then see the disks attached to your system in TestDisk. You can select the drive where your file is stored, followed by the right and left arrow keys, then choose the "Proceed" option and press the ENTER key.
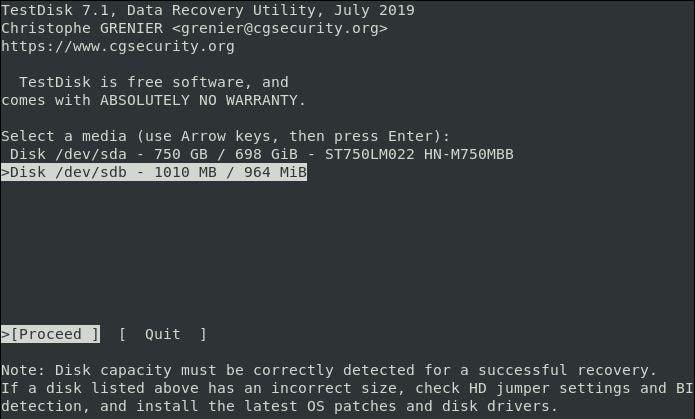
You may not be able to see some drives depending on your security permissions. Click the "Sudo" option next to the Proceed and Quit options, then enter your password.
Once your password is verified, the system will display all attached drives with their specifications.
Step 5. Once you have selected the drive, pick the right table type. Identifying the correct partition table type can be challenging if you are a beginner. However, the system automatically suggests and highlights your best partition table type.
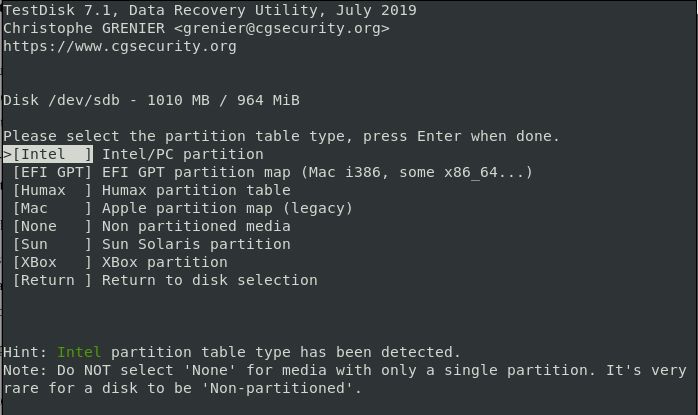
Press ENTER to proceed.
The next screen displays a list of recovery options. You can choose any of them as per your preferences. Then select 'Advanced.'
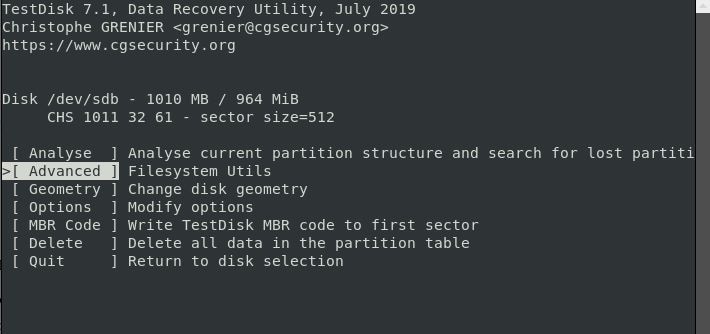
Step 6. Select the partition if your computer has more than one. Press ENTER.
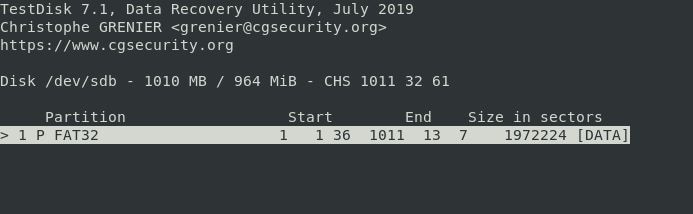
Step 7. When the program shows you all the folders on your computer, go to the folder where you lost or deleted the file.
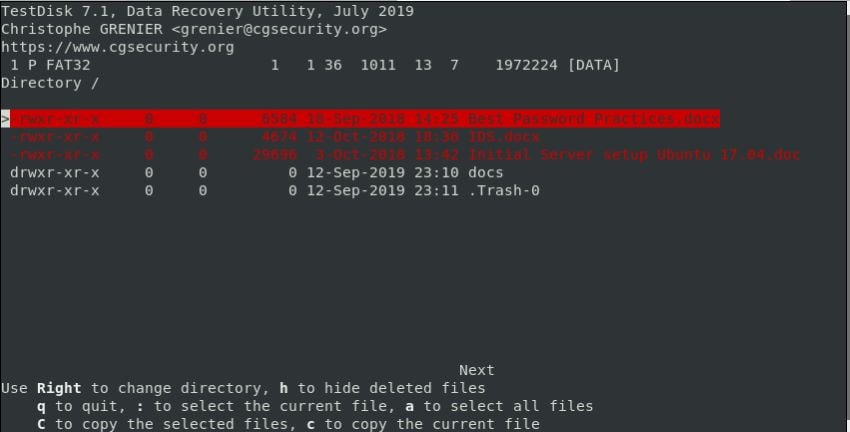
When you get to the correct folder, you will see the deleted files in red. Look for your file in the list and select it by highlighting or checking it.
Step 8: To restore a file, press 'C' on your keyboard to copy it.
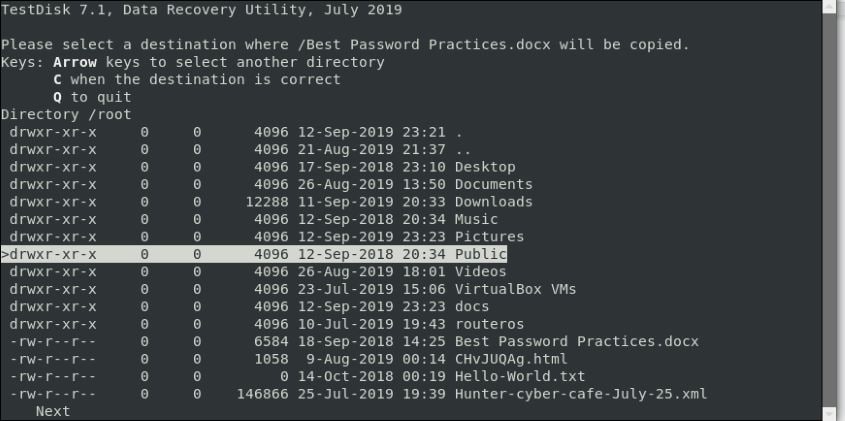
Step 9: The Testdisk utility will present a list of locations for file recovery. Use the scroll function to select the desired destination, then press 'C' to paste the copied file.
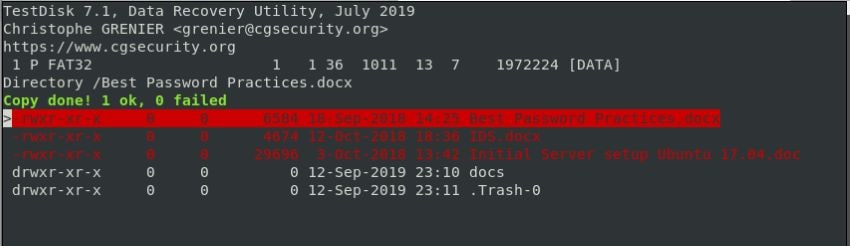
You will get a confirmation of successful file copy will be displayed if the process was successful.
Step 10. To exit the TestDisk utility, select 'Quit' and press ENTER. This will return to the previous screen. Repeat this step to exit TestDisk completely.
Way 3: Recover Overwritten Files on Linux Using Recoverit (GUI Tool)
Wondershare Recoverit is data recovery software that can recover lost, deleted, or overwritten files on various operating systems, including Linux. It has a graphical user interface (GUI) that makes it easy to use.
Some of the features of Recoverit related to Linux file recovery are:

Wondershare Recoverit - Your Safe and Reliable Linux Recovery Software
5,481,435 people have downloaded it.
Recovers lost or deleted documents, photos, videos, music, emails, and other 1000+ file types effectively, safely, and completely.
Compatible with all mainstream Linux distros, including Ubuntu, Linux Mint, Debian, Fedora, Solus, Opensuse, Manjaro, etc.
Assists in 500+ data loss scenarios, such as deletion, disk formatting, OS crash, power outage, virus attack, lost partition, and many more.
The simple point-and-click interface allows you to recover data from Linux hard drives in just a few clicks.
To use Wondershare Recoverit to recover overwritten files on your Linux computer, please follow these steps:
Step 1. Select Linux Recovery
Launch the Linux file recovery tool after downloading and installing. Locate and click on the NAS and Linux option, which can be found on the left side of the main interface. Then press the Linux Recovery button to proceed with the Linux recovery process.
For Windows Vista/7/8/10/11
For macOS X 10.10 or later
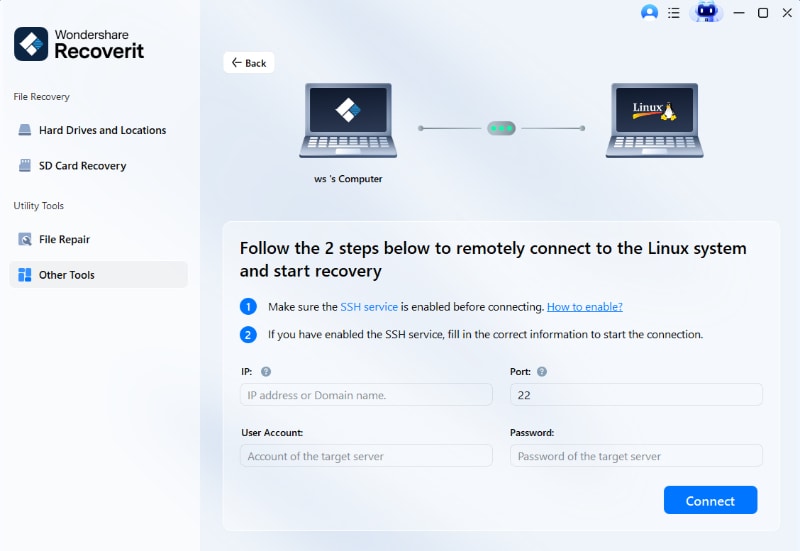
Step 2. Connect to the Linux Device
A new window will appear on your screen. Fill in the necessary information to establish a remote connection between Wondershare Recoverit and your Linux device. Then click Connect.
Once the connection has been successfully established, Recoverit will automatically begin a scan of the connected Linux computer to search for any lost or overwritten files.
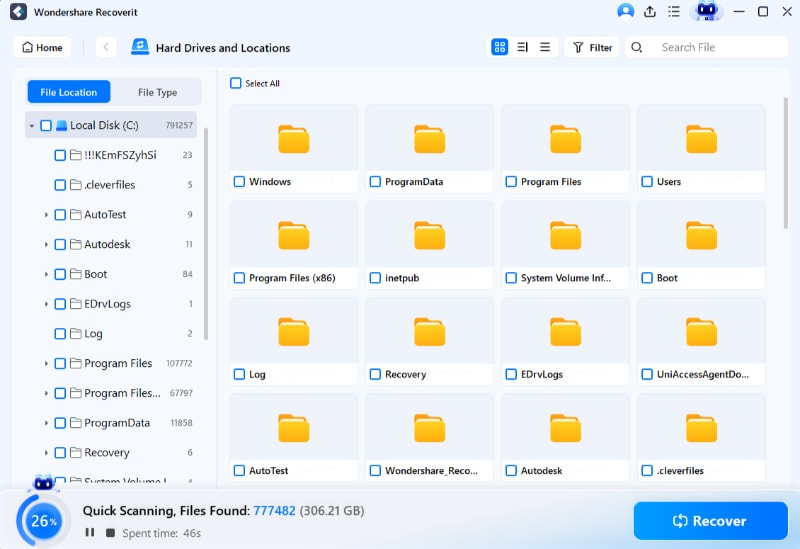
Step 3. Preview and Recover
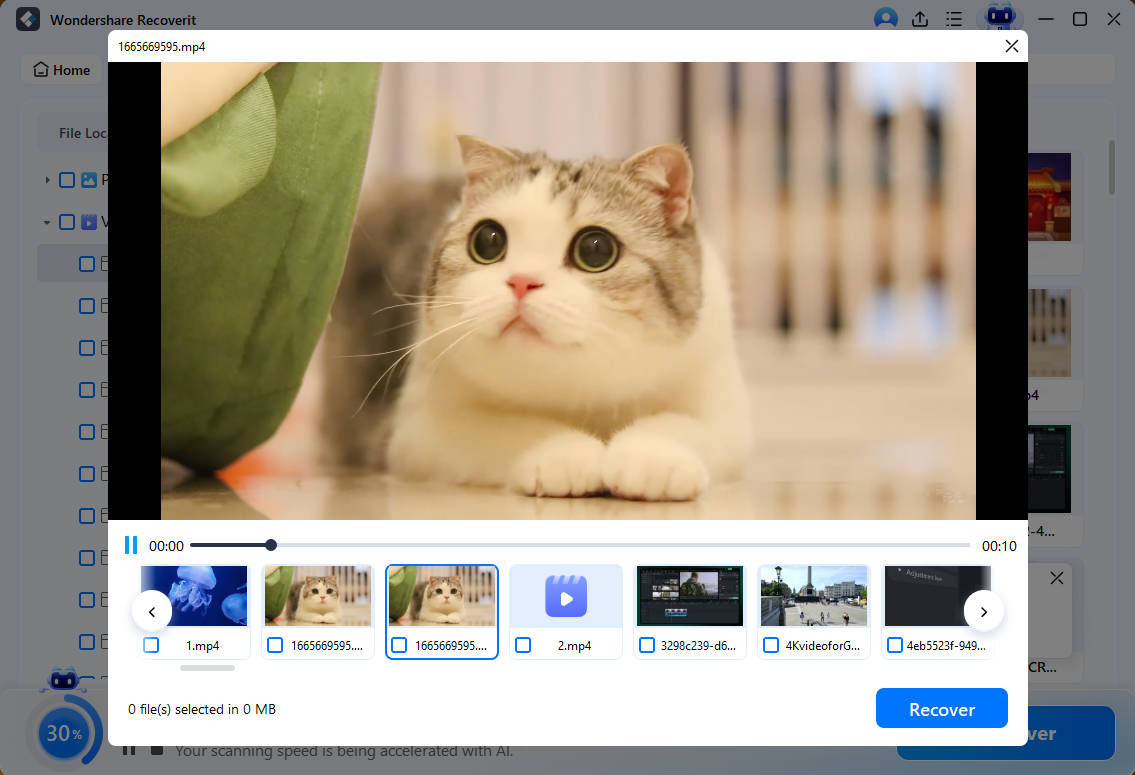
The scanned files will be displayed on the screen. Recoverit allows you to preview the files to ensure that they are the ones you intend to recover. Select the files you wish to restore and press the Recover button to save the recovered files.
Video Tutorial on How to Recover Linux Files?
For Windows Vista/7/8/10/11
For macOS X 10.10 or later
Part 4. Tips to Prevent Data Loss Due to Overwriting
A few strategies help avert losing data because of overwriting, including:
- Keep data on a separate partition from system files. Some experts even suggest using a separate partition for the /tmp directory. This segregation of data and system files will protect data from being overwritten during system updates or other operations.
- Utilize snapshots. These can be implemented at the device level (such as with ZFS or BTRFS), through snapshot tools (such as RSnapshot), or through private clouds that maintain older versions of files. Additionally, specific Network-Attached Storage (NAS) systems have integrated snapshot functionality. These can be found within the '.snapshot' directories.
- Use backup tools: The use of backup tools, such as ShadowProtect, Acronis, and others, allow for frequent incremental backups of online disks. In case of accidental overwriting, the data can be easily restored.
- Preparing a USB drive with recovery tools and appropriate live operating systems. This will enable easy and swift recovery of overwritten files even if the primary system cannot boot.
Conclusion
Restoring an overwritten file on Linux can be done by using data recovery software. The process involves scanning the drive and recovering any lost files, even if they have been overwritten. Regular backups and keeping files in multiple locations can also prevent data loss due to overwriting.

 ChatGPT
ChatGPT
 Perplexity
Perplexity
 Google AI Mode
Google AI Mode
 Grok
Grok






















