
Modern systems run on data. It guides sales, records people, runs apps, and stores the past. When the core information disappears, daily work slows or stops. People search for solutions, asking what went wrong and what steps to follow next. Some cases seem small, like a missing table. Others are spread across many files. Nothing feels calm until things return to normal.
Problems take many shapes, so teams must understand the tools and habits that place data back where it belongs. One day, you may find a damaged log. Another day, a server may refuse to start. You can fix many of these issues with well-known methods.
This guide explains the main ideas behind bringing a database back to life. It discusses what it means, why loss happens, how to act, and how to prevent problems before they spread.
Table of Contents
What is DBMS Data Recovery?
A database stores data in tables, rows, and structured layers. It sits under machines and software that read, write, and update information all day. When this content goes missing or fails, the job of bringing it back is called DBMS data recovery. In simple terms, it means repairing files or restoring copies so you can use the content again. Many workers perform this step during failures or planned maintenance. Some cases require a small repair. Others need more complex help.
When records vanish, people search for answers through tutorials, tools, or help from experts. Some use a backup. Others fix tables through commands. Some lift data from file paths or read logs to rebuild parts. The work may aim at a full rebuild or only small items.
Many also aim to improve their process so they stay ready next time a problem arrives. The subject remains broad because systems vary in size and design. But the theme stays one: bring the lost information back to a healthy state.
How to Recover a Database in DBMS?
Teams step back when data gets damaged or lost. They check logs, inspect builds, and plan next moves. They also search for tools that keep their work simple. Sometimes they turn to clean backups. Other times, they repair parts or call experts.
The best plan depends on what broke and how wide the trouble spread. Each method works best in different scenes.
Method 1: Use Recoverit Data Recovery Software
Sometimes files go missing or folders become corrupted. Well, yes! It is mostly due to accidental deletion, system crashes, or hardware issues. In such cases, a reliable data recovery tool can make all the difference. One such solution is Recoverit, a user-friendly application designed to scan your computer drives and retrieve deleted, hidden, or lost files with minimal effort.
Recoverit works efficiently across various scenarios, including server failures or human error. If someone mistakenly removes important files or a system component malfunctions, the tool can quickly locate and restore the data. Its intuitive interface ensures that even users without technical expertise can navigate the recovery process with ease.
What sets Recoverit apart is its speed and ease of use. It shortens the recovery path, making it ideal for professionals working under tight deadlines. Whether you're salvaging project files or rescuing personal documents, Recoverit helps you act fast and recover with confidence.
How to use Recoverit:
Step 1. Install Recoverit on your computer and open the application to get started. Select the target path, scan, and save files.
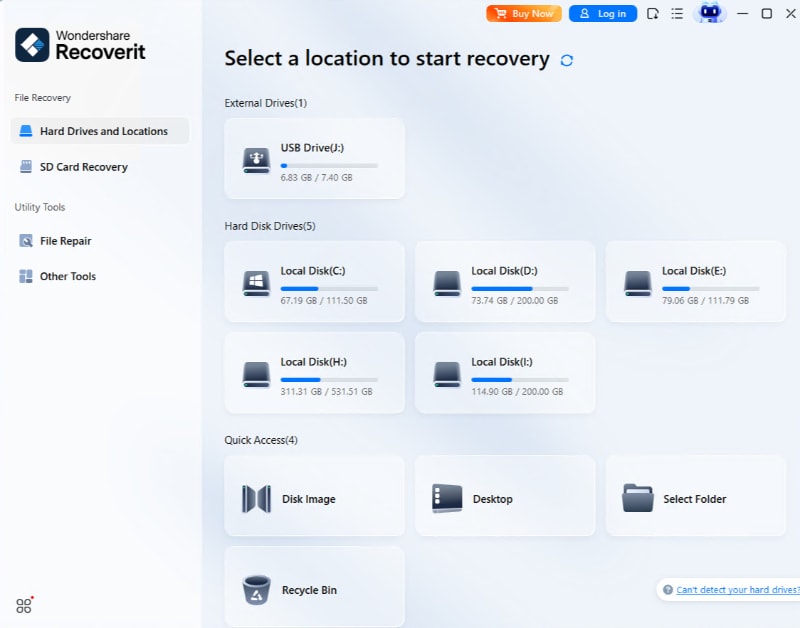
Step 2. Once the scan is complete, preview the recoverable files.
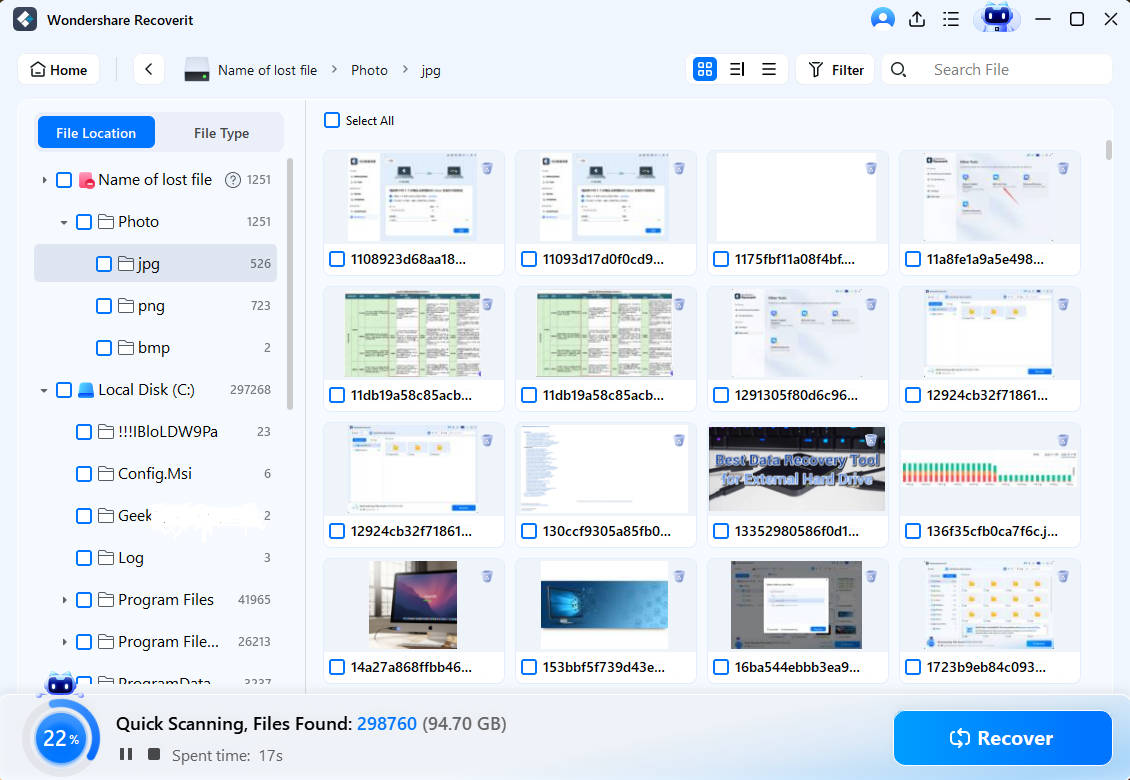
Step 3. Select the ones you want to restore and click Recover to save them to a secure location. \

Many use it when searching for how to recover database steps in simple cases. It works best before heavy operations begin.
Method 2: Restore from Recent Backup
Backups sit at the heart of every safe plan. With them, a team can rebuild systems. Without them, work often becomes hard. If a recent copy exists, you can load it into your system and start again. This returns structure and content fast.
Many offices build daily or weekly plans. They keep copies on safe servers or cloud storage. When things go wrong, this path becomes the fastest fix.
Why use it
It brings systems back quickly
It lowers stress
It suits many sizes
It keeps content safe
Step 1. Choose a recent clean backup.
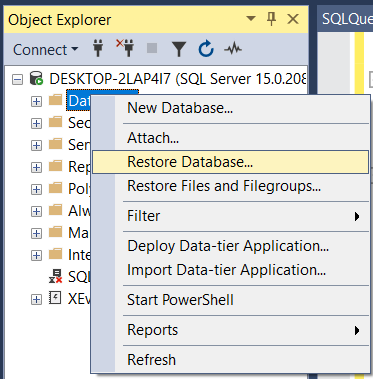
Step 2. Load it and check the data.
This helps when teaching workers how to restore database actions and keep their machines functional.
Method 3: Repair Database Using Built-in Utilities
Most engines have built-in commands. These check and fix tables, indexes, and small errors. They retry reading damaged rows. Then they restore small pieces. These commands help many teams. They work with small incidents and can support mild cases. They can also catch early signs of other issues hiding under the surface. If they fail, a team can switch to a copy and build again.
Why use it
No extra tools
Support for many formats
Quick fixes
Simple to start
Step 1. Run repair instructions.
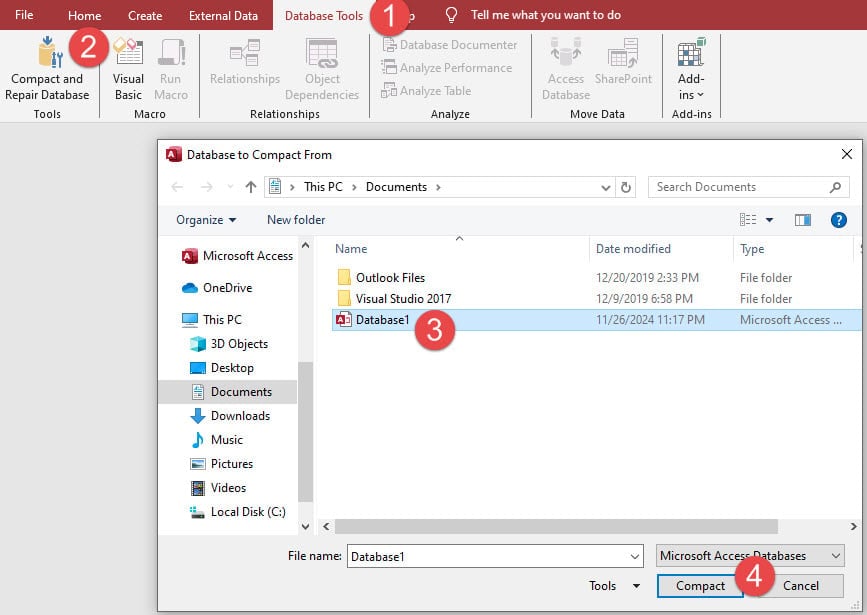
Step 2. Check logs to confirm results.
These tools remain a fast first move if data issues are limited.
Method 4: Recover from Transaction Logs
Logs track how data changed. They show each step between updates. When tables break or new rows get lost, logs can rebuild events. This helps when only small parts need fixing. With logs, workers bring files back to stable states. They inspect details, restore rows, or undo actions. If a backup looks old, logs help catch missing time. But this path needs thought. It should be used with care to avoid mixing data from broken events.
Why use it
It can restore small parts
It helps when backups are old
It offers useful clues
It brings steady results
Step 1. Find the needed logs.
Step 2. Run restore actions as advised.
Logs remain trusted for cautious repair.
Method 5: Consult Database Administrator or Vendor Support
Sometimes damage looks large. One server may go down, then another. Data centers struggle to respond. In these times, teams call experts. Vendor staff or internal administrators understand deeper parts of engines. They examine entries, search large logs, rebuild indexes, and guide people through complex repairs. This helps keep your systems safe during tough cases.
Why use it
Expert skills
Correct tools
Lower risk
Organized work
Step 1. Call support and explain the trouble.

Step 2. Follow their plan and provide all logs.
Even large shops lean on this when systems carry sensitive information or urgent work.
Conclusion
Data creates history. It supports daily plans and future goals. When loss arrives, pressure grows. People search for answers and tools. No matter the shape of the issue, organized steps and helpful tools guide you back. Backups remain your greatest hope. Soft repairs can fix many things. Logs rebuild events. Experts carry deep skills.
Once teams understand the cycle, they learn to prepare. They know the value of neat files, fresh copies, tested patches, and trained starters. A safe culture brings peace. It grows trust. Machines stay stronger when mindful care plays a role.
Soon, you start to see data not only as a target but also as a partner. Handle it with care. Your systems will reward you.
FAQs
-
1. How long can a repair take?
Small repair jobs may only need a moment. Large jobs that involve servers or many files may take long hours. The time also depends on support, logs, and hardware. -
2. When should I call experts?
If you see major trouble, call them right away. Cases that touch many tables or seem strange must be checked. Early help lowers risk. -
3. Do backup plans stop all damage?
No plan is perfect. But a backup will save most content. Keep many good copies.


 ChatGPT
ChatGPT
 Perplexity
Perplexity
 Google AI Mode
Google AI Mode
 Grok
Grok






















