Have you ever deleted a mailbox in Microsoft Exchange and then needed to recover it? Or maybe you need to delete a mailbox for testing purposes but don’t want to lose all the data in it? If you're an Exchange 2016/2019 administrator, you need to know how to delete and restore mailboxes. Further along, we'll show you how. We'll also discuss how to recover deleted Exchange mailbox.
In this article
Part 1: What are Disabled, Soft-deleted, and Permanently Deleted Mailbox in Exchange?
Have you ever stumbled across a mailbox with a red flag lowered? Or maybe you've seen messages in your sent folder that you can't find in your Inbox. The Chances are that the mails are either disabled, deleted, or permanently deleted. Here is a quick overview of each of these mailboxes. We will also explain how each one works and how to restore mailboxes from each type later in this article. But first, let’s understand the three terms.
Disabled mailboxes
When a mailbox is disabled in the Exchange admin center (EAC) or using Remove-Mailbox in the Exchange Management Shell, all Exchange attributes are removed from the corresponding user account in AD (Active Directory). The mailbox is still there, but just disabled. The disabled mailbox will be purged (permanently deleted) based on the mailbox retention phase (30 days by default).
Soft-deleted mailboxes
When a mailbox is soft-deleted using EAC or Exchange Management Shell, the account is removed from AD. They exist in AD's recycle bin until the retention phase (30 days by default) expires.
Both disabled and soft-deleted mailboxes are called disconnected mailboxes.
Permanently deleted mailboxes
The associated Active Directory account gets deleted when you permanently delete an active mailbox, which means that all of your emails will be gone forever, and it's impossible to get them back.
Part 2: How to disable Exchange mailbox — Step-by-Step
The Exchange attributes are removed from an Active Directory user account when you disable a mailbox, but it stays intact still.
Method 1: Use the Exchange admin center (EAC)
To disable a user Exchange mailbox, follow a few steps. First off, in your account settings menu.
- Locate Recipients > Mailboxes
- From the user list mailboxes, click 'mailbox' you want to disable
- Click 'More Options' Icon. Then click 'Disable'
- A window pops up. It seeks your permission to disable Exchange mailbox. Click 'Yes' to disable.
And the mailbox gets removed from the mailbox list.
Method 2: Use the Exchange Management Shell
The following command will disable all user mailboxes linked mailbox features such as resource mailboxes and shared inboxes.
Disable-Mailbox
For example, when you run the command in the picture, a message displays asking if it's okay to disable the Exchange mailbox. Click ‘Yes’. Then, the user mailbox that has the alias danj is disabled.

How to verify if you’ve successfully disabled a mailbox?
To do this, take the following route:
- To ascertain an Exchange mailbox is disabled, you must first access the EAC and click on Recipients. From there, navigate over the top of your desired mailboxes before verifying that it no longer says 'Disabled' next time around.
- When you disable users' mailboxes in Active Directory Users and Computers, right-click their account and click Properties. If the email field is blank on the General tab, this signifies they have no active email address associated with it.
- You can also use the Exchange Management Shell to manage your Exchange settings. First, replace 'Display Name' with the display name for this mailbox and run these commands in order. The Disabled value shows that the mailbox is disabled.
$dbs = Get-MailboxDatabase
$dbs | foreach {Get-MailboxStatistics -Database $_.DistinguishedName} | where {$_.DisplayName -eq ""} | Format-List DisconnectReason,DisconnectDate
Part 3: How to delete Exchange mailbox — Step-by-Step
If you delete the Exchange mailbox from the server, both its attributes and Active Directory user account will be deleted after some time. The contents of that specific folder will be permanently destroyed after its retention period expires—which means it can't come back.
Method 1: Use the Exchange admin center (EAC)
The EAC offers a simple method to delete the Exchange mailbox:
- In EAC, go to Recipients > Mailboxes
- Tap the mailbox from the user mailbox list you want to delete and click ‘Delete’
- You will be prompted to confirm that you want to delete the mailbox. Click on ‘Yes’ to delete.
Method 2: Use the Exchange Management Shell
The following command can delete the Exchange mailbox of users, linked ones (for example, co-workers), resource mailbox, and shared mails: Remove-Mailbox <MailboxIdentity> [-Arbitration] [-PublicFolder].

A confirmation message displays on the screen asking you to confirm that the mailbox and corresponding AD user account should be removed.
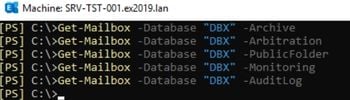
Once all mailboxes have been moved, you can run the below PowerShell commands in the Exchange Management Shell (EMS) to eliminate the Exchange database.
Get-Mailbox -database "database name="""
Get-Mailbox -database "database name=""" -archive
Get-Mailbox -database "database name=""" -arbitration
Get-Mailbox -database "database name=""" -publicfolder
Get-Mailbox -database "database name=""" -monitoring
Get-Mailbox -database "database name=""" -auditlog
How to verify if you’ve successfully deleted a mailbox?
You can confirm the ‘deletion’ with one of the following procedures:
- To verify that the deleted mailbox is gone from your account, click Recipients and then navigate over there. If it isn't listed anymore after a few seconds have passed, you can be sure nothing remains of what was once inside.
- Take a look at the corresponding user account and ensure it no longer shows up in Active Directory Users and Computers.
- Add display name of the mailbox in place of "DisplayName" and execute these commands. The Disabled value shows that the mailbox has been deleted.
$dbs = Get-MailboxDatabase
$dbs | foreach {Get-MailboxStatistics -Database $_.DistinguishedName} | where {$_.DisplayName -eq "<DisplayName>"} | Format-List DisconnectReason,DisconnectDate
Part 4: How to permanently delete Exchange mailbox — Step-by-Step
The ‘Permanent Deletion’ feature is an easy way to delete Exchange mailbox without any data loss permanently. When you activate a deleted mailbox, all its contents are purged from Exchange, and the user account in Active Directory associated with that specific email address will be deleted as well.
You can do another thing—disconnect it. When you remove a mailbox from Exchange, by default, it's retained for 30 days so that the user has an opportunity to reconnect or restore the mailbox before they are purged from storage.
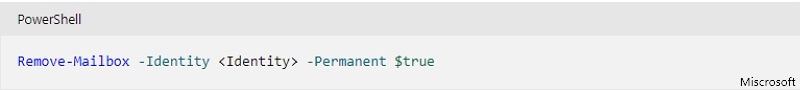
Use Exchange Management Shell to delete an active mailbox permanently.
If no permanent parameter is included when deleting an email account, the system retains it for 30 days before permanently removing it. When you're ready to delete an active mailbox permanently and the associated Active Directory user account, run this command:
Remove-Mailbox -Identity <Identity> -Permanent $true
How to verify if you’ve successfully permanently deleted an active mailbox?
- Go to EAC and check if the mailbox is no longer listed in EAC
- Check the Active Directory and ensure the associated user account is no longer listed.
- Add display name of the mailbox in place of 'DisplayName' and run the commands below in Exchange Management Shell. No results returned if the mailbox is already purged.
$dbs = Get-MailboxDatabase
$dbs | foreach {Get-MailboxStatistics -Database $_.DistinguishedName} | where {$_.DisplayName -eq ""}
Use Exchange Management Shell to delete a disconnected mailbox permanently
Both disabled and soft-deleted mailboxes belong to the disconnected mailbox. You must specify the correct type of the disconnected mailbox, otherwise, the command for permanently deleting the mailbox will fail. Write (Display Name) in place of Name.
You can find out whether a disconnected mailbox is disabled or soft-deleted by running the following command on Exchange Management Shell:
$dbs = Get-MailboxDatabase
$dbs | foreach {Get-MailboxStatistics -Database $_.DistinguishedName} | where {$_.DisplayName -eq "
After confirming the type of the disconnected mailbox, you can now run the following commands to permanently delete the disconnected mailbox.
- Permanently delete a disabled mailbox:
Remove-StoreMailbox -Database MBD55 -Identity "2ab56ce7-afc8-3343-8996-d87e3fe189c3" -MailboxState Disabled
For example, the GUID 2ab56ce7-afc8-3343-8996-d87e3fe189c3 from Exchange Mailbox Database MBD55 is permanently deleted.
- Permanently delete a soft-deleted mailbox:
Remove-StoreMailbox -Database MBD55 -Identity "Alex Johnson" -MailboxState SoftDeleted
For example, the soft-deleted mailbox of Alex Johnson from Exchange Mailbox Database MBD55 is permanently deleted.
Note: When you permanently delete a mailbox, all its contents are purged from the Exchange mailbox database. So perform this activity with caution. Learn how to recover permanently deleted mailboxes here.
Part 5: How to restore a disabled mailbox in Exchange
When you disable Exchange mailbox, the contents of that particular account are retained in the Exchange in its database and are switched to a "disabled" state. The user's attributes are also removed from Active Directory, but the content is still present and requested back.
Method 1: Use EAC to connect the disabled mailbox
If you need to restore a mailbox that is disabled or shared with the corresponding user account, the following procedure will show how.
- In EAC, move to Recipients > Mailboxes.
- Click the ‘More Options’ icon. Then click Connect a mailbox.
- A mailbox list disconnected on the selected Exchange server in your organization will show up.
- Click ‘disabled mailbox’ you want to reconnect. Then click ‘Connect’.
- Exchange connects disabled mailboxes to the user account.
Method 2: Use the Exchange Management Shell
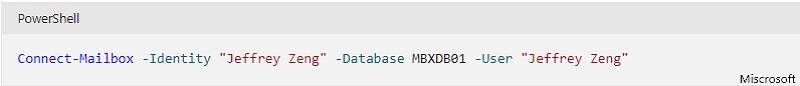
To connect a user account to a disabled mailbox, use the Connect-Mailbox cmdlet in Microsoft's Exchange Management Shell. You need to specify which type of mailboxes you want to connect—personal or professional. For example,
Connect-Mailbox -Identity "Jeffrey Zeng" -Database MBXDB01 -User "Jeffrey Zeng"
How to verify if you've successfully connected a disabled mailbox
If you want to confirm that a disabled mailbox is successfully restored, do one of the following:
- In the EAC, go to Recipients and click Refresh. Your mailbox should be listed under the refresh icon.
- Restore the mailbox for a disabled user's email address by right-clicking their account in Active Directory Users and Computers, tap ‘Properties’ from that menu option. There will be an email box populated with all of this person’s messages on the General tab if they have any.
- You can run the Get-MailBox cmdlet to verify if it exists or not: Get-User "<Identity>
". To replace 'Identity', enter the user account's name into Exchange Management Shell and run this command. The UserMailbox property for 'RecipientType' indicates the connected user account and mailbox.

Part 6: How to restore a deleted Exchange mailbox — Step by Step
When you delete it, Exchange still has the mailbox in the database and switches its state to 'disabled'. When a user's account is deleted, the corresponding active Directory object (mailbox) also gets removed. The mailbox retention period lasts 30 days by default, and then it will be permanently purged from your database—whether or not there are any messages in it.
However, when you delete a mailbox from Exchange, you can still access it with the help of an Active Directory user account. You may use EAC or shells to get your deleted data back and recover what was previously stored within its confines.
Method 1: Use Exchange Management Shell to recover the deleted mailbox
- To restore deleted Exchange mailbox, you need your old email account's display name or legacy and its corresponding GUID.
- Use the Get-MailboxStatistics cmdlet to showcase the properties of the DisplayName, MailboxGuid, and LegacyDN properties for the deleted mailbox you want to restore.
The example shows that the deleted mailbox for Alex Johnson is restored to its original state and can be found on the database MDB55.
New-MailboxRestoreRequest -SourceStoreMailbox e4890ee7-79a2-4f94-9569-91e61eac372b -SourceDatabase MDB55 -TargetMailbox "Alex Johnson" -AllowLegacyDNMismatch
Method 2: Use Stellar Repair for Exchange to recover the deleted mailbox
Using Exchange repair and recovery software can make restoring mailbox a breeze, especially if you need to do so for multiple disconnected users.
Stellar Repair for Exchange ensures that your email is accessible no matter where you are. The intuitive and easy-to-use software can fix a corrupt mailbox and export it back up onto a Live server or Office 365 directly.

- Use the offline Exchange mode to run this tool.
- Select ‘accidentally deleted the mailbox’ from this list to recover your emails.
- Save the mailbox (restored) as PST file
- Re-sync your mailbox with the Exchange Server
You may now want to know why you should use third-party software. Well, there are several advantages, and some of them are listed below.
- Third-party tools provide automatic failover like what is provided by an active-passive cluster.
- You are free to switch servers as and when required.
- With our ‘No Hardware Dependency’ feature, the Active Server will run on any server without specific hardware specifications.
- Removes ‘streaming backup’ requirement
- The automatic backward replication will help update the database after an agent server has been brought back online.
Summing up
Exchange mailbox deletion and recovery is critical for any organization, no matter how big or small. This article showed you how to delete and restore/recover mailboxes in Exchange 2016/2019. Hopefully, it helps!

Wondershare Recoverit - Recover your deleted and lost data from any disaster
5,481,435 people have downloaded it.
Recover accidentally deleted emails that were purged by mistake or lost due to unplanned system formatting.
Recover all mailbox components within the files such as emails, attachments, contacts, calendar items, journals, notes, etc.
Support all common email file types: MSG, PST, OST, EML, EMLX, MBOX, BKL, BKS, EDB, etc.
Restore data from all kinds of storage drives like USB Drive, SD card, SSDs, HDDs, Floppy Disks, Pen Drive, etc.
Save your accidentally deleted videos, and also repair the broken videos.
Preview files before you recover them.

 ChatGPT
ChatGPT
 Perplexity
Perplexity
 Google AI Mode
Google AI Mode
 Grok
Grok






















