Have you ever been wondering if Thunderbolt 4 is the same as USB C or if Thunderbolt 3 is the same as USB C? If you come across Thunderbolt and USB C ports, you’ve noticed they look almost the same. In fact, if you test them, you’ll see that both USB-C and Thunderbolt can do pretty much the same things, with one slight difference – Thunderbolt 3 and 4 can do everything the USB-C port can – only faster.
The two connectors are almost identical and compatible, making it hard for the user to tell the differences between the two, but there are differences, especially regarding data transfers and connection speed.
With that in mind, let’s define both connection systems to identify the similarities and differences between Thunderbolt and USB C you should know about.
In this article
What Is USB C?

USB Type-C, or just USB C, is one of the popular connector systems used to transmit power and data to and from supported devices over a Universal Serial Bus (USB) cable. USB-C connectors are bi-directional, universal, and symmetrical.
They enable users to link a power or data source like a phone, computer, or tablet to a storage device like an external or internal hard drive. USB-C ports can also connect two or more devices. Aside from USB Type-C, there are other USB types, such as USB-A and USB-B.
The former is compatible with smaller devices like keyboards, while the latter supports larger equipment like computer monitors. Compared to USB-A and USB-B, USB-C supports various types of peripherals. It can also send data and power in both directions.
Some USB-C cables can transmit video and DisplayPort audio signals, but the USB-C port must support DisplayPort to transmit data to a TV or external monitor.
Depending on the port’s specific USB SuperSpeed rating, the USB-C connector can support mind-bending data transferring speeds of up to 20Gbps. In addition, you can use it to charge your Mac or Windows laptop, tablet, or smartphone due to its capability to deliver almost 100 watts of power.
What Is Thunderbolt?

Many Apple users consider USB-C to be the almighty universal oval-shaped connector. However, Thunderbolt 3 and Thunderbolt 4 can do everything USB-C can expect better and faster. The Thunderbolt connector is a superset of USB-C.
It’s compatible with a number of USB-C devices, and you can use it to connect a USB Type-C device to your PC, laptop, or tablet via a Thunderbolt 3 or 4 port. Modern-day Thunderbolt devices support incredible data transfer speeds.
They are twice as fast as USB-C ports and can transfer data at up to 40Gbps. Compared to the original Thunderbolt interface, the latest Thunderbolt 3 and 4 versions do much more than just send and receive data to and from storage devices, hard drives, etc.
They can unlock additional functions, such as transferring huge chunks of data, such as 4K video signals, to and from supported devices. Thunderbolt 4 can seamlessly transmit video signals to multiple external displays, such as two 4K monitors or one 8K display.
Thunderbolt vs USB C - How to Tell Them Apart
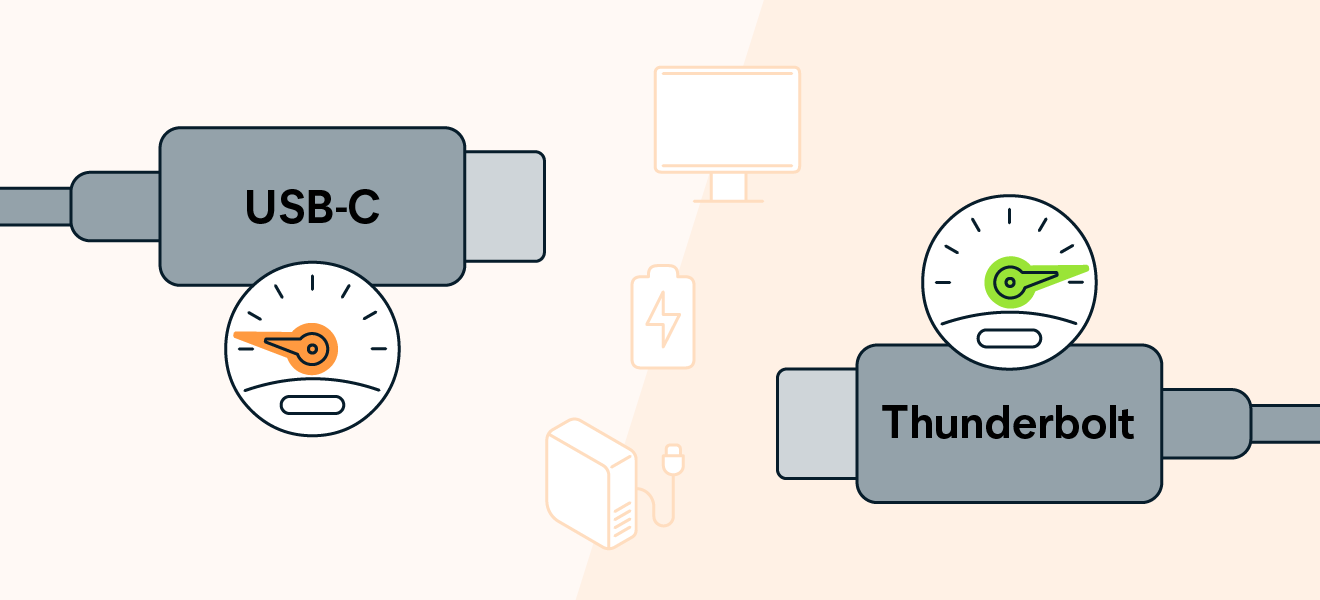
Telling the difference between Thunderbolt and USB-C ports isn’t as easy as many would think. Though they aren’t the same, their ports look almost identical. In addition, their performance is also nearly the same.
Since the ports and cables are compatible across most devices, you can connect them seamlessly. However, the biggest difference between the two isn’t in their appearance but in their data transfer capability.
Thunderbolt connectors support ultrafast data transfers and are much faster than USB-C. That’s why you shouldn’t connect a Thunderbolt cable to a USB-C port and vice versa. Though both connection systems have the same 24-pin connector, they are visually different.
Thunderbolt cables and ports usually will have the trademark lightning-bolt symbol on them. If they don’t, you’ll need to read the packaging to tell the difference. Thunderbolt tends to be a more expensive option, so you can tell the difference by the pricing and the labeling.
Key Differences: Thunderbolt 4/3 vs. USB C

Here’s a comparison table of the main distinctions between USB C and Thunderbolt to get a better picture of how they differ.
| Feature | Thunderbolt | USB C |
| Launched by | Intel/Apple collaboration | USB Implementers Forum (USB-IF) |
| Year of launch | 2011 | 2014 |
| Versions | 4 versions (Thunderbolt 1, 2, 3, 4) | No USB-C variants (USB 3.0. Has two versions - 3.1 and 3.2) |
| Number of pins | Thunderbolt 1&2 - 20 pins;Thunderbolt 3&4 - 24 pins; | 24 |
| Cable length | 3m | Up to 4m |
| Data transfer speed | 10Gbps-40Gbps | 10Gbps-20Gbps |
| Charging speed | 15 Watts | 2.5 Watts |
| ID | Thunderbolt logo | No ID |
| Use | Apple and other devices | Newer laptop models and other devices |
| Price | Expensive | Average |
Similarities: Thunderbolt vs. USB C

For most users, Thunderbolt and USB-C are the same. They do the same things with slight differences. In fact, if you take a better look at it, you’ll notice that Thunderbolt 3 and 4 support USB C connectors. Both models have 24-pin connectors and are excellent at transferring data quickly.
Though both solutions share the minimum data transfer speed (10Gbps), Thunderbolt is a faster port. Thunderbolts also have hubs available for extended connections, thus significantly increasing the types and numbers of ports you can use.
As you can see, both connection systems have so much in common, yet they are still different.
Which One to Choose?

Thunderbolt and USB-C support several use cases, such as connecting computing devices to peripherals such as external storage devices, hard drives, and monitors. They can transfer data or charge devices, depending on your needs.
Thunderbolt’s ultra-fast data transfers are ideal for professional uses, such as transferring large amounts of data or moving large files between two systems. If you need to move a large amount of data between an external storage device and a computer, Thunderbolt is the best choice.
It will transfer data seamlessly without interruption or data loss. Thunderbolt supports expanded usability and can ease clutter by reducing the need for separate power sources.
Here are some use cases to help you make an informed decision on how to choose between USB-C and Thunderbolt:
- Thunderbolt is the preferred option if data transfer speed is a priority;
- If you’re working in an Apple ecosystem, Thunderbolt provides the best performance;
- If price isn’t an issue, Thunderbolt is always a better choice;
- If you’re connecting multiple accessories or monitors, a Thunderbolt connection is a better option;
- Thunderbolt is also a better option when you’re backing up your local storage and need to migrate large amounts of data to external storage devices and hard drives;
- USB-C is ideal if a 10 Gbps data transfer speed is enough for you;
- USB-C comes with a longer cable length;
- USB-C ensures comparable performance to Thunderbolt at a lesser price.
Common Problems

Here are the most common Thunderbolt and USB-C problems most users face while using these connection systems.
Thunderbolt problems:
- Windows can’t detect Thunderbolt device;
- Thunderbolt device isn’t available or working;
- Defective Thunderbolt port (port isn’t working);
- Slow file transfer speed;
- Devices can’t connect, or they keep disconnecting;
- Thunderbolt device stops working;
- Thunderbolt device crashes or freezes;
- Unable to transfer data or files;
- Thunderbolt ports aren’t detectable.
USB-C problems:
- Limited USB-C device functionality;
- USB device not recognized;
- Slow charger;
- PC isn’t charging;
- Limited display connection;
- Unsupported USB-C audio adapter.
While you can troubleshoot most of these problems using Windows troubleshooter, some could lead to data loss. If your USB-C or Thunderbolt freezes, crashes, and stops working in the middle of a file transfer, you could lose some of your data, or it could render your files unusable.
Thankfully, you can recover corrupted or lost data from internal and external storage devices using a data recovery tool like Wondershare Recoverit. It’s one of the best tools available for effective large-scale data retrieval across Mac and Windows devices.
Wondershare Recoverit can retrieve data from thousands of storage devices, including SD cards, USB drives, SSDs, HDDs, etc. In addition, it supports various data types and file systems and can recover files from across a range of data loss scenarios.
Recovering your data with Wondershare Recoverit is easy and requires only a few steps. Download it for Windows or Mac and install and run the program on your system.
Follow these steps to recover your files:
- Select a location – navigate to the Hard Drives and Locations section and select a location to start recovery;
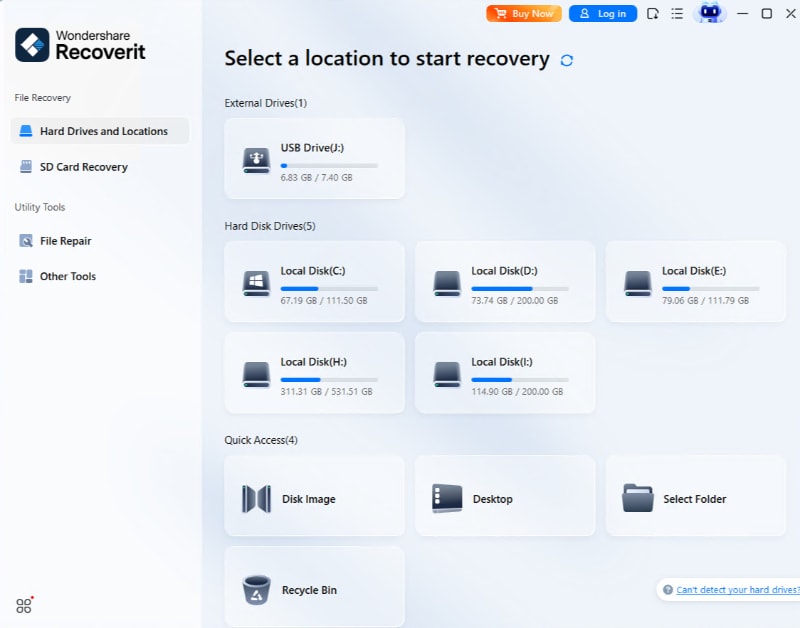
- Click Start to scan the flash media for lost files, this allows Recoverit to scan your flash media and discover retrievable files; During the process, you can locate the targeted files, as well as pause or stop it.
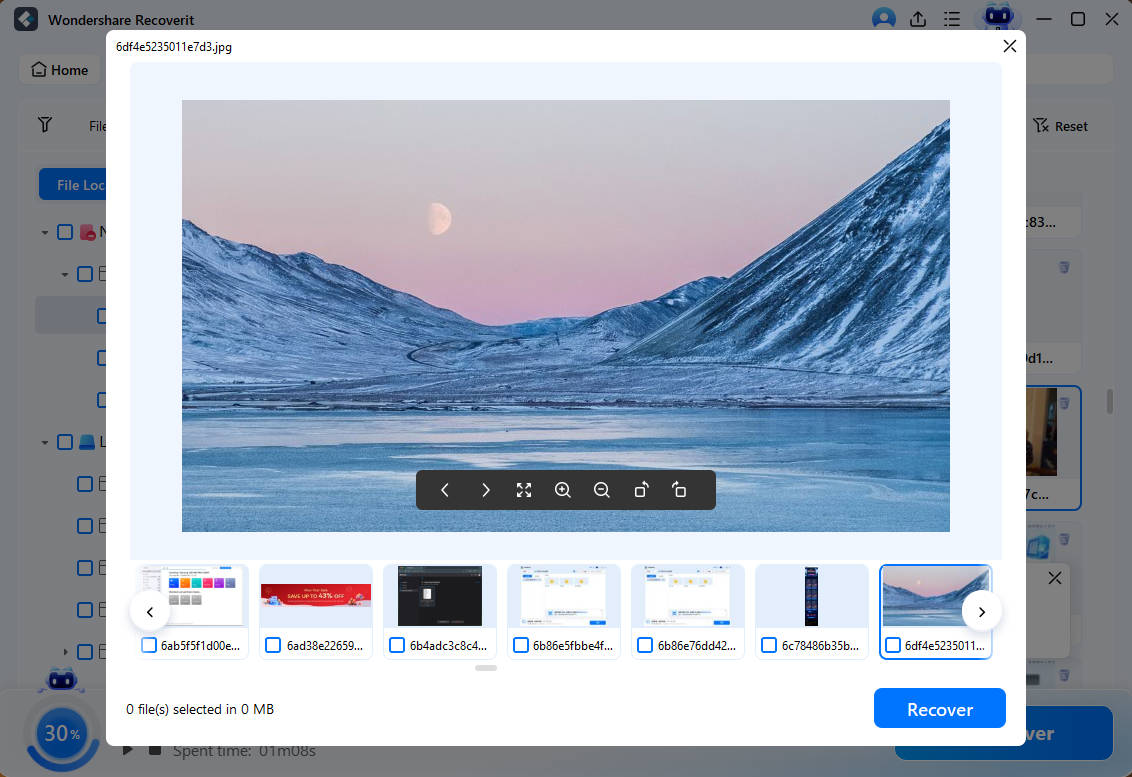
- Preview your recoverable data to select only the files you wish to retrieve;
- Click Recover to get back your data.
Conclusion
In the Thunderbolt vs. USB-C debate, both parties can be the winners. Though Thunderbolt takes the win in terms of data transfer speeds, usability, and connectivity, USB-C is still the most used connection system across countless devices.
However, technology never stands still, and tech standards are rapidly getting higher and higher. While you can still accomplish most private and professional tasks using USB-C, Thunderbolt is the future.
Ultimately, you should opt for Thunderbolt if you plan to connect multiple accessories or monitors and transfer lots of data. Otherwise, USB-C will do just fine.