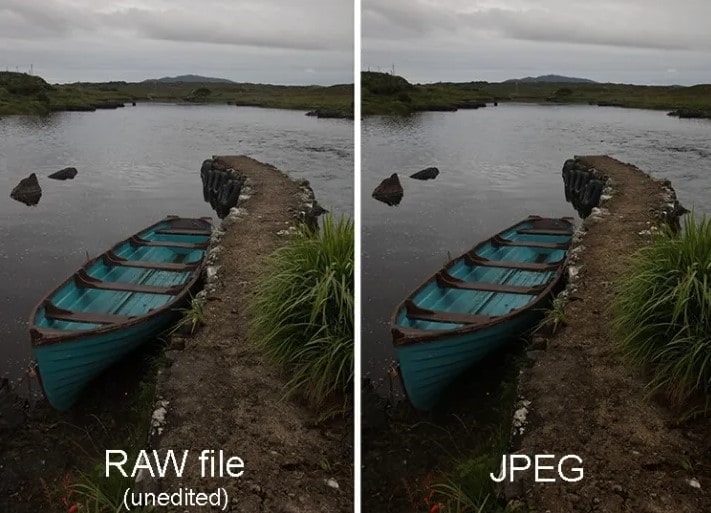
Whether one is a pro or not, the decision between RAW and JPEG remains. Both these image modes affect the quality of your photos, and it is important to know how each format appears best. Between the RAW vs. JPEG debate, the mode you use affects storage and how fast you are able to get your photos out.
With a few advancements in camera tech, both of these formats are beneficial based on your workflow and how much control you have over your images. If you're having difficulty figuring out which one to select, then read this article. It will give you all the information you need, such as the big differences, case scenarios, and so forth.
Try Recoverit to Perform RAW and JPEG File Recovery

In this article
Part 1. An Overview of RAW File Format
What is RAW file? In simple terms, it is an unprocessed and uncompressed picture directly retrieved through a sensor of a camera. The RAW files, unlike JPEGs or most other modes, preserve and hold all detail, color, and information of an image. In addition, this means there is a file with maximum detail and dynamic range that yields a beautiful final photo.

Main Highlights
- Once a RAW file has been created, everything from the image is inserted into the file, so you have full control over how your images appear.
- A RAW image has a far greater and dynamic range and color than JPEG, thus appearing more professional-looking.
- The photographs end up looking sharp and clear with bright colors that can be scattered later using the editing program.
- Unlike other formats of images, RAWs have a lossless compressed format; therefore, they do not need any equalization.
- In case the image covered with shadows and then highlights were not correct, then you could quickly restore them a lot better, and they could give a dynamic appearance.
Main Concerns
- The file size is bigger than a JPEG image format, as they store the necessary image information in the memory card.
- It can slow down the processing and workflow efficiency when you are trying to deal with hundreds of images.
- Most editing software are not even compatible with this type of image format, due to which photographers might have to convert them.
- They might also look a little dull as they initially provide a neutral starting point compared to the other formats.
- These RAW files are difficult to manage, as you need to change the settings to an XMP file that can store these post-processed JPEG images.
Part 2. JPEG File: What is the Image Format
What is JPEG file? It is clear that RAW images should be opted for when photographers want a more dynamic and flexible image processing. However, what is a JPEG file? It is the default format of most digital cameras and cell phones, and it is also the most common picture format on the Web. When you photograph in JPEG, the camera processes all the image data, compresses and delivers to you a finished picture.

Main Highlights
- It accommodates up to 24-bit color, which makes it well-suited to rich, colored images and graphics.
- It is of a smaller file size, thereby very convenient to share and manage.
- JPEGs are already processed with all of the camera settings, such as color saturation, tone curve, white balance, etc.
- Since it is small, it will not slow down the processing and workflow of the camera, yet enable you to shoot at higher frames per second.
- You have much greater control over its exposure settings, which enables you to capture a greater range of highlights and shadows.
Main Concerns
- The JPEG image format is limited to 8 bits, which means it does not have a color depth of 16.8 million colors.
- With less lossy compression, you may lose certain image data, details, and overall quality of your image.
- Users can lose various details while editing this format, as they are compressed artifacts that might be noticeable to the naked eye.
- It is not recommended to capture images with text, sharp lines, and graphics, as it does not store that much clarity.
- This format contains less image data, which can cause potential risks and problems in recovering these formats.
Part 3. RAW vs. JPEG: Key Differences Explained [Tabular Data]
This part will help you understand the difference between JPEG and RAW in a more comparative way, allowing you to choose the one that serves you better:

| Metrics | RAW | JPEG |
|---|---|---|
| Image Quality | Rich image quality | Degraded image quality |
| Color Accuracy | More color accurate | Less color accurate |
| Compression | Uncompressed | Compressed |
| Editing Flexibility | ✅ | ❌ |
| File Size | A few megabytes to over 100MB per image | 3 to 7 MB |
| Brightness & Contrast | Less | More |
| Sharpness | More sharpness | Less sharpness |
| Dynamic Ranges | Better underexposed and overexposed images | Fewer underexposed and overexposed images |
| Storage Capacity | High (20 to 30 MB) | Low (7 to 10 MB for a 24-megapixel image) |
| Bit-Depth | 12 to 14 bits | 8 bits |
| Color Space | No specific color space | sRGB |
Part 4. What Do Professional Photographers Prefer: RAW or JPEG?
You might be wondering, do professional photographers shoot in RAW or JPEG? Photographer experts like to take photos in high-quality resolution, and they look for the following reasons for choosing RAW:

- Photo Quality: RAW format offers maximum possible quality and, in addition, enables professionals to adjust exposure, white balance and color grading of the photographs.
- Post-Processing Control: With flexible post-processing abilities, experts prefer RAW, as it can capture pictures with better shadow and highlight details.
- Professional Photography: In landscape, portrait, and sports photography, RAW offers a better range, processing, and color spacing than JPEG, which photographers need.
- Better Technical Values: RAW format catches all the photograph's unprocessed data directly from the camera sensor, including its vibrant range, color, and bit depth.
- Easy Editing: Since the format contains all the information, professionals can easily revisit the photo and make desired changes without disrupting its quality.
Part 5. Use Case Scenario: When To Use RAW or JPEG?
In the dynamics of RAW vs JPEG, you might consider one format over the other due to various reasons. Therefore, let’s dive into the various case scenarios where these formats are used, so that you can choose which one to use in which situation:
When to Use RAW
- Challenging Light Conditions: When you are shooting low-light photos, capturing them in RAW format gives you a more dynamic look.
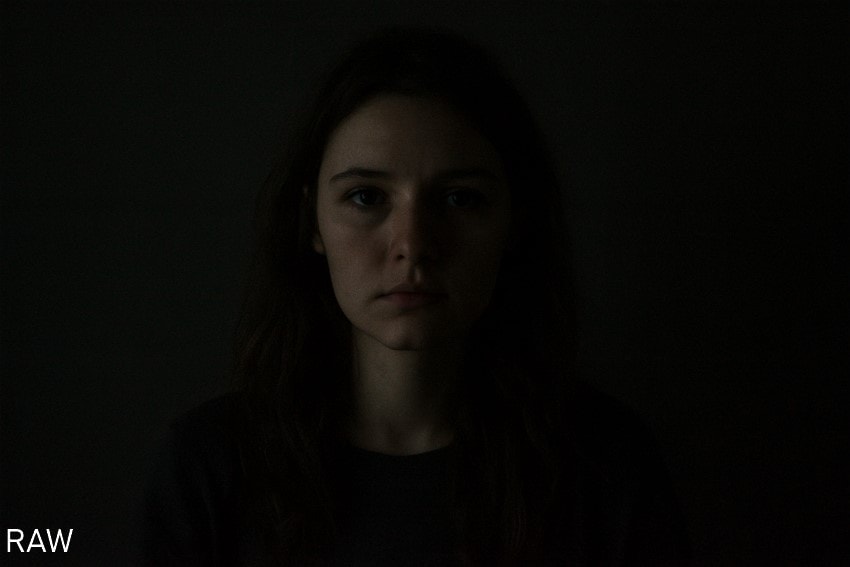

- Maximum Flexibility: This format conserves the sensory data of the picture, which enables you to make extensive adjustments during editing.
- Professional Photography: Various experts prefer RAW for important and rich photography sessions to get the best, high-quality results.
- Dynamic Range: With RAW files, you can get strong contrast, smoother transitions, and more color depth to your shots.
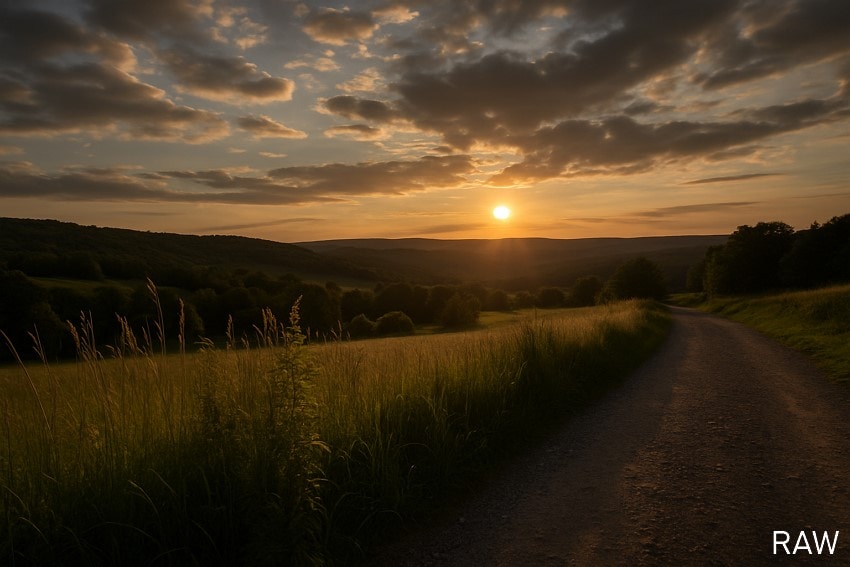

- Creative Control: These formats are non-destructive during editing and let you experiment with different looks, colors, and layers.
When to Use JPEG
- Social Media Quality Images: You can use this format when you need the ultimate image quality for your social media posts.
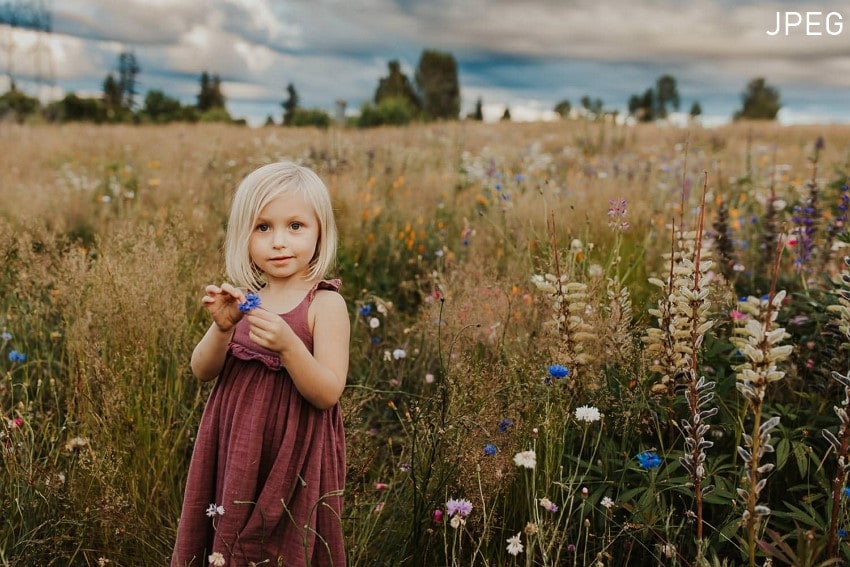

- Fast Action Pictures: Users can get multiple fast-action sequences of images without the camera buffering or disrupting.

- Quick Sharing: These formatted pictures are processed in the camera and are compatible with all devices, thus allowing seamless picture sharing.
- Limited Storage Space: If you are running low on storage space, convert your images to this format to make them smaller in size.
- Everyday Photography: Due to the convenience and efficiency of these formats, users can capture beautiful scenes, landscapes, objects, and more.
Part 6. Top Cameras For Shooting in RAW Format
Whatever you end up deciding after learning about the difference between JPEG and RAW, let’s go through the following list. It is the best camera that can help you shoot outstanding images in RAW format:
1. RICOH GR III
For street photographers, this camera offers an exceptional result with its APS-C sensor and an IBIS system that helps stabilize shots at slower shutter speeds. Moreover, its Snap Focus feature has a great zone for focusing and capturing quick snapshots of the streets. Despite its size, it offers impressive quality images with its built-in lens that has a wide aperture of f/2.8 and a 40mm equivalent lens.

2. Canon EOS R5
It features a 45-megapixel full-frame sensor that delivers the best RAW pictures, perfect for professional use. You can easily shoot 20 frames per second in burst mode, along with 8K 12-bit videos. Also, its advanced image stabilization and autofocus system make the images sharper and of higher quality. This camera is weather-resistant, meaning you can shoot photo RAW files in any weather.

3. Nikon Z8
If you are a new photographer, the Nikon Z8 is a good investment to capture amazing RAW photos in various locations. With up to a 120FPS shooting speed, you can easily take moving objects, such as wild animals, sports cars, athletes, among others. You can also use the camera to take night images and, using its night vision mode, take photos of the stars at night.

4. Olympus OM-D E-M1 Mark II
This camera is a Four Thirds body, which has very good in-body image stabilization and a solid build. Even though it has a smaller sensor, it can handle high-quality photo RAW files. Even when it’s in continuous autofocus, its high-resolution mode can shoot multiple stunning RAW shots. Also, with its 121 cross-type phase-detector, it can seamlessly track subjects at high speeds.

5. Sony α7 IV
Sonyα7 IV is a hybrid photo/video camera that has a built-in weather-sealed body and an image stabilization feature. With its illuminated backside, full-frame sensor, it has a wide range and a 33-megapixel resolution, perfect for capturing RAW pictures. Additionally, it can shoot RAW from 10 to 6 frames per second with excellent quality. You can shoot several stunning pictures, as it contains a large buffer.

6. Nikon Z6 III
Lastly, this camera is a well-suited candidate for taking photo RAW files. Its quick-sensory readout and continuous high shooting provide 20fps in shutter release mode and 14fps in mechanical release mode. Additionally, it shoots 1000+ shots in 20fps in continuous mode, which means that professionals can shoot as many action shots as required without slowing down. All these features ultimately facilitate flexible post-processing and reframing.

Part 7. RAW/JPEG Files Lost When Transferring to Computer via SD Card? Try Recoverit!
Say you were copying all your valuable RAW/JPEG files to the computer through an SD card, but through various technical reasons, you ended up losing them. In a situation like this, the best course of action is through the Wondershare Recoverit photo recovery software. Whether you lost it from your SD card, HDD, USB, or other camera devices, this software can salvage lost files with a 95% restoration rate.
Moreover, you can recover 150+ image formats with its advanced scanning technology that searches every corner of the SD card. With its real-time preview feature, ensure the quality and availability of the images before downloading them. Not only that, users can seamlessly recover their image files on both Mac and Windows without any hassle. While recovering, this tool ensures 100% safety of your images and their data.
Key Features
- Variety in Scanning Data: The quick scan can be used to recover files mid-scanning, while the deep scan looks for every lost RAW/JPEG file from the SD card.
- Filter Image Information: By using the filter system, narrow down the search by choosing specific file size, file type, and more.
- Searching for Specific File: If you're in a rush to restore lost RAW files, use the search bar to type in the image name and recover them on your device.
Comprehensive Stepwise Guide on How to Recover Lost RAW/JPEG Files from SD Card
To recover both the photo RAW files and JPEG files from your SD card, go through the following easy-to-follow steps:
Step 1. Open Recovery Software and Connect the Specific SD Card
Install and access the main interface of Recoverit on your Windows. Now, head to the left panel, click the "SD Card Recovery" tab, and connect the card to your laptop.
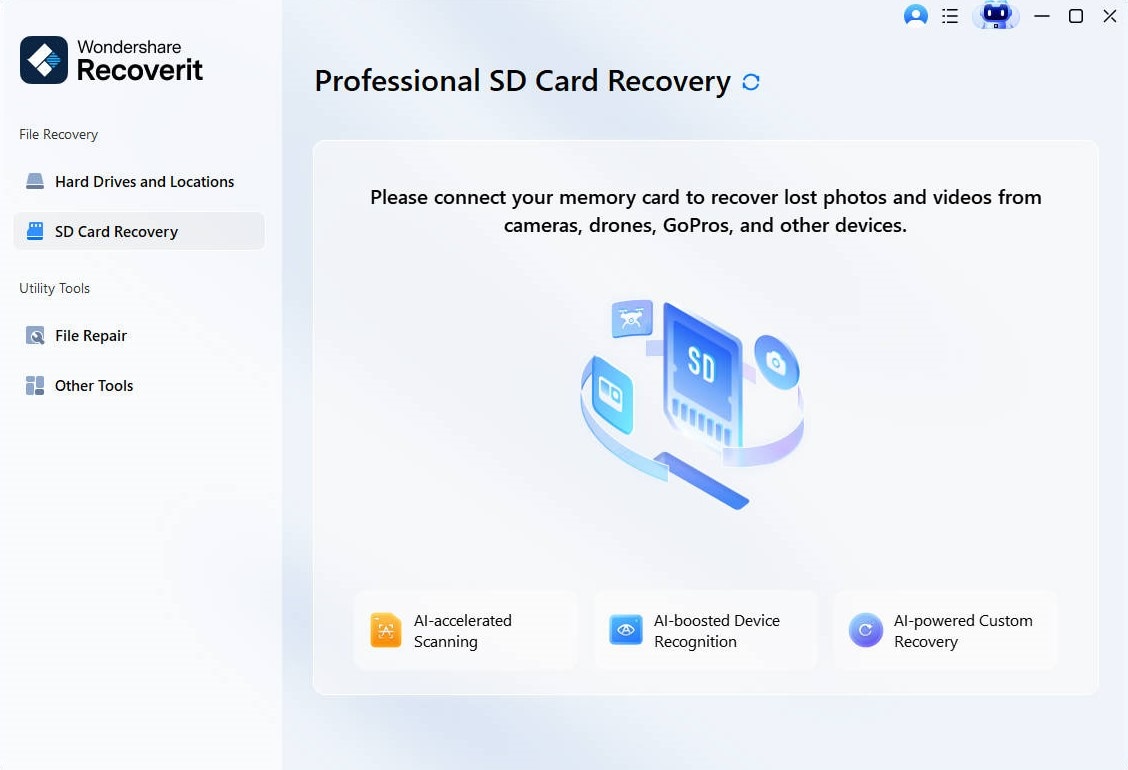
Step 2. Allow Detection and Initiate Scanning Process
After the card is connected, give the software time to properly detect the device. Once it's detected, press the "Scan" button on the detected SD card to start the scanning process.
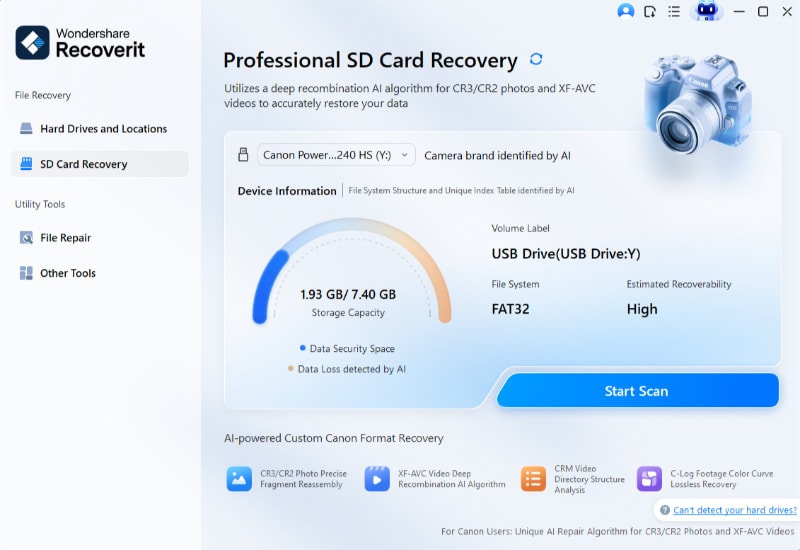
Step 3. Preview the Lost Images and Recover on Your Device
During or after the scanning process, select and preview the RAW/JPEG image files, and hit "Recover" to save them on your device.
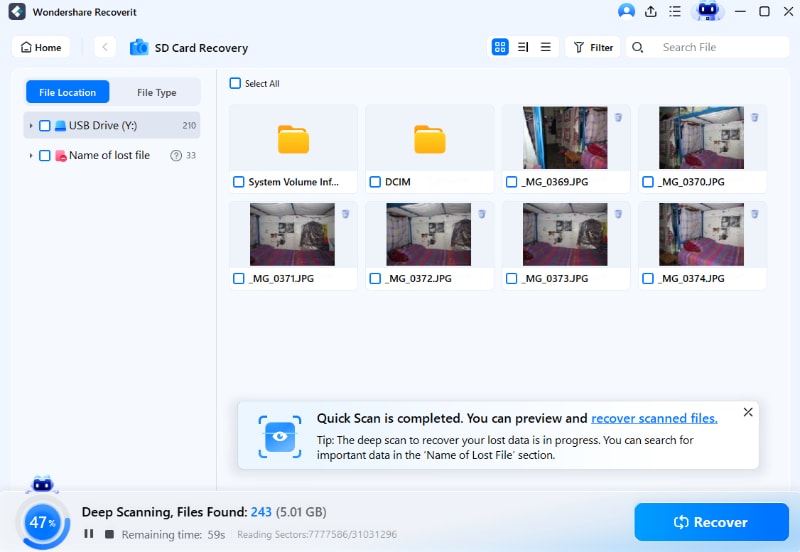
Conclusion
In the end, this article dealt with the comparison of RAW vs. JPEG in detail. The difference revealed that professional photographers prefer to use the RAW format. However, whatever you choose should be on the basis of superior color accuracy, recovery rate, and sharpness. Aside from that, in case you lose important RAW/JPEG files, turn to Wondershare Recoverit.
FAQ
-
1. Do RAW files require special editing software to edit?
Yes, the RAW files contain all the unprocessed image data and require special editing tools to view these images. Software can easily interpret them into viewable content. -
2. Can I shoot both RAW and JPEG at the same time?
There are various modern DSLRs and mirrorless cameras, like Canon, Nikon, and Fujifilm, that can shoot in both formats simultaneously. The setting is referred to as RAW + JPEG shooting mode, and it contains both the data and versions of the format. -
3. Is it possible to convert a RAW file to JPEG later?
You can convert the photo RAW files into JPEG using different software, such as Capture One and more. Moreover, while converting, you can adjust the brightness, color, and sharpness before pressing Done.




 ChatGPT
ChatGPT
 Perplexity
Perplexity
 Google AI Mode
Google AI Mode
 Grok
Grok






















