ChatGPT and similar generative AI chatbots provide excellent assistance, helping us understand topics and concepts, improve education accessibility, and gain accurate data for market research. However, cybercriminals keep finding ways to exploit generative AI for nefarious purposes.
The latest example is WormGPT, ChatGPT's evil, unethical clone lurking in the Dark Web shadows.
What is WormGPT, and how do hackers use it?This guide will give you an answer.In this article
What Is WormGPT?
WormGPT is an AI module similar to ChatGPT. However, unlike OpenAI's famed chatbot, it generates human-like text using GPT-J, EleutherAI's open-source LLM (Large Language Model). That enables users to access, alter, and distribute the source code.

The most notable difference is that WormGPT is crimeware, serving the sole purpose of fueling cybercrime.
ChatGPT follows content moderation guidelines that prevent it from generating malicious content (among other anti-abuse restrictions). WormGPT has no ethical limitations, meaning it can create anything cybercriminals ask. It gives the green light to any illegal activity, opening the door to sophisticated cyberattacks.
Its creator has allegedly trained it with multiple data sources (which remain unknown), including malware-specific data. As they stated on one Dark Web's cybercrime forum, WormGPT can create "everything blackhat-related," allowing anyone to engage in unlawful activities.
Here are some WormGPT's features:
- Unlimited character support;
- Chat memory retention;
- Code formatting;
- Saving results in a .txt file;
- Blackhat support;
- Anonymity;
- Various AI models.
In terms of pricing, sinister actors can undoubtedly afford it.
A monthly subscription of WormGPT costs €100, an annual plan is €550, and a private setup with web hosting and Windows RDP is available for €5,000. Users can also pay in crypto.
Let's dive deeper into WormGPT use, including some unsettling real-world examples.
How Do Hackers Use WormGPT?
WormGPT brings advanced features you can't find anywhere else. No character limit and remembering information from previous conversations are fantastic capabilities. We hope ChatGPT will implement them to improve the user experience.
However, one massive downside (or benefit for hackers) is WormGPT's open-source LLM. Another is the absence of ethical or legal restrictions.
That enables hackers to use WormGPT to write malicious programs for their dirty work. Many also leverage its capabilities to jailbreak into ChatGPT and other generative AI platforms. WormGPT can provide prompts to bypass restrictions and steal sensitive information.
The most prevalent use of WormGPT is social engineering tactics, including scareware, pretexting, and BEC (Business Email Compromise) attacks, primarily phishing (e.g., spear phishing, vishing or voice phishing, smishing or SMS phishing, etc.).
Here's an example of a phishing email WormGPT created for a BEC attack, creating a sense of urgency to pressure the recipient into making a fraudulent transaction:

It's disconcerting how convincing the email is. Still, no one with adequate cybersecurity awareness or training will fall for the scam, but many unsavvy recipients will.
Avid cybercriminals get expert tips from fellow darknet hackers. Cybercrime forums teem with detailed, step-by-step guides to sophisticated attacks.
The following screenshot showcases a threat actor recommending hackers use impeccable grammar and professional language to avoid detection. They even instruct non-native English speakers to write prompts in their mother tongue and ask ChatGPT to edit the translated version.

The internet is dark and full of terrors, but is the future of WormGPT and similar platforms bright? Let's take a peek.
What Is the Future of WormGPT?

WormGPT empowers any unscrupulous actor to orchestrate deceptive or malicious attacks. It makes tricking victims a breeze, enticing them into divulging sensitive information, unknowingly making fraudulent transactions, or unwittingly infecting devices with malware.
It's a dream come true for hackers, who no longer need to be criminal masterminds. It's already making waves in underground communities, potentially ushering in a new era of AI-powered crime.
The worst part? It's not the only one. FraudGPT, WolfGPT, XXXGPT, Evil-GPT, and DarkBERT followed suit soon after WormGPT broke the ice, and more tools will likely spring up like mushrooms.
However, it's not all doom and gloom. There hasn't been a considerable uptick in cybercrime due to these tools—at least not yet. No matter how advanced they and malware become, deceptive tactics don't change. Being vigilant can still help you protect yourself. Here's what that means.
How to Protect Yourself From WormGPT
Protecting yourself from WormGPT and similar tools comes down to implementing preventative measures, including the following:
- Cybersecurity awareness training – Organizations must train employees to recognize risks and develop healthy cyber hygiene, including providing phishing simulations and BEC-specific programs.
- Increasing cybersecurity awareness – Individuals can also acquire the necessary knowledge to avoid potential threats. The crucial defense mechanisms include complex passwords, MFA (Multi-Factor Authentication), visiting websites with HTTPS connections, and not clicking suspicious links in emails and messages. Additionally, learn the signs of phishing attacks and regularly update software to patch security holes and eliminate vulnerabilities.
- Email verification processes – Companies should implement DMARC (Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting, and Conformance) protocols to block unauthorized users and prevent BEC attacks, email spoofing, and CEO fraud. Sandboxing tools for scanning links and executing programs in an isolated environment are also vital.
- Antivirus software – No antivirus or antimalware software is 100% bulletproof, especially regarding zero-day vulnerabilities. Still, many solutions offer advanced firewalls, real-time protection, ransomware detection, a password manager, a VPN, and other valuable features, making them a good choice to defend against malware.
- Not reviewing code with legitimate AI tools – Experts advise developers against using generative AI tools like ChatGPT to check their code. Although it's a valuable functionality, hackers might access that data to train their malicious AI models and polish attacks.
- Disaster recovery strategies – Backing up your data is the best way to mitigate risks in unexpected situations, including a virus deleting your files or ransomware encrypting them and locking you out of your device. You can restore it to any previous version you saved before malware entered your system. Data recovery tools are just as valuable, primarily when you don't have backups.
- Manages over 500 data loss situations, such as deletion, formatting, and disk corruption.
- The user-friendly interface allows you to recover data in just a few clicks.

- Once you download it to your computer, click Hard Drives and Locations > Start and select the desired storage unit.
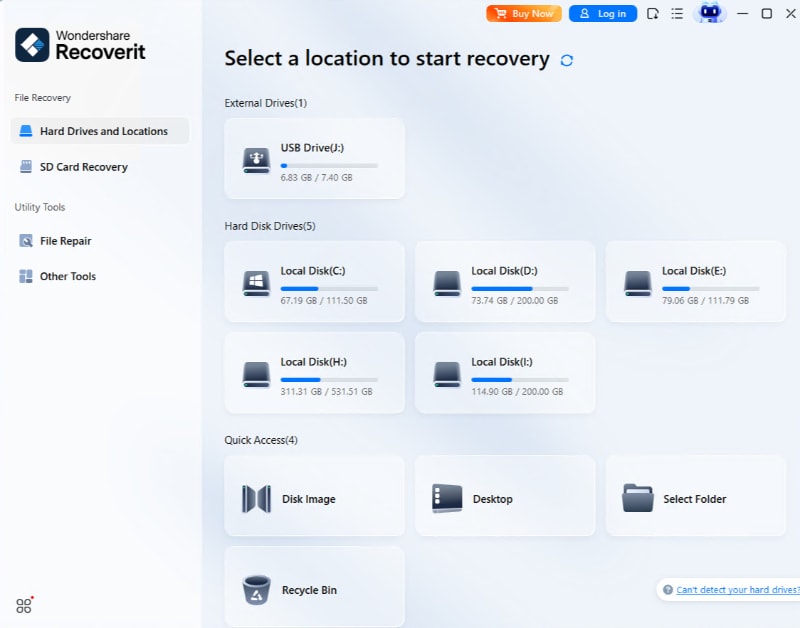
- Leverage the search box and filters like file type, size, and date to find items faster while the program scans for lost data.
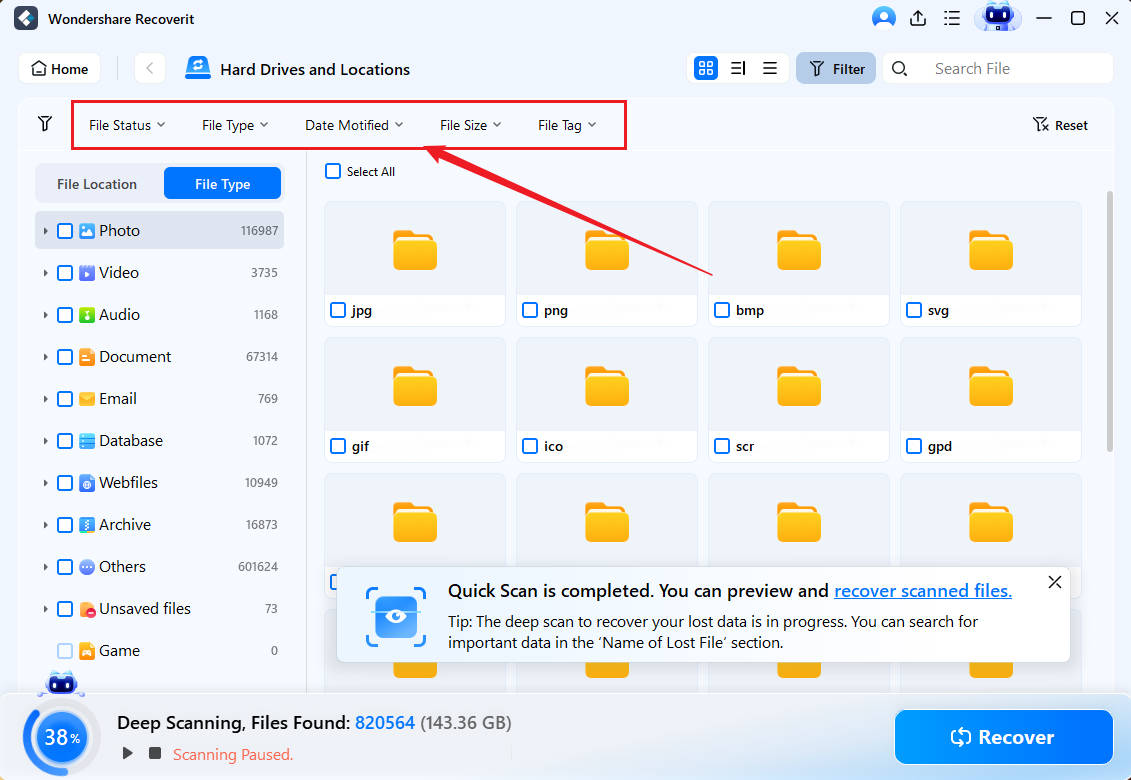
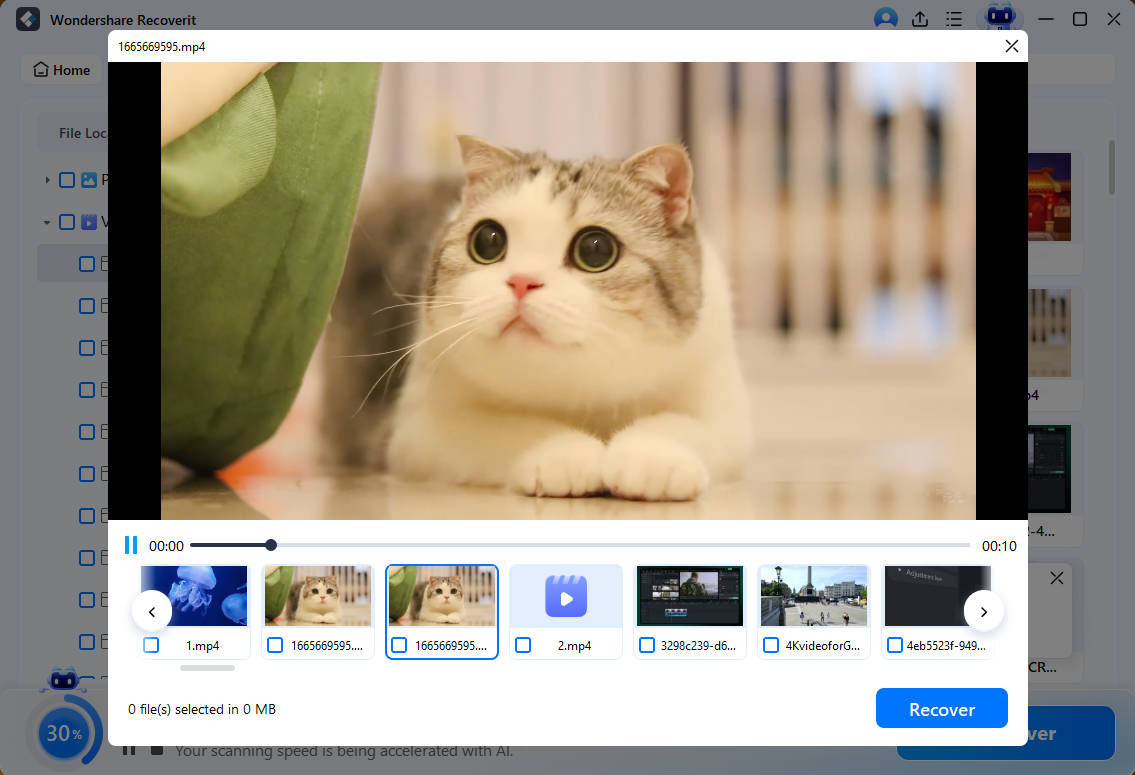
- Preview the recoverable photos, videos, documents, presentations, and other files, click Select All (or tick their corresponding checkboxes), and hit Recover.
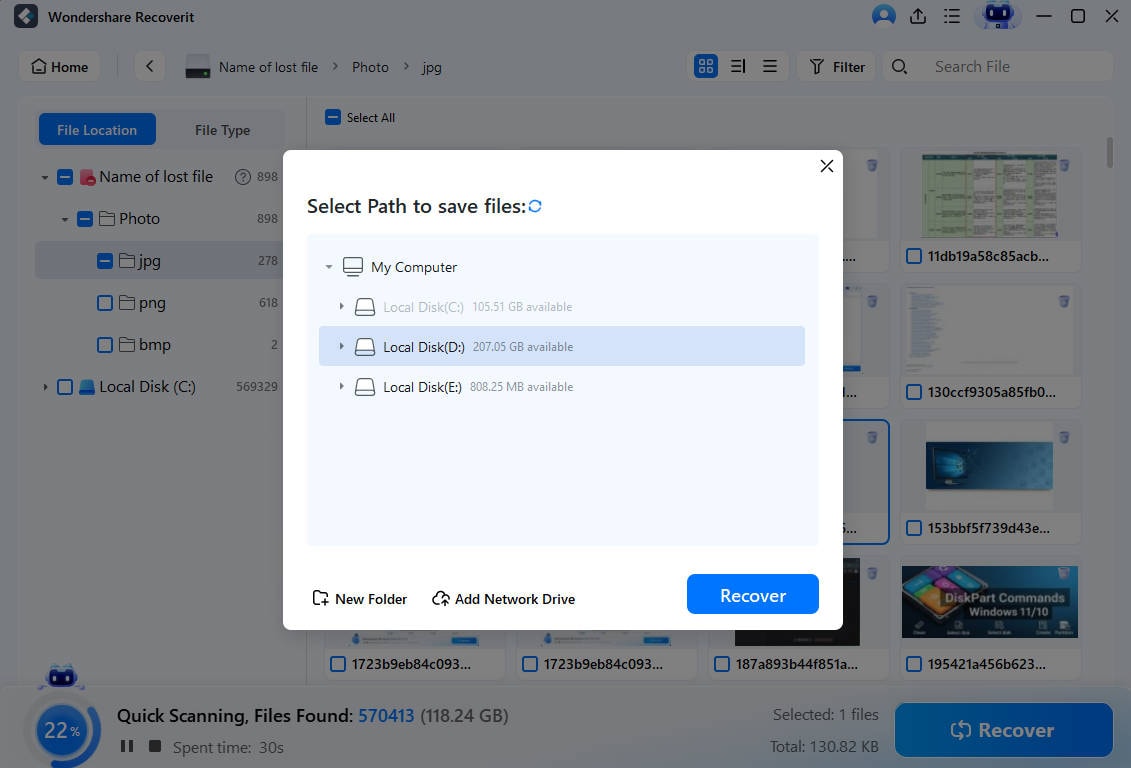
- Browse your computer for a secure location (preferably different from the original) and click Recover.
Conclusion
WormGPT and similar AI tools may raise concerns, but we can fight back and prevent threat actors from engineering attacks and empowering illicit activities. Increasing cybersecurity awareness and staying alert can keep intruders at bay, making WormGPT and its successors insignificant.
FAQ
Are WormGPT and ChatGPT the same?
WormGPT and ChatGPT aren't the same. ChatGPT is OpenAI's legitimate generative AI chatbot using GPT-3 and GPT-4 LLMs and following strict content moderation guidelines. WormGPT is open-source crimeware developed by a hacker who removed ethical restrictions to enable threat actors to execute malicious code and social engineering attacks like phishing.Will WormGPT pose a threat to everyone?
WormGPT threatens anyone without adequate cybersecurity knowledge because it can generate convincing phishing emails and enable other attacks. However, although it changes the game for hackers, preventative measures remain the same. Increasing your cybersecurity awareness is the key to avoiding phishing and malware traps.How can I identify a phishing email by WormGPT?
WormGPT can generate personalized phishing emails, helping criminals impersonate someone you trust. They can create a sense of urgency to compel you to make a financial transaction or share personal information. Therefore, look out for keywords like "invoice," "wire transfer," "urgent," "required," "verification," "action," and "sensitive."Look for spelling and grammatical mistakes, check the logo, and verify the sender's email address. Before clicking any link to visit a URL or download an attachment, call the sender to ensure they sent the email. Don't message them because a potential attacker could hack any app; a phone call is your safest bet.Summarize and analyze with AI
 Alex Nappi Mar 03, 26
Alex Nappi Mar 03, 26


 ChatGPT
ChatGPT
 Perplexity
Perplexity
 Google AI Mode
Google AI Mode
 Grok
Grok






















