When buying a flash drive, most people don’t think about formatting. However, this is a crucial process that offers many advantages, and when using a flash drive, you must format it regularly. Formatting allows you to prepare the flash drive for your device and creates a filing system that organizes your data while improving storage capabilities.
The formatting process includes selecting the allocation unit size for USB. Many people don’t understand allocation unit size and how it affects formatting your drive. Today, we’ll talk about allocation size and how to select the correct one when formatting your drive.
In this article
What Is Allocation Unit Size?

Allocation unit size, block size, or cluster size is the large pieces of data your flash drive is divided into. When an allocation unit size is larger, the number of units on the drive is reduced. If there’s a small allocation unit size on a drive, there’s a higher number of allocation units.
If you move a large file to a drive bigger than a single allocation unit, this file will be divided and put on multiple blocks. If you move files smaller than the block, those files will be stored entirely on a single allocation unit. To explain better, let’s present an example.
If you have a 16 MB USB drive and decide to use the NTFS system, the default allocation unit is 4069 bytes. In other words, the drive will have four allocation units of 4 MBs within 16 MBs. Modern drives with much more space contain thousands and even millions of blocks, but they work on the same principle.
Why Consider Changing Allocation Unit Size on USB?

Changing allocation unit size allows you to optimize storage space and drive speed. However, an average user probably won’t notice any changes compared to the default values, as modern drives offer lots of storage space and excellent performance.
However, there are two scenarios when changing allocation unit size can be very helpful:
- When storing and moving several large files;
- When storing many tiny files.
When you store several large files, it’s best to have fewer allocation units with enough size to store files individually. The less time the file is divided, the lower the chances are for fragmentation. On the other hand, if you have a lot of smaller file sizes, you will need smaller allocation unit sizes to avoid wasting storage space.
What Is the Best Allocation Unit Size for USB?
Unless you have one of the previously mentioned scenarios, we recommend sticking with your USB’s default allocation unit size. When formatting the device, the system will recommend the default size for that drive.
The default size changes depending on the file system and the partition size. In general, the larger the partition is, the larger the allocation size will be. Here are some tables of different formats used for USB flash drives and what you can expect. By checking the table below, you’ll have a better understanding of how to choose the best USB allocation unit size for exFAT, NTFS, FAT32 formats.
| File format | Partition size | Default allocation unit size |
| NTFS | 7 MB – 2 TB | 4096 bytes (4 KB) |
| FAT32 | 32 MB – 64 MB, 256 MB – 8 GB, 8 GB – 16 GB, 16 GB – 32 GB; | 512 bytes (0.5 KB), 4 KB, 8 KB, 16 KB; |
| exFAT | 7 MB – 256 MB, 256 MB – 32 GB; | 4096 bytes (4 KB), 8 KB; |
For example, if you have an NTFS flash drive under 8 GB, you can format the USB allocation size to 4096 bytes, but if it’s larger than 8 GB but has less space than 16 GB, you should double the allocation size to 8192 bytes.
If the size is over 16 GB, you should increase to 16 kilobytes. Of course, if you have a 1 TB USB drive and are using it to transfer large movie files, you should increase the allocation size as much as possible to ensure whole files are placed on different clusters.
Bonus Advice: How to Recover Data From a Formatted USB Device?

If you accidentally lose your vital data while formatting allocation unit size, don’t worry. You can still recover this data using a tool like Wondershare Recoverit.
Wondershare Recoverit can recover files for USB flash drives, SSDs, HDDs, NAS storage, etc. Even if your device gets fragmented or corrupt, Recoverit can successfully recover its files. Here are the steps for recovering data from a USB using Recoverit:
- Download and install Wondershare Recoverit.
- Plug the USB flash drive into your computer.
- Start Wondershare Recoverit.
- Click on Hard Drives and Locations, select your flash drive, and click Start.
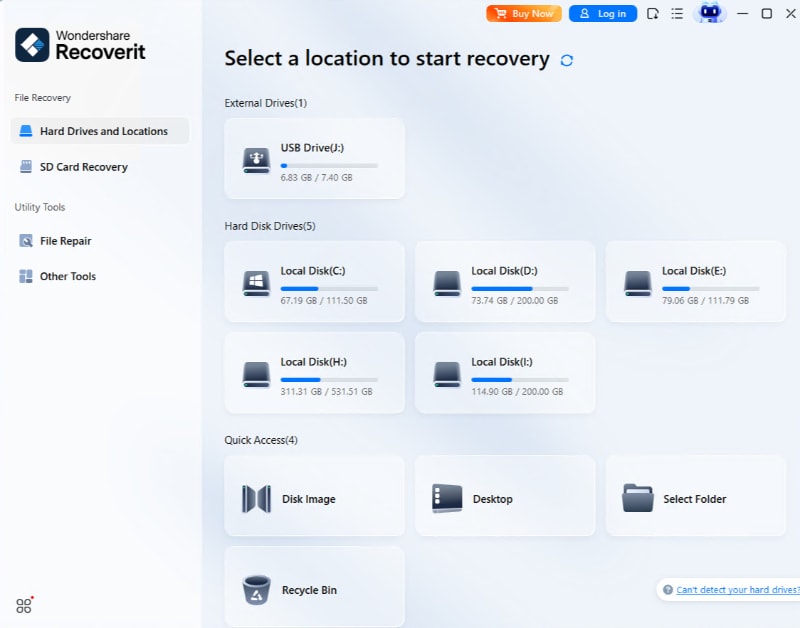
- Scanning will start automatically. Wait until the whole drive has been scanned.
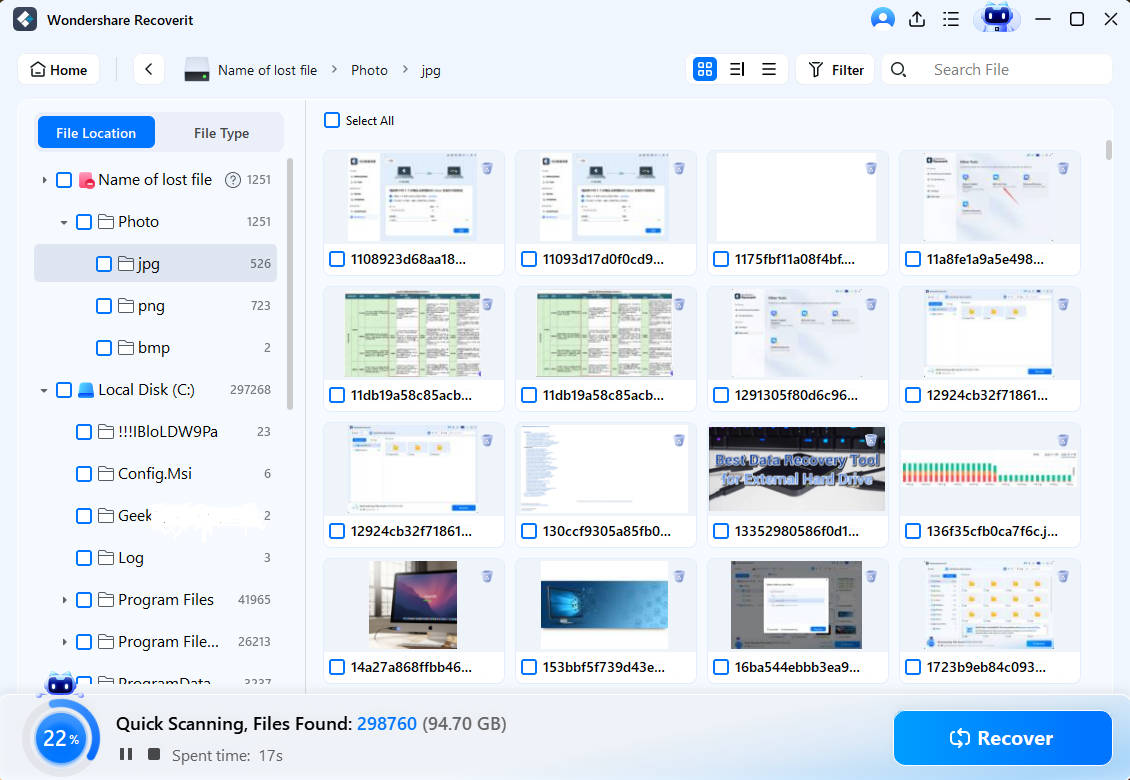
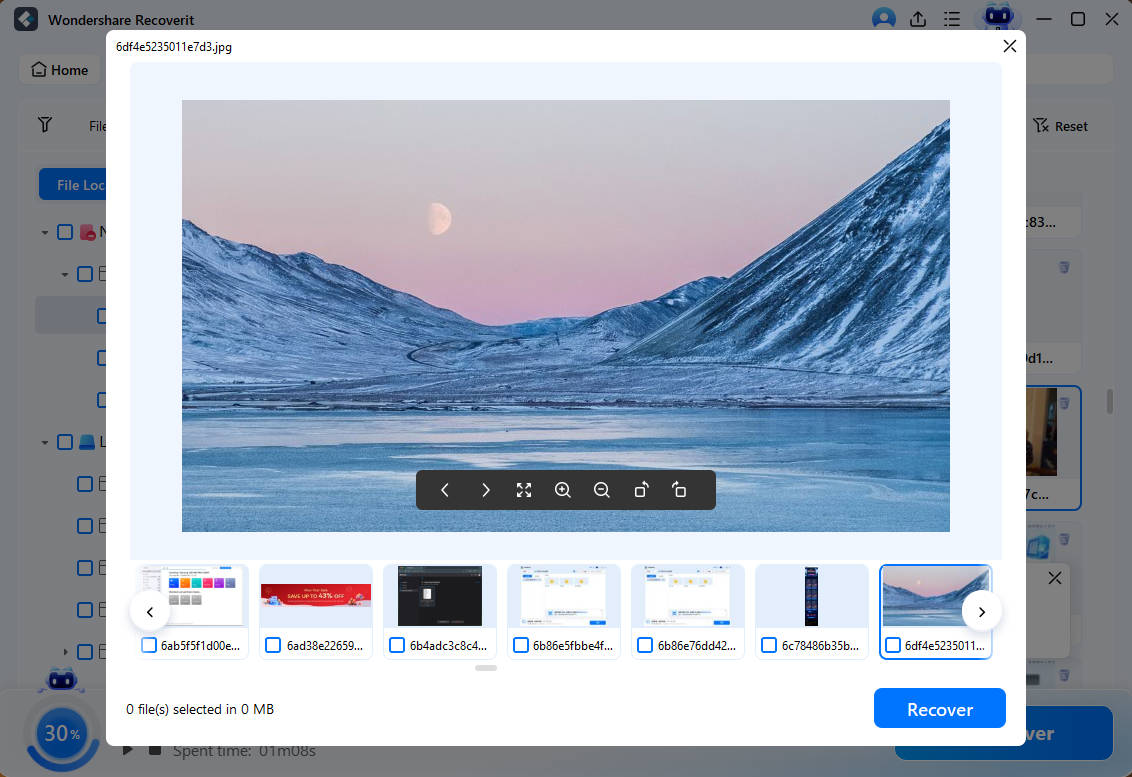
- Preview the discovered files, select the ones you want to recover, and click Recover when ready.
Conclusion
The allocation unit size refers to chunks on your USB partition for storing files. Always use your drive’s default allocation unit size, depending on partition size and file format. However, if you’re using the drive to store large files, create an allocation unit size that can fit the whole file.
Alternatively, if you’re transferring really small files, create a smaller allocation size to use all the space efficiently. Refer to our table to format your USB to the right allocation unit size.
FAQ
What happens if my cluster size is too large?
If your allocation size is large and you’re using a large volume of small files, it’s a good idea to reduce the allocation size to a minimum for better management. However, if you have a few large files, using a large cluster size will allow you to get the most out of your storage.Does block size affect transfer speed?
If you have a small block size, your device might run slower and take longer to format the drive and transfer files. But if it’s too large, you will lose a lot of valuable space.How do you change allocation unit size on a USB?
When formatting your USB, you will size the allocation unit size setting. Change to your desired size before you start formatting.



 ChatGPT
ChatGPT
 Perplexity
Perplexity
 Google AI Mode
Google AI Mode
 Grok
Grok






















