Before the operating system loads each time you turn on your PC, the computer first goes through the Basic Input/Output System, or BIOS for short. This fundamental piece of software loads up your hardware components each time the PC boots and contains a feature called “legacy USB support.”
Today, we’ll dive deeper into legacy USB support in BIOS, explain why it’s fundamental, how it works, what you’ll need to do to turn it on, and the problems it can cause. We’ll also examine a quick method of retrieving your lost USB files in case legacy USB support has failed you.
In this article
Legacy USB Support Explained
Before explaining legacy USB support in BIOS, we must first discuss what USB devices are and how they work. Don’t worry. Everything will make sense soon.
USB, which stands for Universal Serial Bus, was a joint effort of Compaq, DEC, IBM, Intel, Microsoft, NEC, and Nortel. These companies aimed to create a universal connector that would replace PS/2 ports that keyboards and mice at the time used and serial and parallel ports that other peripherals needed.
However, older operating systems don’t recognize these USB devices, so you need legacy USB support in BIOS. This feature lets you use the newer USB devices in BIOS before the operating system’s drivers load.
You might ask, “Why would I ever need to use a keyboard and mouse outside the operating system?” That’s an entirely valid question, as not many users will ever require these before the OS loads. Nonetheless, the feature is still necessary for providing backward compatibility, troubleshooting capabilities, and access to bootable USB drives, even on older computers.
Different BIOS Compatibility Modes
Unfortunately, the legacy USB support in the BIOS feature can have a minor negative impact on your computer’s boot time, so the BIOS on most computers allows users to configure USB legacy support and engage different compatibility modes. Most PCs have four different settings for legacy USB support, including the following:
- Auto – It’s the option that most users should use. In this mode, the BIOS will automatically detect whether your USB devices need the feature on or off and deactivate or activate it accordingly. Most computers come with this mode as the default one.
- Enabled – As the name suggests, this mode explicitly enables legacy USB support for all your USB devices. Although it’s unnecessary if you have newer USB devices, this mode is most compatible with older ones.
- Disabled – Like there’s a fully enabled mode, BIOS software also allows you to entirely turn off legacy USB support, leading to faster boot times by skipping USB initialization. It’s the best option if you exclusively own newer USB devices and want a quick boot-up.
- Manual – A few BIOS software implementations allow users to configure legacy USB support manually. In essence, it lets users turn the feature on or off for each USB device connected to the PC, which is excellent if you use many USB devices simultaneously, some of which are older.
Only some BIOS settings are unlocked, and this feature might have different options on different computers, but you should always be able to turn it on or off.
How USB Legacy Support Affects Device Functionality
As mentioned, the legacy USB support in BIOS does impact your computer’s boot time, but that’s not the only thing it affects. Let’s dive deeper into how this feature affects USB device functionality. Below are the three main aspects of the feature’s impact:
- 💻 Keyboard and Mouse – These peripheral devices used the PS/2 connector before the USB protocol came along. Therefore, many users purchased PS/2 to USB adapters instead of upgrading to newer peripheral devices. Even today, keyboards and mice with these ports can still be bought, but they require legacy USB support to function on modern computers without PS/2 ports.
- 👀 Recognizing Devices – You also need legacy USB support, as the feature recognizes and initializes older USB devices, making them usable in BIOS and helping the operating system load the necessary USB drivers. Otherwise, your older USB devices would be unusable on a newer operating system.
- 💫 Booting From a USB Device – Since the days of CDs and DVDs are long gone, and we’ve moved to USB flash drives, it’s necessary to make USB drives capable of installing an operating system. Legacy USB support allows precisely that, and it’s pretty useful whether you’re troubleshooting an installed operating system or installing a fresh one on your PC.
- 🔐 Enhanced Security – With limited USB access during boot-ups comes an increase in security, as the BIOS will prevent unauthorized access by USB devices during start-up. Potential malware and viruses on these USB drives will not access your BIOS. Otherwise, they can wreak havoc.
It’s worth noting that although we’ve mentioned the impact on performance and boot times, the delays here are minimal and not something the average user will ever notice.
How to Turn On Legacy USB Support in BIOS
Now that we know what legacy USB support in BIOS is and its pivotal role in increasing USB device functionality and compatibility, let’s see how you can turn it on. Here’s what you should do:
- Reboot your PC and keep pressing the F12 key on your keyboard. Depending on your computer’s manufacturer, it can also be the F1, F2, F10, Del, or Esc keys, but it will usually say which key enters BIOS when the first black screen with white text pops up.
- You’ll have to rely on your keyboard for navigation once you’re in BIOS. Head to the Advanced tab and search for USB Legacy Support.

- Set the option to either Auto or Enabled.
- Head to the Exit tab, select Exit Saving Changes, and hit Enter on your keyboard when prompted.

The steps above work for Phoenix Award BIOS, but an AMI BIOS will require these steps:
- Press the appropriate key on your keyboard to get into BIOS after you reboot the PC.
- Head to the Advanced tab and then look for USB Ports.

- Find the All USB Devices option and set it to Enabled.

- Then, go into the Boot tab.

- Find UEFI/BIOS Boot Mode and set it to Legacy or UEFI.

You might need to explore this blue interface independently, but it’s vital to remember not to change any other options you’re unsure of.
Known Problems of USB Legacy Support in BIOS
Although quite valuable for the abovementioned reasons, legacy USB support in BIOS also has certain drawbacks. Some of the most common ones include the following:
- 🐌 Delaying Boot Times – However minor the effect, initializing USB devices takes time and is particularly noticeable on older computers with slower hardware. You should consider turning off the legacy USB support feature if you don’t need it.
- 🌋 System Crashes – Some computers can experience Blue Screen of Death, or BSoD for short, and other system crashes when the legacy USB support feature is enabled. It’s especially true when the AMD64 mode is enabled, as these two features don’t work well together.
- 🤚 UEFI Feature Interference – Most modern computers use UEFI instead of BIOS, which stands for Unified Extensible Firmware Interface. It’s a software tool that inherited the role of BIOS, and it connects the computer’s firmware to the OS. However, this software’s features don’t play well with legacy USB support.
- 🙁 Secure Boot Incompatibility – The most common UEFI feature affected by legacy USB support in BIOS prevents unauthorized USB device access during boot. However, you can’t have both features turned on simultaneously.
- 🆙 Updates to BIOS – Although these are incredibly rare, and most manufacturers only update their motherboard’s BIOS for the first few years, it’s worth noting that these will revert your settings to default, including legacy USB support in BIOS.
Understanding what legacy USB support is, how it works, and whether you need it on your operating system will help reduce the number of issues with your USB devices. Otherwise, you might face problems and lose data from your USB devices.
How to Recover Data if You Lose It From Your USB Device
Since newer USB devices sometimes don’t show up on older operating systems, and older OSs like Windows 7 and earlier don’t have USB 3.0 drivers out-of-the-box, data loss is imminent. Using this combination of devices will likely display a formatting error and ask you to format the USB device, which will wipe it clean of any data.
Fortunately, there’s a way to get your files back, even if you’ve accidentally formatted the USB device or the older operating system corrupted your newer USB device’s data. Dedicated data recovery apps, like Wondershare Recoverit, have your back in such cases.
On top of various USB flash drives, Wondershare Recoverit supports over 2,000 other devices of different types from multiple manufacturers and different models.
The app can recover over 1,000 different file types, including pictures, videos, music, and documents. Whether it’s malware, accidental deletion, USB drive formatting, or something else entirely, it will get your files back.
Below is a step-by-step guide for recovering lost USB device data with Wondershare Recoverit. Here’s what you’ll need to do:
- Plug your USB device into the computer and launch the Wondershare Recoverit app.
- On the left side of the screen, select Hard Drives and Locations, then select your USB device.
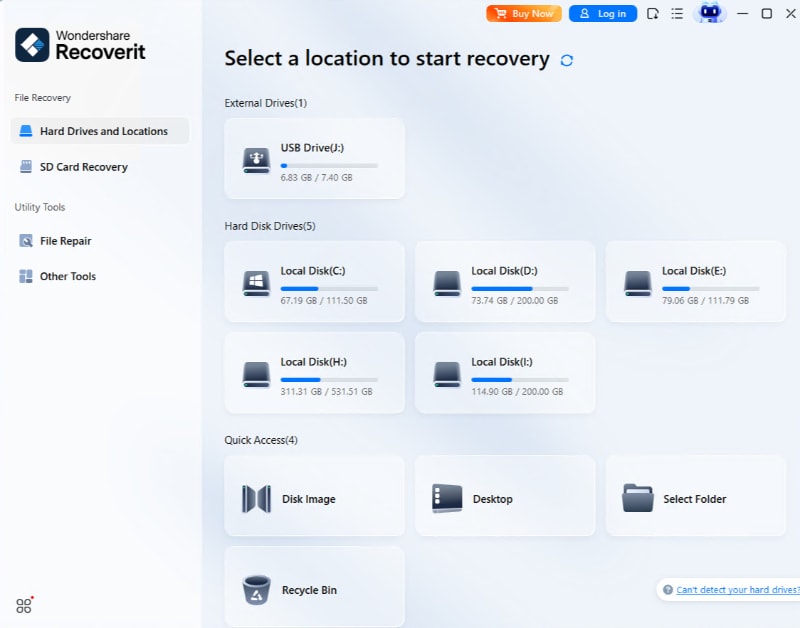
- The app will automatically begin scanning your USB device and show you the files it finds.
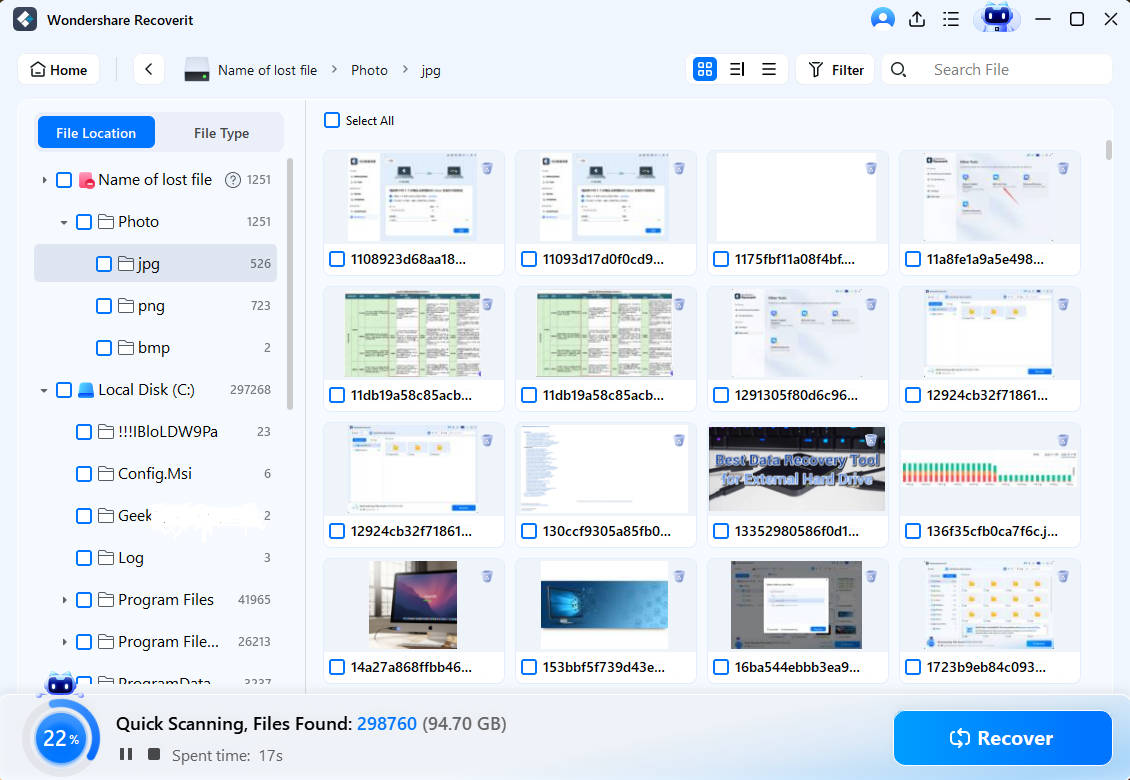
- The app also lets you preview files it finds, so you can ensure those are the files you’re looking for.
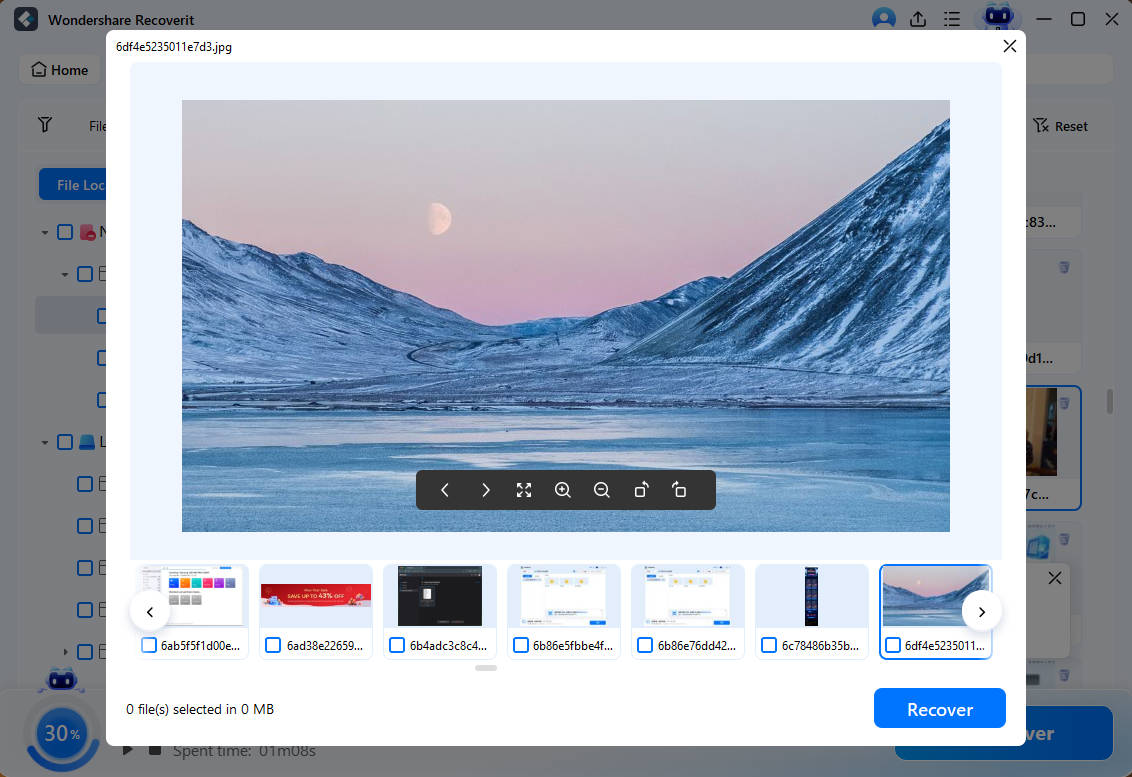
- Once the app finds the files you want to retrieve, select them and hit the Recover button.
It’s worth noting that Wondershare Recoverit lets you use keywords and adjust multiple file size, type, and location filters to speed up the scanning process. Regardless of the filters, the scan will only take a few minutes, and you’ll have your files back in no time.
Conclusion
Legacy USB support in BIOS is crucial in ensuring backward compatibility and increasing the functionality of your older USB devices. This feature allows computers to recognize, initialize, and configure older USBs to run on newer operating systems, but it also makes newer USB devices usable on older operating systems.
Although helpful, the feature is not without its disadvantages, as it can cause system crashes, slow down your computer’s boot times, create incompatibility issues with other BIOS/UEFI features, and even cause your USB devices to lose data.
Fortunately, turning it on and off is relatively straightforward, and you can always recover your vital USB drive’s data with the help of a dedicated and trustworthy data recovery application like Wondershare Recoverit.



 ChatGPT
ChatGPT
 Perplexity
Perplexity
 Google AI Mode
Google AI Mode
 Grok
Grok






















