Have you ever felt really worried when you noticed that your important files on a small storage device called a flash drive have disappeared? This is a common problem!
Whether caused by accidental deletion, formatting errors, or hardware failures, loss of critical data is a nightmare. What if users could recover the files from their flash drive using something already part of their computer? Enter CMD, a powerful recovery option to restore files on Windows.
The following is an article on how to recover flash drive files with CMD, or Command Prompt, and other effective methods, so you can restore your treasured data whenever disaster strikes.
In this article
What is CMD?
CMD, short for Command Prompt, is a powerful text-based interface in Windows operating systems that allows users to interact directly with the computer's file system and execute various commands.
This versatile tool has been a staple of Windows since its early days, offering features like file management, system diagnostics, and network configuration. The beauty of CMD lies in its ability to perform complex operations with simple text commands, making it an invaluable asset for both casual users and IT professionals.
One of the key benefits of CMD is its efficiency in performing batch operations and automating tasks. However, it does have limitations, such as a steep learning curve for beginners and the potential for unintended consequences if commands are entered incorrectly. Despite these drawbacks, CMD remains an essential tool for flash drive recovery and various other system maintenance tasks.
Reasons Behind Flash Drive Files Getting Lost
Understanding why files disappear from flash drives is crucial for prevention and recovery. Here are some common reasons:
- Accidental deletion: Users may inadvertently delete files or folders.
- Formatting errors: Improper formatting can wipe out all data on the drive.
- File system corruption: Damaged file systems can make data inaccessible.
- Virus or malware attacks: Malicious software can delete or encrypt files.
- Hardware failure: Physical damage to the drive can result in data loss.
- Improper ejection: Removing the drive without safely ejecting it can lead to file corruption.
- Power surges: Sudden power fluctuations can disrupt file-writing processes.
- Software conflicts: Incompatible or malfunctioning software can cause data loss.
- Overwriting: Saving new files to a drive can sometimes overwrite existing data.
- Human error: Mishandling or misplacing the drive can result in lost files.
Is It Possible To Restore Flash Drive Files?
The good news is that in many cases, it is indeed possible to restore flash drive files. When a file is deleted from a flash drive, it isn't immediately erased from the physical storage.
Until this space is overwritten, there's a chance to recover the lost files. This is where tools like CMD and specialized recovery software come into play.
By utilizing these methods, users can often recover files that seemed lost forever. However, the success of flash drive recovery depends on factors such as the cause of data loss, the time elapsed since deletion, and whether the drive has been used since the loss occurred.
How To Recover Files From Flash Drive Using CMD
Recovering flash drive files using CMD can be an effective method when other options fail.
Follow these steps to recover files from flash drive using CMD on Windows:
Step 1: Before you begin, make sure that the USB flash drive is connected to your Windows PC. Open Command Prompt as an administrator. You can either right-click on the Windows icon or perform a quick search.

Step 2: Type "chkdsk X: /f" (replace X with your flash drive letter) and press Enter. This command will check the drive for errors and attempt to fix them.

Step 3: Once the check is complete, type "X:" (again, replace X with your drive letter) and press Enter to switch to the flash drive.
Step 4: Now, type "attrib -h -r -s /s /d ." and press Enter. This command will attempt to restore hidden files. Wait for the process to complete. If successful, you should see your recovered files on the flash drive.

Step 5: Once the process is complete, check your flash drive for recovered files.
Remember, CMD flash drive recovery methods may not always be successful, especially in cases of severe corruption or physical damage. In such instances, professional data recovery software or services may be necessary.
How To Recover Flash Drive Files Using Recoverit
While CMD is a powerful tool for flash drive recovery, sometimes a more user-friendly and comprehensive solution is needed. This is where Recoverit Data Recovery Software comes in. Recoverit offers advanced data recovery capabilities that can help users recover their data effortlessly.
Here's a table showcasing some of Recoverit's features:
|
Feature |
Description |
|
Deep Scan |
Thoroughly scans the drive to find even deeply hidden files |
|
Multiple File Types |
Recovers over 1000+ file formats, including documents, photos, and videos |
|
Preview Function |
Allows users to preview files before recovery |
|
Selective Recovery |
Enables users to choose specific files to recover |
|
Cloud Recovery |
Offers cloud-based recovery options for added convenience |
|
User-Friendly Interface |
Intuitive design makes the recovery process simple for all users |
Now, let's go through the step-by-step process of using Recoverit to recover flash drive files:
Step 1: Install Recoverit on your computer. Launch the software and select your flash drive from the list of available drives. Click "Start".
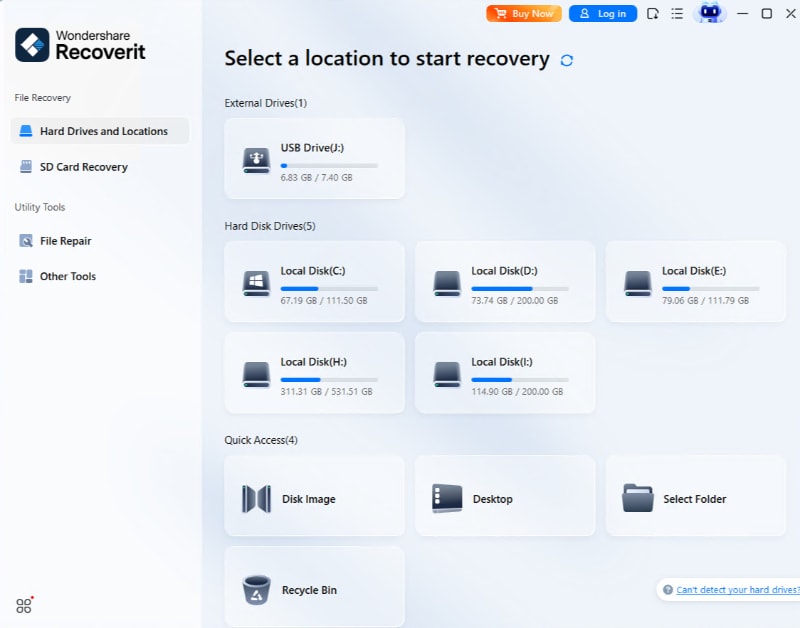
Step 2: Wait for the scan to complete. You can pause or stop the scan at any time if you see the files you need.
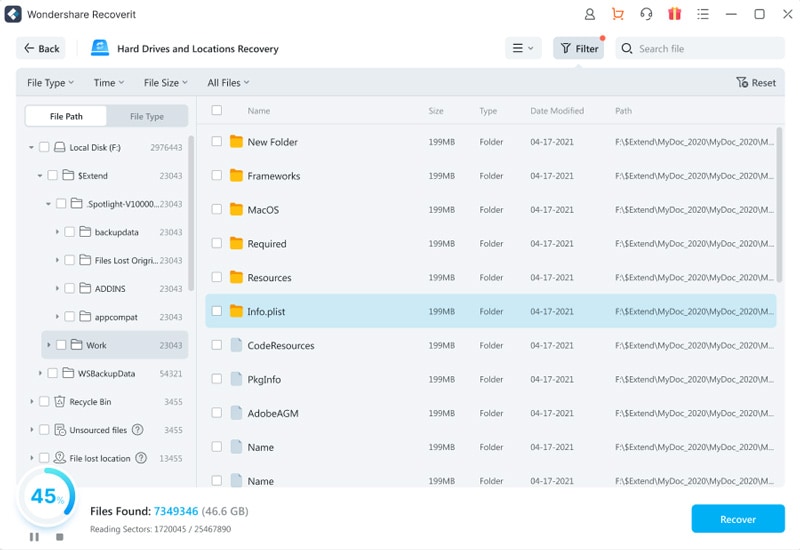
Step 3: Preview the recoverable files to ensure they're the ones you want to restore. Select the files you wish to recover and click "Recover" to save them to a safe location on your computer.
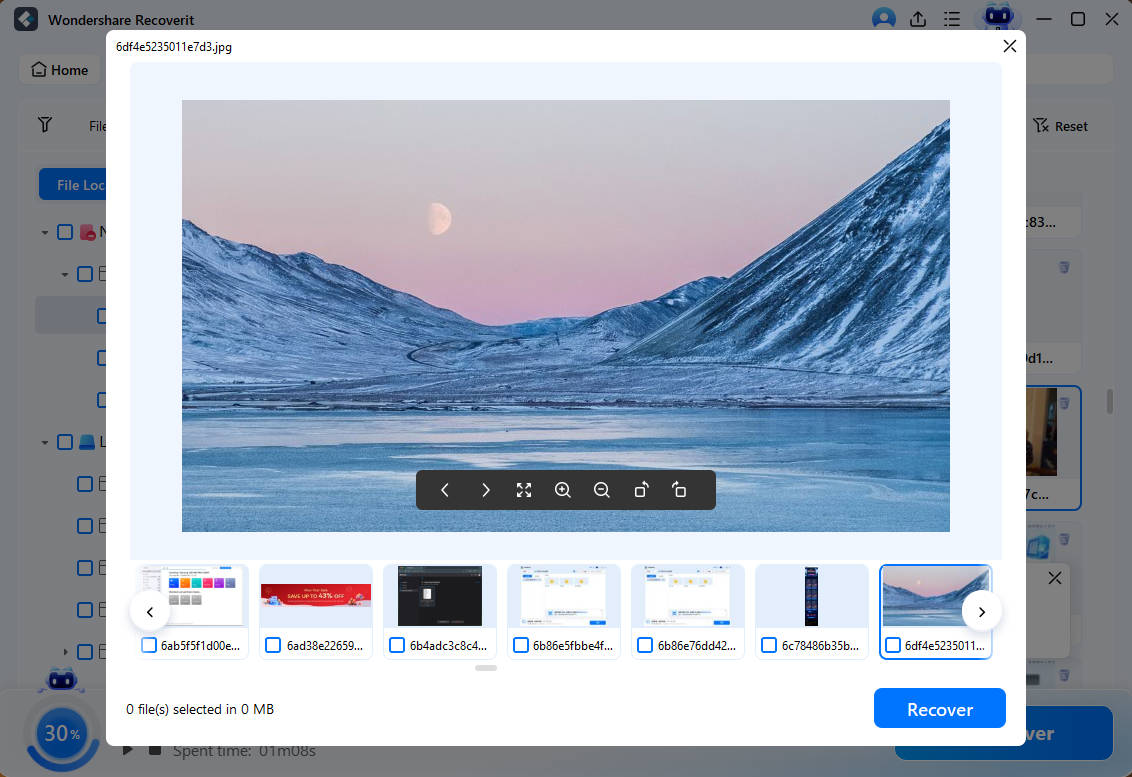
Step 4: Choose a destination folder for your recovered files. It's recommended to select a location different from your flash drive to prevent overwriting. Wait for the recovery process to complete and verify that your files have been successfully restored.
Using Recoverit can often yield better results than CMD alone, especially for less tech-savvy users or in cases of more complex data loss scenarios.
Tips & Notes
- Always back up your important files regularly to prevent data loss.
- Use the "Safely Remove Hardware" option before unplugging your flash drive.
- Keep your flash drive protected from physical damage and extreme temperatures.
- Run antivirus scans on your flash drive periodically to prevent malware-related data loss.
- If you suspect hardware failure, seek professional help immediately.
- Avoid writing new data to the flash drive if you've experienced data loss, as this can overwrite potentially recoverable files.
- Consider using cloud storage as an additional backup for critical files.
- Regularly update your operating system and drivers to prevent compatibility issues.
If one recovery method fails, try another before giving up hope.
Conclusion
Recovering flash drive files using CMD and other methods like Recoverit can be a lifesaver when facing data loss. By understanding the causes of file loss and the various recovery techniques available, you can increase your chances of restoring valuable data.
Remember to act quickly, avoid writing new data to the drive, and always maintain regular backups to protect your important files.
FAQs:
-
What is attrib command in CMD?
The attrib command in CMD is used to display, set, or remove attributes assigned to files or directories. In the context of flash drive recovery, it can be used to reveal hidden files by removing hidden attributes. -
Can I recover files from a corrupted USB?
Yes, it's often possible to recover files from a corrupted USB drive. Methods like using CMD, specialized recovery software, or professional data recovery services can help retrieve files from corrupted drives. -
How can I attrib a flash drive using Command Prompt?
To attrib a flash drive using the command prompt, first open CMD as an administrator, then navigate to your flash drive by typing its letter (e.g., "E:"). Next, use the command "attrib -h -r -s /s /d ." to remove hidden, read-only, and system attributes from all files and folders on the drive.
















