In this article
What Is NTFS File System - Definition
New Technology File System or NT File System (NTFS) is a customized journaling file system created by Microsoft in 1993. It became the default file system for the Windows NT family with Windows NT 3.1. In addition to being supported by Linux and BSD, it replaced the File Allocation Table (FAT) as the primary file system on Windows. The Windows NT operating system (OS) uses it as the file system for storing and retrieving files from hard disk drives (HDDs) and solid-state drives (SSDs).
The Windows operating system uses three file systems to store data on a storage device: NTFS, FAT32, and exFAT. Some of you might be interested in learning more about the distinctions between the three or may be unsure which one to use for your hard drive or USB format. After learning the brief of the NTFS, let's have a fundamental understanding of FAT32 and exFAT.
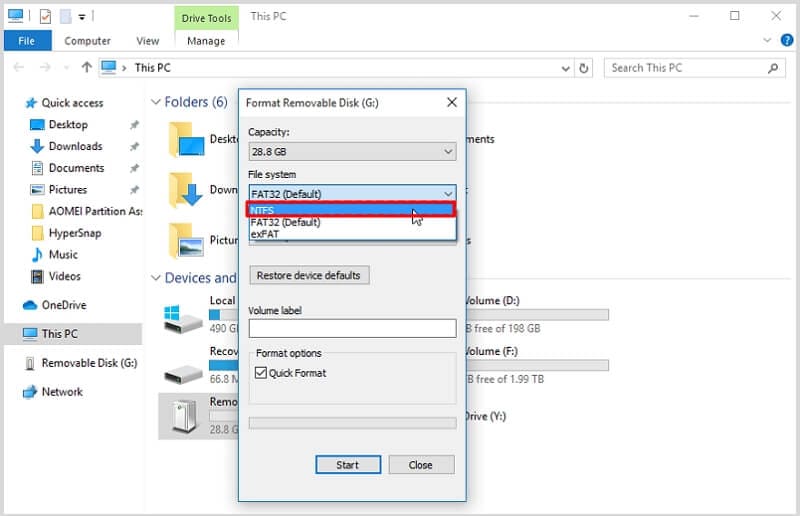
All operating systems are compatible with File Allocation Table 32 (FAT32), an earlier version of the standard format used before the NTFS file system. Meanwhile, the Extended File Allocation Table (exFAT) transmits files larger than 4GB. Additionally, it is more compatible than NTFS because it runs smoothly on both Windows and Mac devices.
So, NTFS, FAT32 or exFAT, which is better? Here is a comparison of NTFS, FAT32, and exFAT in a table. You can read on to discover the differences:
FAT32 |
NTFS |
exFAT |
|
| Compatability | All Windows versions, macOS, Linux, videogame consoles (Playstation 3 & 4), media players, Android, iPhone, and other devices. | All Windows versions, Mac OS X (have read-only access), Linux | All Windows versions, videogame consoles (Playstation 4 & 5) |
| Max Volume Size | 32GB | 16TB | 128 PB, 512 TB recommended |
| Max File Size | 4GB | 16TB | 128 PB (theoretical 16 EB – 1 byte) |
| Cluster Size | 4 KB to 32 KB | 4 KB | 32MB |
| Fault Tolerance | No | Auto repair | Yes, if TFAT activated |
| Conversion | Possible | Not Allowed | Not available |
| Compression | No | Yes | No |
| Performance | High on small volumes Low on large | Low on small volumes High on Large | High |
How to Find Out If a Drive Is Formatted as NTFS
There are few techniques to determine whether a hard drive has been formatted with NTFS or another file system is being used.
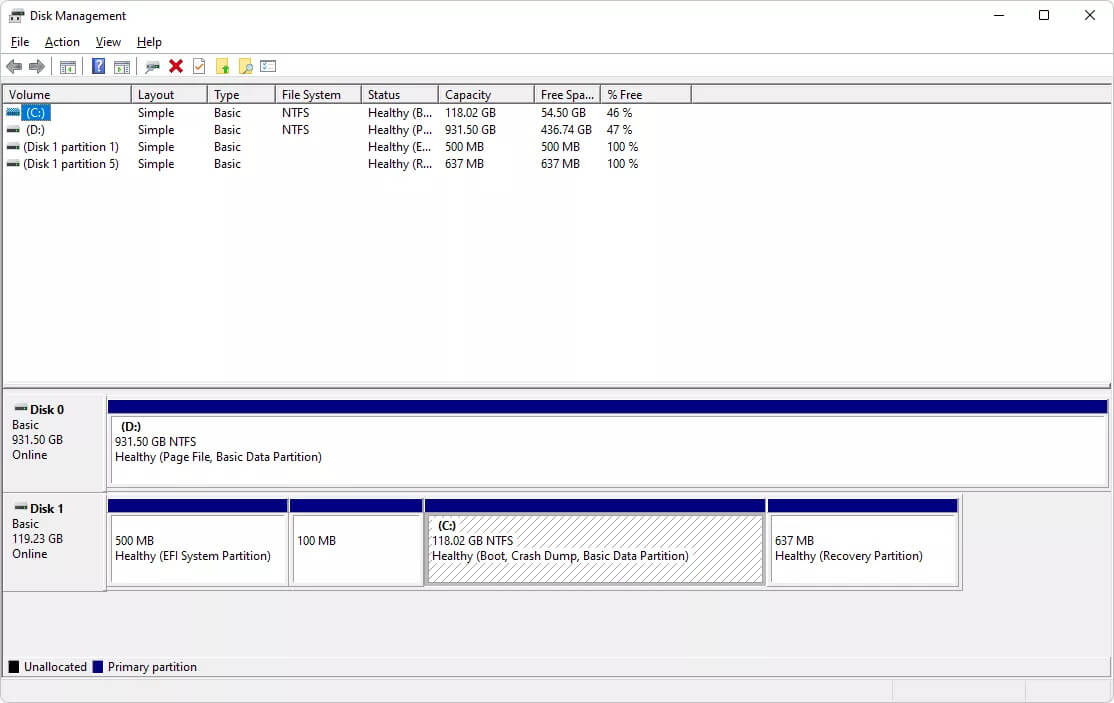
1. Use disk management
Utilizing disk management is the first and possibly most straightforward method to view the status of one or more disks. The volume and other information about the drive are listed right here, along with the file system.
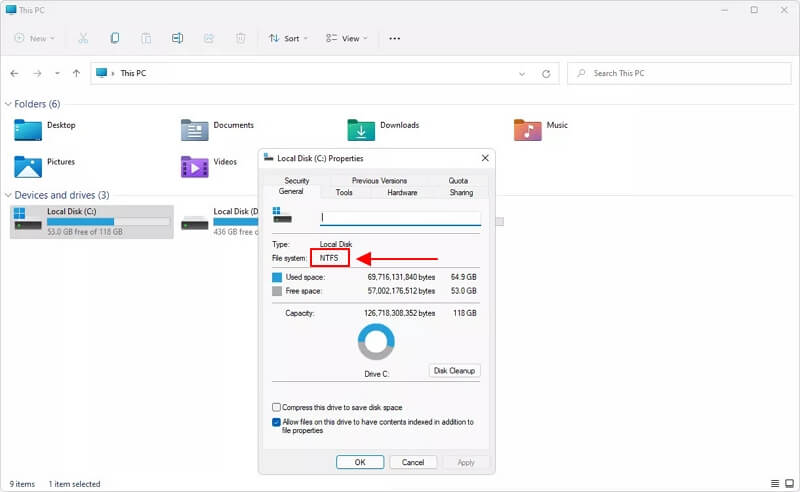
2. Open File Explorer
By right-clicking or tapping and holding the hard drive in File Explorer, you may check to determine if it was formatted with the NTFS file system. Select Properties from the drop-down menu after that. Examine the information under File system on the General tab. File system: NTFS will appear if the drive is NTFS.
3. Use CMD
The command-line interface is yet another method to check which file system a hard drive operates. To display different information about the C: drive, including its file system, open a Command Prompt (in some Windows versions, this may require an elevated Command Prompt) or Windows Terminal and type the following:
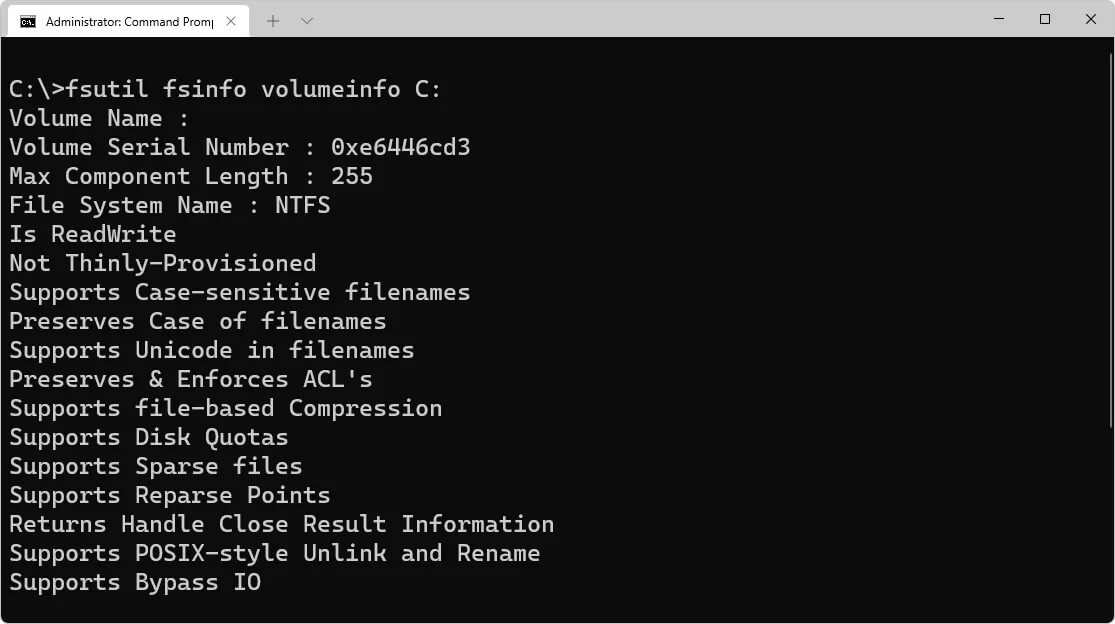
Use the volume letter of the drive in place of C to check a different hard drive. Get an on-screen print-out using the fsutil fsinfo drives command if you are unsure of the drive letter.
NTFS File System Structure - How NTFS Stores Data
NTFS consists of several components, such as
- an information-containing partition boot sector (PBS)
- the master file table, which keeps a record of all files and directories in the filesystem
- a set of meta files that facilitate more effective structuring of metadata
Partition boot sector (PBS)
The boot sector of an NTFS-formatted drive is described in the following table. The format program sets aside the first 16 sectors of an NTFS when formatting it for the boot sector and the bootstrap code.
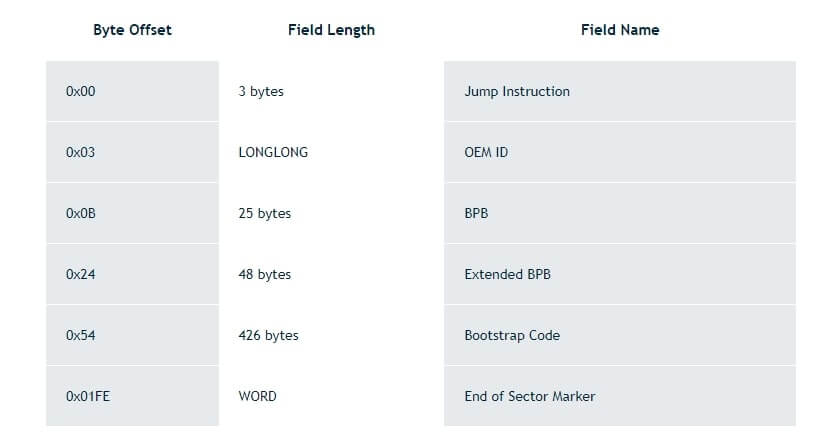
The data fields that follow the BPB on NTFS disks create an expanded BPB. Ntldr (the NT loader program) can locate the master file table (MFT) on startup, thanks to the information in these fields. NTFS volumes do not have a designated sector where the MFT is placed.
Because of this, if a faulty sector is present in the MFT's usual place, it can be shifted. Windows thinks the drive has not been formatted if the data is corrupted or the MFT cannot be found.
Master File Table (MFT)
The master file table is a unique file that contains records for every file on an NTFS drive (MFT). NTFS sets the table's first 16 records aside for special data. This table's first entry describes the master file table in detail, followed by an entry for the MFT mirror.
If the first MFT record is corrupted, NTFS scans the second record to locate the MFT mirror file, whose first record is identical to the first record of the MFT. The boot sector stores the locations of the data segments for the MFT and MFT mirror files. The logical center of the disk contains a copy of the boot sector.
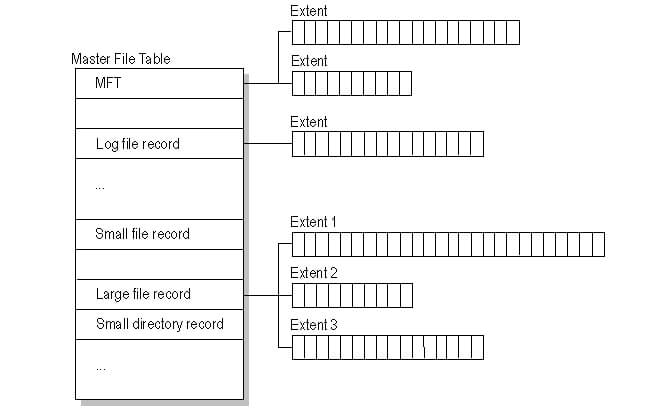
The log file, which is utilized for file recovery, is the third record of the MFT. Each file entry is given a specific space in the master file table. A file's attributes are written to the MFT's designated space. Small files and directories can fit totally inside the master file table record if they are 1500 bytes or less in size.
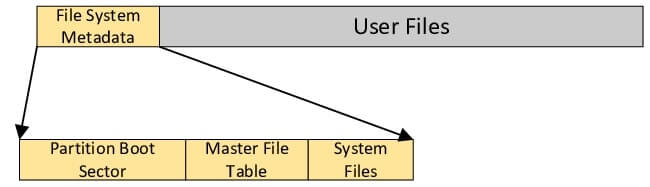
NTFS File System Metadata
Several system files are part of NTFS and are all hidden on the NTFS drive. A system file is one that the file system uses to implement the file system and store its metadata. The Format utility writes system files to the volume.
How Does NTFS Work?
A file system is selected by the user while installing an OS. The file system that will be used is chosen by the user when formatting an SSD or HDD. Each drive type requires a somewhat different formatting procedure, but both are NTFS compatible.
The entire physical hard disk space is partitioned when a hard drive is formatted. The operating system records all the files stored by that operating system within each partition. Then, each file is kept on the hard drive in a single or several clusters that are all the same size. Windows NT offers a recommended default cluster size for any given drive size. When utilizing NTFS, cluster sizes vary from 512 bytes to 64 kilobytes.
Note that clusters cannot be divided; the smallest file occupies one cluster, a 4.1 KB file occupies two clusters, and an 8 KB file occupies eight clusters on a 4 KB cluster system.
It is anticipated that a system user will choose to boost performance (fewer disk accesses) at the expense of a small amount of wasted space. Thus, the larger the default cluster size for NTFS is, the larger the hard disk.
Highlights of NTFS File System - When Should You Use NTFS
The fact that NTFS supports file permissions and encryption is one way in which it differs from the latter. NTFS has the following notable key features:
Disk usage quotas
An administrator establishes these limits to limit how much disk space a user can occupy. It is mainly employed to regulate the amount of accessible shared space, typically on a network drive. You can monitor the amount of free hard drive space without employing disk use quotas.
Encryption of file systems
Individual files and folders can be secured since EFS offers file-level encryption. Full-disk encryption, which encrypts the entire drive, differs from this capability.

Journaling file system
It offers a technique to log or journal system changes before they are written to the file system. This feature enables the file system to return to earlier functional states in the event of failure because the new changes have not yet been committed.
Volume Shadow Copy Service
Windows itself utilizes an NTFS feature to keep copies of your data and online backup service programs and other backup software tools to back up files that are now being used.
Transactional NTFS
It is a new feature included in this file system. As a result, software developers might create apps that are either entirely successful or ultimately unsuccessful. Programs that take advantage of this avoid the risk of making some modifications that work well and some that don't.
Hard links, sparse files, and reparse points are some of the additional features offered by NTFS.
Advantages & Benefits of NTFS
Control
Access control for mission-critical data is made possible by NTFS's ability to provide permissions to files and folders.
Performance
NTFS supports file compression, giving your company access to more drive space.
Security
Administrators can set rights on sensitive data using NTFS's access control features to limit access to specific users.
Simple logging
Administrators can track files that have been added, removed, or altered, thanks to the MFT's logging and auditing of the drive's data.
Reliability
Because NTFS keeps the consistency of the file system, data and files can be promptly restored in the event of a system failure or malfunction. It has an MFT mirror file that the system can turn to if the original MFT becomes corrupt because it is a fault-tolerant system.
NTFS has advantages over other file systems of a similar nature, such as File Allocation Table 32 (FAT32). The two file systems are utilized in various computing scenarios, from personal to business. NTFS is the most well-known of the two due to its association with Windows.
Find out more on the article “NTFS vs FAT32” about the distinctions between these two credible file systems and how they are currently employed in businesses.
Drawbacks of NTFS - When Should You Choose the NTFS Alternatives
The main drawback of NTFS is that outdated equipment cannot use its cutting-edge features. Because NTFS was created to work with a Windows operating system, it isn't necessarily compatible with Mac or Android devices. For instance:
- Mac OS systems can read drives formatted in NTFS, but they can only be written to NTFS via third-party software.
- NTFS is limited to other devices. Media equipment like DVD players, TVs, and digital cameras are used to use NTFS storage systems.
- NTFS lacks a framework for ensuring file system performance and bandwidth, which can be problematic for some users.
In terms of security, partition size, file rights, and other factors, NTFS is superior to FAT32. But with the NTFS drawbacks, you must consider converting to FAT32. Compared to the NTFS file system, FAT32 is more compatible with old operating systems and other external storage devices. Good thing that there are various ways to convert NTFS to FAT32 without losing data.
On the other hand, exFAT is a file system you can use if your storage devices are not NTFS compatible and you don't want to be constrained by FAT32. exFAT conversion requires formatting the partition, which makes it different from FAT and NTFS conversion. So, you can format your storage drive from NTFS to the exFAT file system.
NTFS Errors and Troubleshooting
1. How to Use NTFS Hard Drives on Mac or Linux
Since macOS is such an exclusive operating system, macOS does not entirely support the Linux and Microsoft NTFS file systems. But because Windows continues to dominate the market, many storage devices try to drive out with the NTFS file system.
The NTFS-formatted disk won't let you write anything by default on macOS. You will discover different methods with step-by-step instructions in our article how to use NTFS drives in macOS and how to mount NTFS on Linux.
2. NTFS Drive Corruption
A virus or malware assault may also cause NTFS corruption, resulting in unexpected data loss in the system. The NTFS file system can become corrupt for various reasons, including disk partition corruption. With these issues, is it still possible to repair the NTFS file system or NTFS partition? The answer is yes. You can now easily repair the NTFS file system any time a problem suddenly shows up.
3. Lost Data in NTFS hard drives
Have you recently experienced file loss on an NTFS hard drive? If not, you are lucky. But if data loss is your main problem, you may need to use a recovery tool to be able to retrieve your lost files from NTFS disk.
4. NTFS.sys Missing or Corrupted Errors
If the NTFS.sys file is missing or corrupted, your computer will encounter an NTFS.sys blue screen error and the missing boot.ini file, which usually happens. Thus, knowing how to fix NTFS.sys missing or corrupted errors is essential. Don’t worry. There’s a solution to fix missing and corrupted errors for you. You can do it either with the help of a third-party app or by just checking your installed drivers.
5. NTFS_FILE_SYSTEM Error
Allow yourself to no longer be terrified by the NTFS FILE BSOD Windows error since you can now solve it. But before you fix the NTFS file system error in your Windows device, make sure you have checked what causes the issue.
Video Tutorial-Anatomy of an NTFS FILE Record
If you want to learn more about the NTFS file system, this video will introduce you to the struction and composition of an NTFS file record.
Conclusion
The NTFS file system is a great file format for Windows hard drives and has ample file storage and transmission. We discussed the NTFS file system structure and its advantages and disadvantages.
Do you think NTFS is a great file system for your devices? Well, go ahead and format the hard drive partition using NTFS or convert the FAT32/exFAT device to NTFS or vise-versa now. Wondershare Recoverit has a lot of guides and tutorials that made these complex procedures easier for everyone.
For Windows XP/Vista/7/8/10/11
For macOS X 10.10 or later

 ChatGPT
ChatGPT
 Perplexity
Perplexity
 Google AI Mode
Google AI Mode
 Grok
Grok






















