A partition table is data stored in the boot sector of an HDD or SSD describing how it is divided into drives. The system loads and reads a partition table to determine which partition holds the active operating system. If the partition table fails, users won't be able to write new data or the disk or read its data for some reason. In this brief, we offer an understanding of what a partition table is, and then we provide you with different types of partition table styles, MBR and GTP, and partition table data formats as in FAT and NTFS. Let's continue reading to learn more on that subject:
1. What Is a Partition Table?
A partition table is a table that contains data of partitions on a disk, divided into segments, called partitions. In this table, partitions data or a map of partitions is stored and organized for users to comprehend. That is probably why "partition map" is another word to describe a partition table. The common location of such data used to be the first sector when Master Boot Record (MBR) was the primary partitioning scheme in PCs. Nowadays, other more advanced formats divide a disk drive into partitions, like GUID Partition Table (GPT) or Apple partition map (APM). As for GPT, this partitioning scheme is saved in sector 2 and keeps sector 1 empty for Master Boot Record (MBR) data for backward compatibility.
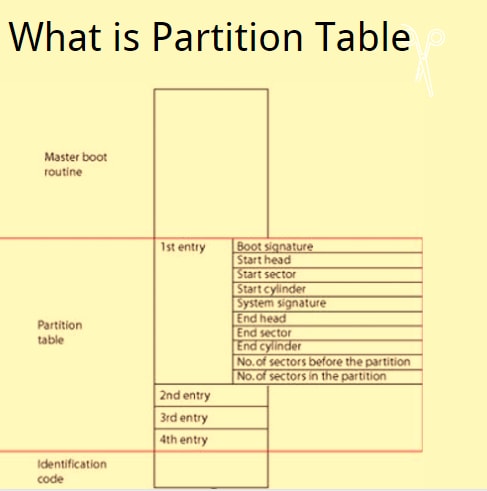
There is a discussion over which partition table is better and more comfortable for users, and many recommend choosing based on the type of your operating system. MBR is the older partitioning method, more compatible with an older OS. In systems using MBR partition tables, information on partitions is laid out on the same drive as the MBR. A data detailing the number of partitions, type of file systems are loaded on them, and whether the partition is bootable or not.
On the other hand, GPT is the latest and more flexible method of partitioning disks, which is offered as part of Intel's Extensible Firmware Interface (EFI). With GPT, a faster boot, with theoretically unlimited numbers of partitions and much bigger sizes, are available. This is a new model for the interface between operating systems and platform firmware, and so far, it has been able to attract users' attention.
Accidentally deleted or lost an important partition?
No worries. Wondershare Recoverit can get back your lost partitions within 3 steps. The ultimate and professional partition recovery software is totally reliable and 100% safe.
2. Common Types of Partition Table
Mainly, two types of partition styles are used and widely available. A hard disk is usually partitioned in either "MBR" or "GPT". A partition is often formatted as "NTFS" or "FAT" like FAT32. "NTFS" and "FAT" are file systems; thus, each partition is formatted to one of these particular file systems. Furthermore, the OS can be installed and works properly.
Here, we briefly describe the concepts mentioned further and render a summary of common partition table types:
MBR Partition Table
First is MBR, which stands for Master Boot Record. It is the traditional partitioning scheme and saves partition data on the first disk sector (MBR sector). Here, Each partition entry is 16 bytes, and the total is 64 bytes. Hence, in this approach, the partition table is limited to a maximum of 4 entries. This means an MBR-based hard disk can only support 4 partitions. And you can only have 4 partitions using MBR, which is not very ideal. Even with the extended partition introduced, the number of partitions wasn't satisfying. The size of a single partition in an MBR disk can be only as big as 2 TB. After all, an MBR-based partitioning scheme was limited, and there was a need for a better table partitioning method.
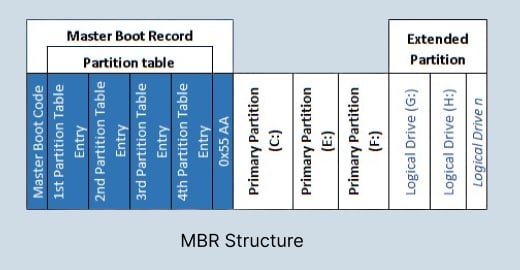
GPT Partition Table
The second type of partition style is GUID Partition Table (GPT) which uses Globally Unique Identifier (aka GUID) and has many features that trump MBR. GPT as a partition table format is created as a successor of the MBR.
It is a standard for the partition table layout on a physical hard disk. For one, with GPT, users can create up to 128 partitions on a hard disk. This supports 18 EB volume, a much larger amount compared to MBR. Plus, in GPT, all vital data are stored in partitions rather than hidden sectors. Overall, GPT is more advanced, reliable, and safe, as it provides a backup that can be accessed in case the first copy encounters problems.
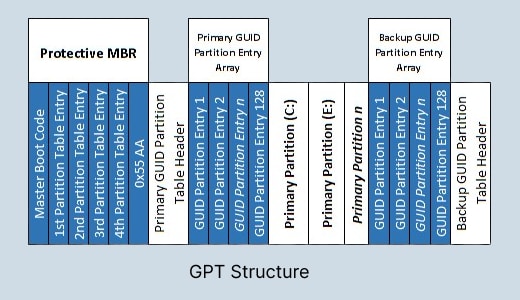
Dig deeper into the: Difference between MBR and GPT.
FAT
FAT stands for File Allocation Table and is a file system developed for personal computers. The FAT file system was originally designed for small disks and simple folder structures. FAT is named for its method of organization, the file allocation table, which occupies the beginning of the volume.
There are two copies of the table for recovery, and in case the first one fails, the second acts as a backup file allocation table. There are three types of FAT, including FAT32, FAT16, and FAT12.
Related:
How to Convert FAT32 to NTFS on Windows
In addition, there is a fixed place to save the file allocation tables and the root folder, considering these files are essential for starting the system flawlessly, and they must be located correctly.
A volume with FAT file system format is allocated into clusters. The size of the clusters is decided by the size of the volume by default.
NTFS
New Technology File System (aka NTFS) is a journaling file system developed by Microsoft. NTFS is a well-functioning and self-healing file system proprietary to Windows NT, 2000, XP, Vista, Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 10, and Windows 11 desktop systems. It is also commonly used in Windows Server 2019, 2016, 2012, 2008, 2003, 2000, and NT Server. NTFS superseded FAT as the preferred file system on Windows, and is also supported in Linux and BSD.
Related: How to Repair NTFS File System
Data integrity (transaction journal) is a major feature of NTFS. It is the ability to encrypt files and folders to protect your sensitive data and the most excellent flexibility in data handling. Therefore, an advanced NTFS file system supports file-level security, encryption, transactions, compression, auditing, etc.
Related:
Where Did My 4TB Go? Fix Hard Drive Showing Incorrect Size
Upgrade or Start Fresh? Disk Clone and Fresh Install Explained
Conclusion
A partition table is a data structure that provides essential information for a computer's operating system. There are two main partition table styles - either "MBR" or "GPT"- commonly used for hard disk partitioning. In return, "NTFS" and "FAT" are file systems and the common formats used in partition tables.
Now you have a grasp of what Is a Partition Table? And what you need for a system to work properly as a whole.

 ChatGPT
ChatGPT
 Perplexity
Perplexity
 Google AI Mode
Google AI Mode
 Grok
Grok






















