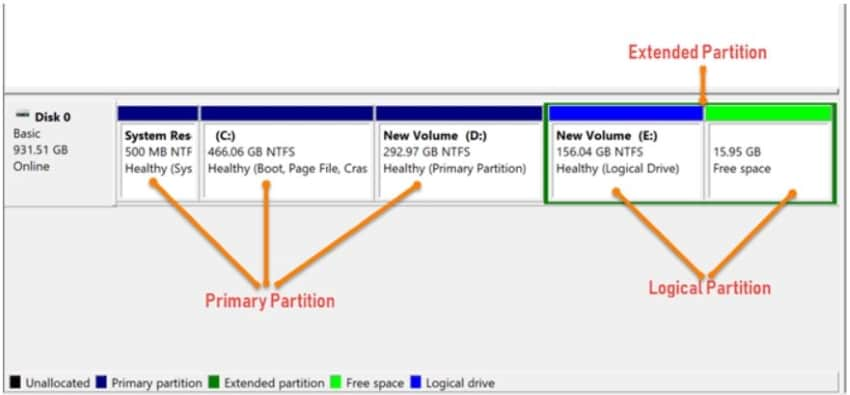
Each computer owner can learn some things about how a computer works. Technical knowledge helps when you encounter issues with your computer or upgrading it. Disk Partitions are one of the first things you should understand.
There are different types of partitions: primary, extended, and logical. Are you struggling to know their differences? Fret not. This article will explain primary partition and the difference between primary and logical partition.
Part 1. What is a Primary Partition?
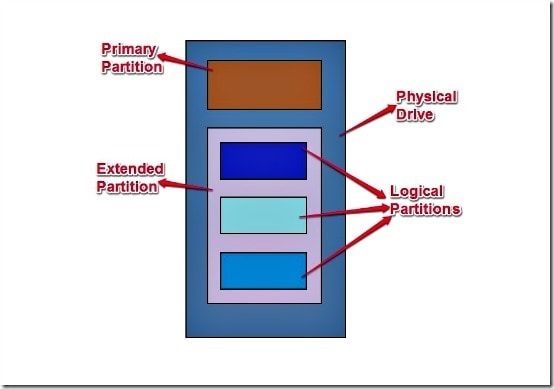
First, let's discuss what a partition is. You can divide a hard disk into several storage units. That makes it look like a single drive has multiple disks. These units are called partitions.
You can divide a hard disk into two partitions: primary partition and extended partition. A disk drive can have a maximum of four primary partitions, and each can have its operating system. That said, only one primary partition can be active, and the others will be hidden. A primary partition has a type of code indicating the file system it contains or whether or not it has a particular usage.
Here's something that makes it easier to remember a primary partition: if you need the drive to be bootable, it must have a primary partition. Also, a hard disk requires at least one primary partition. Furthermore, you can create a primary partition using DiskPart.
Part 2. How Do You Find the Primary Partition?
You can locate the primary partition or the system partition in Disk Management. Follow the steps below:
Step 1. Click Start or press the Windows Key on your keyboard. Click Computer Management.
Step 2. Click Storage > Disk Management.

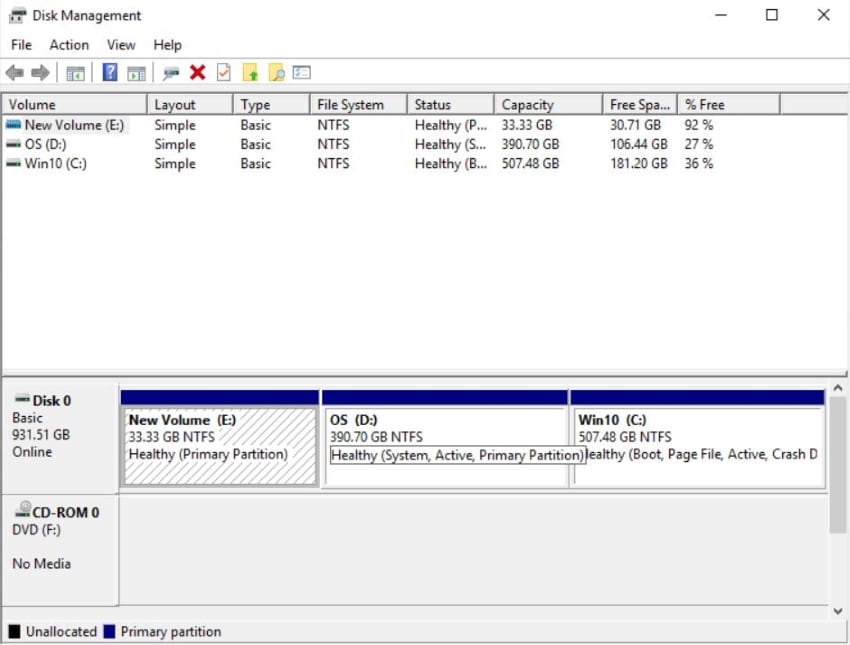
Step 3. You will see a table of drives or partitions on your computer. Click a drive from the table. Check the details and look for Primary Partition.
Part 3. Primary vs. Logical Partition: What’s the Difference?
As the three types of partitions are mentioned, there are also significant differences between primary and extended partitions. But in this section, we'll focus more on primary partition vs. logical partition.
The easiest identifier is whether the partition is bootable or not. If the answer is yes, it is a primary partition. And if the answer is no, it's probably a logical partition. Also, you can store both the operating system and data on a primary partition. Meanwhile, you can only use logical partitions for data storage.
That said, a primary partition is more critical than a logical partition. It is the partition that can be marked as active for BIOS to locate. A computer would not boot without a primary partition. And what is the sense of having a computer if you can't turn it on?
A disk drive can have different configurations. For example, you can set up four primary partitions, or three primary partitions and one extended partition. You can have as many logical partitions as you want in an MBR disk.
Furthermore, you can convert the logical partition to a primary partition. You can also convert the primary partition to a logical partition.
Partition Type |
Maximum Number |
Bootable |
Can it store data and OS? |
Structure |
| Primary Partition | 4 | Yes | Yes | Standalone, Self-contained |
| Logical Partition | Unlimited in MBR disks | No | Data only | Subdivision of an extended partition |
Part 4. Is It Okay to Delete the Primary Partition?
"Is it safe to delete system partition?" - Quora
If the primary partition in question is labeled as “Active,” it is not advisable to delete it. That is the system partition, and deleting it could compromise the proper working of your computer. It may also not boot anymore.
Suppose you want to delete a primary partition currently not in use. You can do that. Deleting the partition can free some space for your other programs. Or you can use that to extend another partition.
Before you proceed, you need to know a very important thing: deleting a partition also deletes all data stored on it. Therefore, you must first check the partition's content to see if anything valuable is stored there. Then, copy those files onto external drives or flash drives. Also, you can upload them to the files you want to save to the cloud. Once certain you need no data exclusively found in the partition, you can delete it.
Steps to Delete the Primary Partition
So, how do you delete a primary partition? You can use DiskPart to do so. Diskpart is a Windows built-in disk partitioning utility.
Follow the steps provided below. Please stick to these instructions, as doing something slightly different may produce other results. Worse, that could be undesirable results.
Step 1. Check the Numbers of the Primary Partition
Right-click the Windows icon on the bottom-left corner of the computer screen. Select Disk Management. Check the number of primary partitions on your target disk.
Step 2. Use DiskPart to Delete the Primary Partitions
Open the Command Prompt by clicking Start > searching for Command Prompt > Run as administrator. Then, type the following commands one by one. Remember to hit Enter after each line.
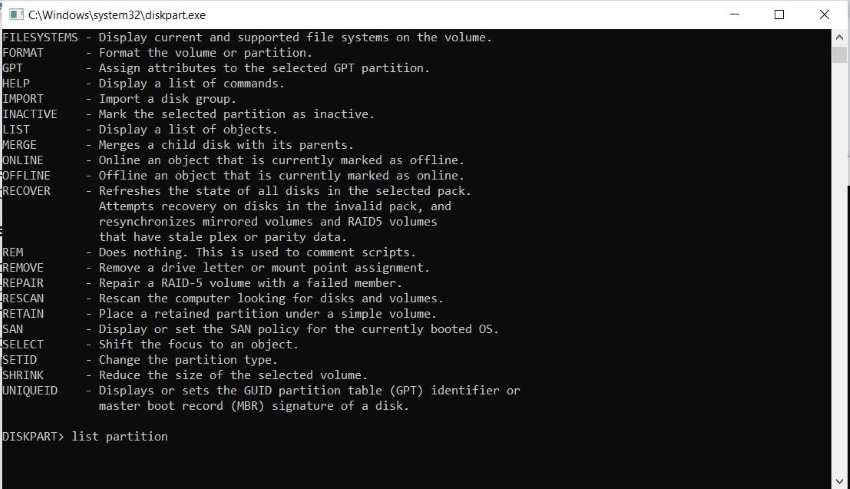
- diskpart
- list disk
- selected disk # (Replace “#” with the correct disk number)
- list partition
- select partition # (Replace “#” with the correct partition number)
- delete partition
Repeat the procedure until you've removed all primary partitions you want to delete. Finally, type exit to close DiskPart.
Part 5. How To Recover Deleted Primary Partitions?
What if you accidentally deleted a primary partition? That could be a nightmare. Fortunately, some tools allow you to restore the deleted or lost partition. One of the best choices is Wondershare Recoverit. Recoverit is a data recovery tool with a high success recovery rate. If you still doubt its ability, please know that this tool has over 35 data recovery patents.

Wondershare Recoverit – Leader in Data Recovery
5,481,435 people have downloaded it.
Efficiently handle various data loss scenarios, including lost partition, accidental deletion, formatting, virus attack, blue or black screen of death.
Ability to recover more than 1000 file types from almost any storage media, such as SSDs, HDDs, USB drives, SD cards, external hard disks, etc.
An intuitive interface that lets you preview the files before recovery. No payment is required if the files are unrecoverable.
How To Recover a Deleted Primary Partition Using Wondershare Recoverit
Wondershare Recoverit uses a simple three-step process for recovering lost partitions. Follow these simple steps:
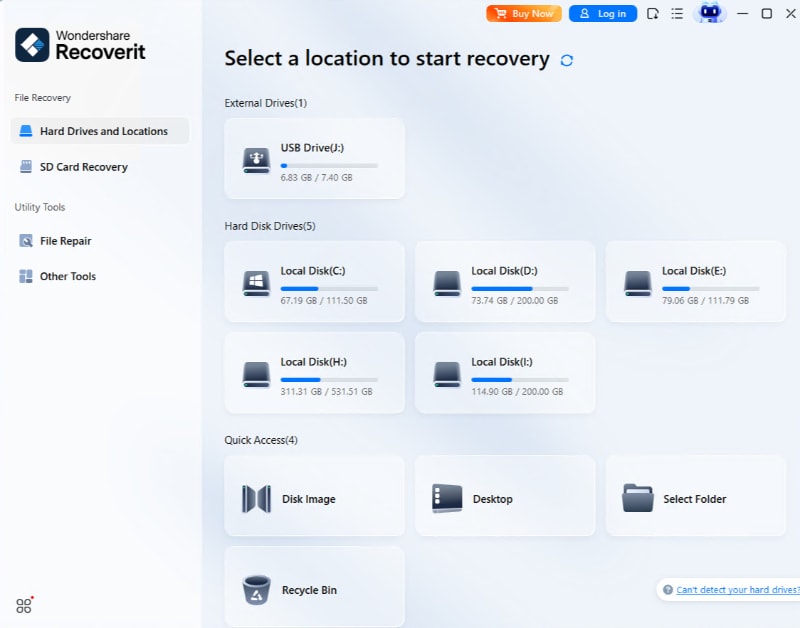
Step 1. Select the Lost Partition
Launch Wondershare Recoverit. Under Hard Drives and Locations, select Lost Partition.
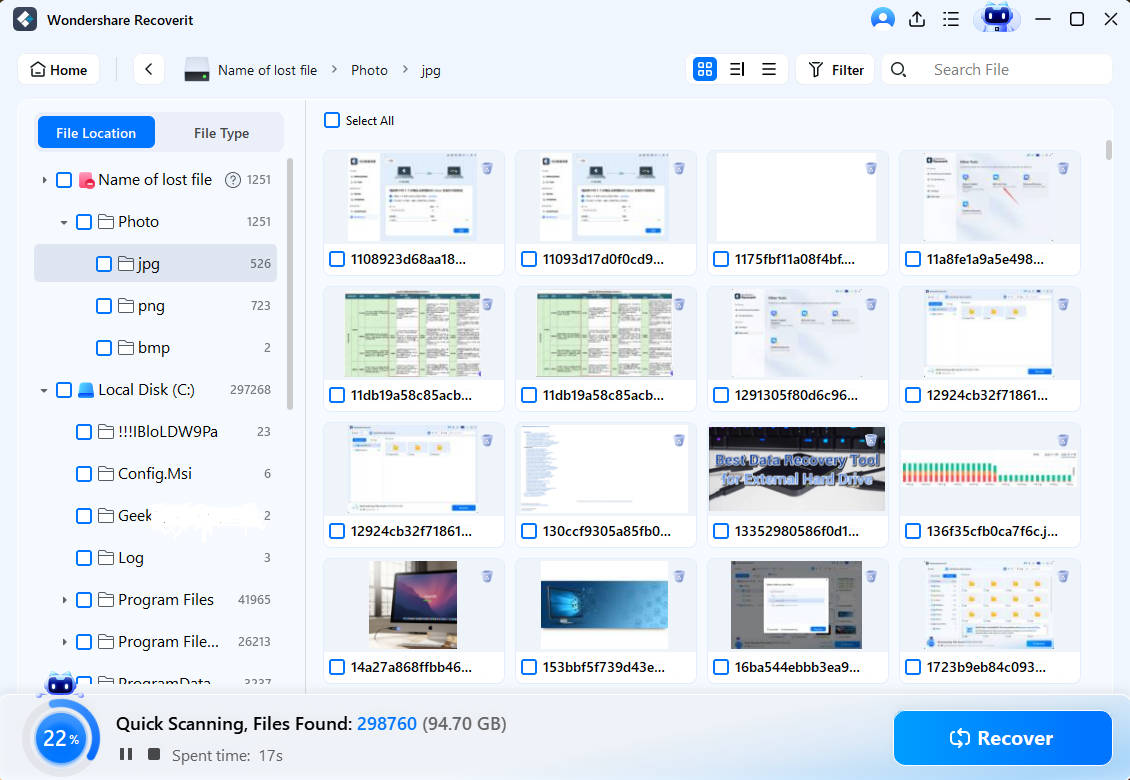
Step 2. Scan the Lost Partition
Recoverit will quickly scan the deleted or lost partition. Once the scanning is complete, you can check the recoverable files. You can use the Preview button to ensure they are the files you want.
Step 3: Restore the lost files
Click Recover to get your lost data back.
For Windows XP/Vista/7/8/10/11
For macOS X 10.10 or later
Summing Up
The main difference between primary and logical partitions is that the former is bootable. A disk drive can have a maximum of four of them. Meanwhile, a drive can have as many logical partitions as an MBR disk. But unlike primary partitions, they cannot store operating systems.
You can delete primary partitions, but you must be extra careful. If you accidentally delete an extended partition, you can use Wondershare Recoverit to recover your lost data.

 ChatGPT
ChatGPT
 Perplexity
Perplexity
 Google AI Mode
Google AI Mode
 Grok
Grok






















