A disk partition is a specific area of storage on a hard drive. Disk partitions can help users organize their data more effectively when storing classified data. Partitions are classified into three types: extended partition, primary partition, and logical partition.
When using disk partitions, we always consider the distinction among the three partitions, their respective functions, and whether you can convert them. This article will explain the extended partition and the difference between primary and extended partitions in the hopes of helping users better understand and apply them.
Part 1. What Is an Extended Partition?
An extended partition is a specific location where logical drives are stored. A hard drive can only hold one extended partition at a time. However, the extended partition could be divided into several logical partitions. The Extended Boot Record provides information about the extended partition's logical partitions and overall structure (EBR). Users’ data may be stored on an extended partition and are protected from corruption issues or when the operating system crashes.
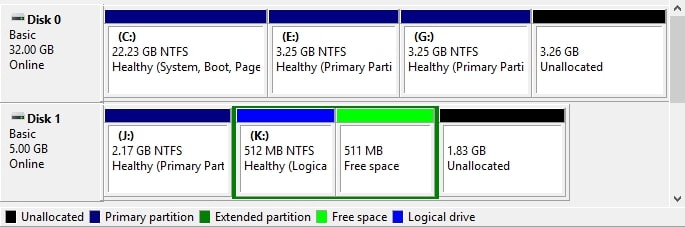
Part 2. Primary vs Extended Partition: What's the Difference
The primary partition is a bootable partition that consists of the computer's operating systems, whereas the extended partition is non-bootable. Extended partitions are used to store data and typically contain multiple logical partitions. Furthermore, a disk drive can include several primary partitions but only one extended partition.
See this table to assess its other differences.
Distinction |
Primary Partition |
Extended Partition |
| Total number | On a standard disk, you can create up to 4 primary partitions. | On a single disk, only 1 extended partition can exist. |
| Identification | Primary partitions are assigned the first letters of the alphabet (C & D). | The other letters are assigned to logical drives in the extended partition (E, F & G) |
| Uses | It configures multiple operating systems without interfering with each other. | Extended partitions don't directly store files but create logical partitions to store data. |
Part 3. Can I Delete Extended Partition?
Yes, you can delete an extended partition safely. It is because it is just an empty space on your drive and contains no logical partitions containing valuable data. It will become an unallocated space, which you can then format however you want.
You can delete your extended partitions using DiskPart and Disk Management. But before deleting an extended partition, you must first remove all the logical drives in that partition. Here are some scenarios that may necessitate the removal of an extended partition:
- Your system partition is running low on disk space. After using your new computer for a while, you may encounter a low disk space issue due to daily increased files, folders, photos, videos, etc.
- You fail to specify the size of the extended partition. When you create an extended partition for the first time, you may forget to specify its size, which will take up the entire unallocated space on your hard drive. It may confuse you, and you want to use a portion of the unallocated space for something other than saving personal files.
- The extended partition takes up a lot of space. Your new computer does not require partitioning. However, this is the source of incorrect disk space distribution. After a while, you may receive a message indicating that your C: drive is full, but some partitions still have a lot of space.
Part 4. How To Delete Extended Partition
You can follow the steps to delete an extended partition using Disk Management and DiskPart.
Delete Extended Partition Using Disk Management
Some users may use Disk Management. However, you can only delete the extended partition at a time because you can only select one logical partition. As a result, you must first delete all logical partitions before deleting the extended partition.
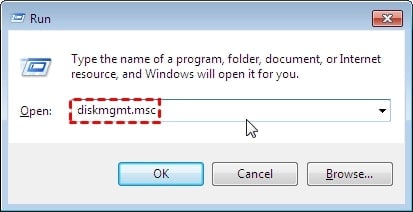
Step 1. To open Disk Management, press Windows + R on the desktop and type diskmgmt.msc.
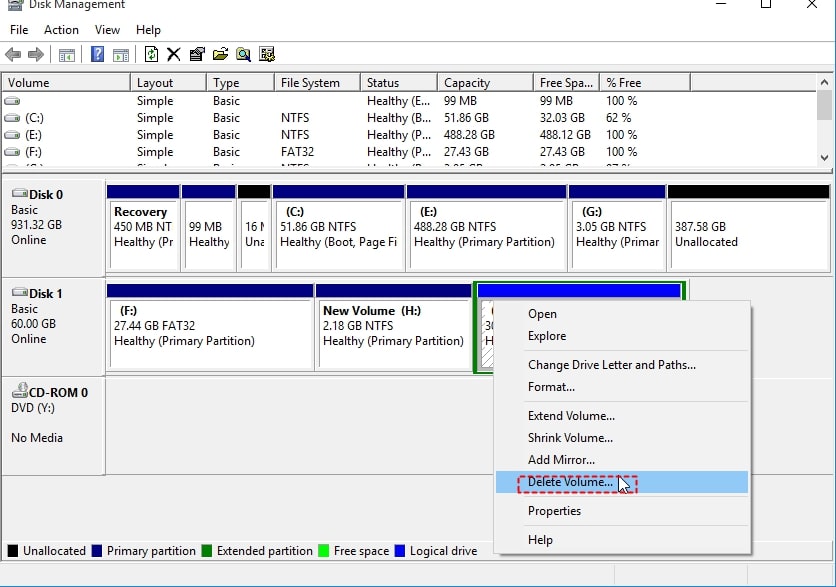
Step 2. Right-click the logical partition and select Delete Volume. You should repeat the steps to delete the remaining logical and extended partition. Finally, an unallocated space will be assigned to you.
You can also use it to expand any partition you want. You will know when you successfully deleted the extended partition when you got the unallocated space. However, you can only extend primary partitions in Disk Management by using unallocated space on the right side.
Remove Extended Partition by DiskPart
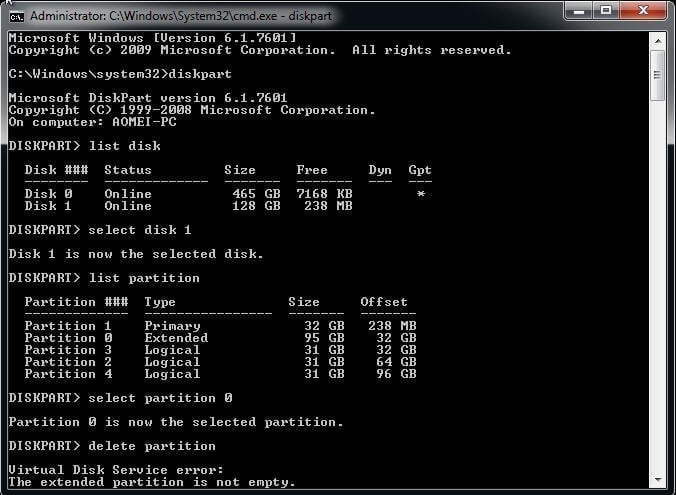
When you remove an extended partition with DiskPart, you may receive a message such as "virtual disk service error the extended partition is not empty." Because you have already created one or more logical partitions within the extended partition, you cannot erase it directly. The extended partition is directly divided by a disk and cannot be used unless it contains only one logical partition.
To resolve this, you must first delete all logical partitions. Then, you can delete the extended partition.
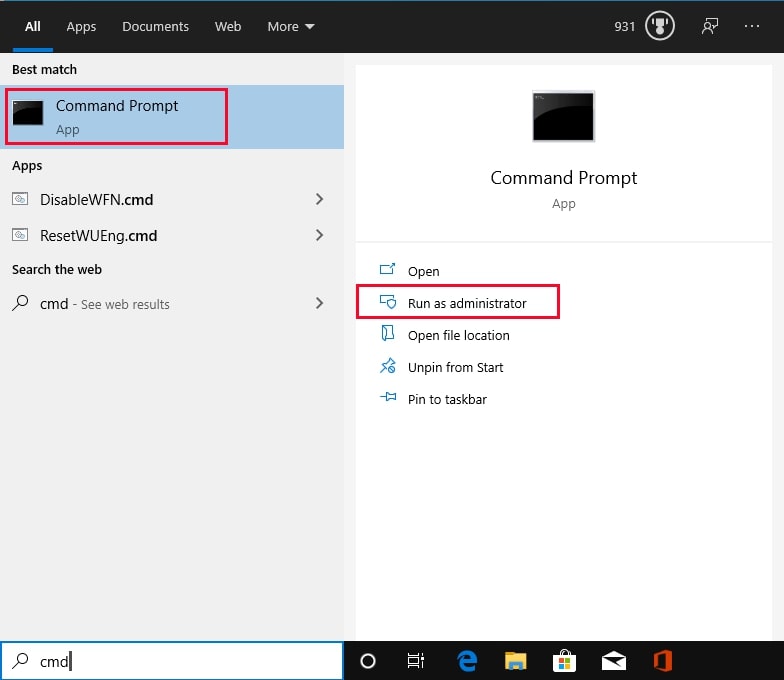
Step 1. Search for cmd and Run as administrator.
Step 2. Type the following commands and press Enter after each one.
- diskpart
- list disk
- select disk n
- list partition
- select partition m
- delete partition
Select and delete the partitions repeatedly to delete the remaining logical and extended partitions.
Part 5. How To Recover Deleted Extended Partition?
When deleting the extended partition, all of the data on your drive will be erased. It is strongly advised to back up partition data ahead of time. However, many people still fail to back up their partitions and suffer data loss.
But don't be concerned. One of the well-known software for creative recovery is Wondershare Recoverit. It has robust features that can help you retrieve your deleted extended partition data in a few minutes.

Wondershare Recoverit – Leader in Data Recovery
5,481,435 people have downloaded it.
Ability to recover more than 1000 file types from almost any storage media, such as SSDs, HDDs, USB drives, NAS Servers, SD cards, etc.
Efficiently handle various data loss scenarios, including accidental deletion, lost partition, formatting, virus attack, and computer crash.
An intuitive interface that lets you preview the files before recovery. No data, no payment.
Recover Deleted Extended Partition With Wondershare Recoverit
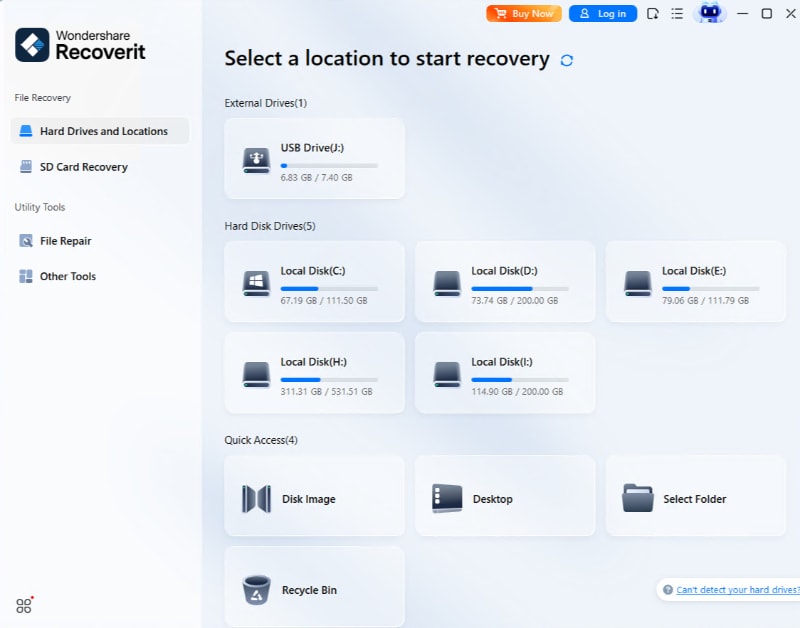
Step 1. Choose Lost Partition
Open Wondershare Recoverit. Under Hard Drives and Location, choose Lost Partition.
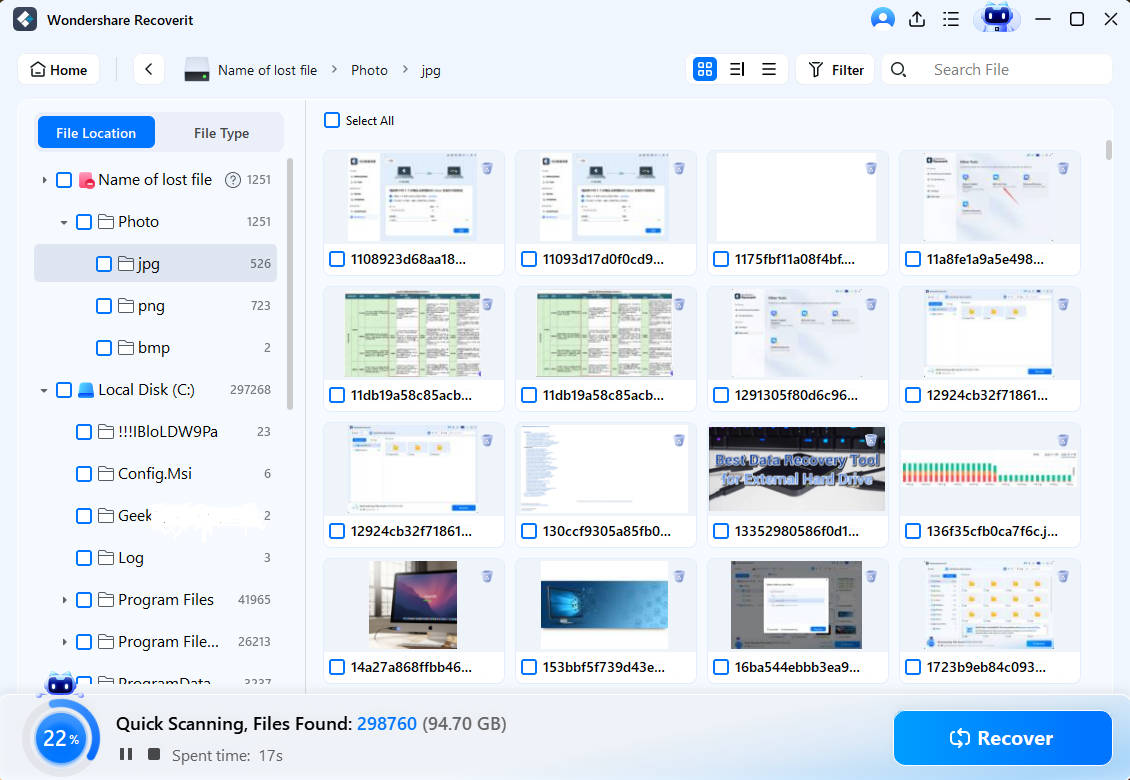
Step 2. Scan the Lost Partition
Recoverit will quickly scan the data in the deleted or lost partition. When the scan is finished, you can go through all recoverable files. Then, click Preview to make sure they are the files you want.
For Windows XP/Vista/7/8/10/11
For macOS X 10.10 or later
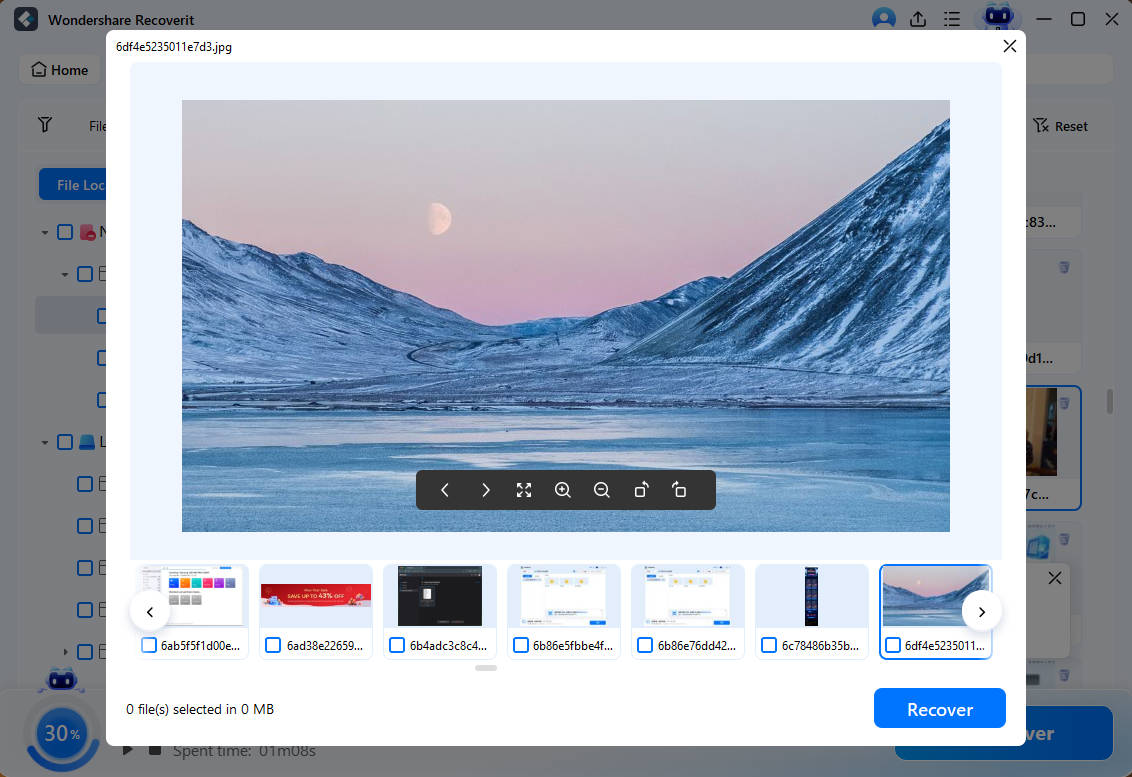
Step 3. Lost Partition Preview and Recovery
Following the deep scan, you can review the list of recoverable files on the left panel. You can preview recoverable files and select your data. Click Recover to get them back.
Conclusion
After reading this article, I hope you learn about the differences between primary and extended partitions. Also, deleting the extended partitions mentioned may help you do what you must do. If you need to recover essential data after deleting the extended partition, download Wondershare Recoverit to help you with recovery issues.

 ChatGPT
ChatGPT
 Perplexity
Perplexity
 Google AI Mode
Google AI Mode
 Grok
Grok






















