Are you struggling to reinstall the operating system or fix critical disk errors because your computer won't boot? You can leverage MacOS Internet Recovery to save the day, whether you are using a MacBook Pro, MacBook Air, or an iMac. This powerful feature allows you to restore your Mac directly from Apple’s servers, bypassing the need for a local recovery partition.
Before we dive into the step-by-step guide on how to start a Mac in Internet Recovery Mode, let's walk through how this built-in system works. Understanding the mechanics of MacOS Internet Recovery will help you troubleshoot effectively, manage distinct steps for Intel-based versus Apple Silicon chips, and maximize your chances of a successful restoration.
Table of Content
What Is Internet Recovery Mode on a Mac?
MacOS Internet Recovery has been around since 2011—when Apple launched Mac OS X 10.7 (Lion). It underwent two name changes to reflect Apple's branding, matching the shortened OS X version in 2012 and macOS in 2016.

Initially named Mac OS X Internet Recovery, this built-in system lets you troubleshoot problems online and restore data from the cloud. Does it offer the same features as its standard counterpart? It does; the only difference is you need an internet connection to access MacBook Internet Recovery Mode.
Here's what you can do when accessing macOS Recovery from the internet.
What You Can Do in Mac Internet Recovery Mode?

Internet Recovery Mode on Mac computers offers the following features for Intel-based processors:
- Restoring system files from a Time Machine backup
- Reinstalling macOS
- Getting help online from Apple Support documentation
- Using Disk Utility to repair or erase disks
- Modify settings in Terminal
- Setting a secure boot and firmware password
- Setting the startup disk
Users with an Apple silicon Mac can also share the startup disk, seamlessly transferring files between Mac computers.
Whether you wish to reinstall macOS from Internet Recovery or use another feature, you must meet specific network requirements. Here's what they are.
Network Considerations When Accessing Internet Recovery Mode on a Mac

Before starting MacBook Pro Internet Recovery (the device doesn't matter), check your network configuration to ensure you can access the desired utilities.
The following security mechanisms, protocols, and networks will prevent you from accessing Internet Recovery on macOS:
- WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy)
- WPA-Enterprise
- Public Wi-Fi
- PPPoE (Point-to-Point Protocol over Ethernet) without a router
- Networks requiring proxies
As for reinstalling macOS with Internet Recovery, you must ensure your network uses the DHCP (Dynamic Host Communication Protocol) whether you use an Ethernet or Wi-Fi connection. If you connect via Wi-Fi, set the WPA (Wi-Fi Protected Access) or WPA2 security protocol.
Once everything is in order, follow the steps below to start your Mac in Internet Recovery Mode.
How To Start Internet Recovery on Apple Silicon macOS
Internet Recovery for Mac M1 and M2 chips using Apple silicon offers the same features as its Intel-based counterpart. The only difference is how you access it.
Here's a step-by-step guide on starting Internet Recovery for Mac M1 (Pro, Max, and Ultra) and its M2 equivalent:
- Go to the Apple menu and shut down your Mac to boot into Internet Recovery.

- Long-press the Power or Touch ID button until you see the loading startup screen. Click Options > Continue.

- Select the desired disk, click Next, log into your admin account (if necessary), and hit Continue to enter Internet Recovery Mode.
- Choose a macOS utility from the available options, click Continue, and follow the on-screen instructions.

As you may have noticed, the process is identical to accessing standard macOS Recovery. Apple streamlined it on Apple silicon computers.
How To Start Internet Recovery on an Intel-Based Mac
Starting Internet Recovery on a Mac with an Intel-based processor is slightly different. Here's what to do:
- Restart your Mac computer.
- Once it starts powering on, long-press the Option + Command + R or Option + Shift + Command + R keys to access macOS Internet Recovery. The former keyboard shortcut lets you upgrade your macOS to the latest compatible version, while the latter limits you to your computer's original OS or its closest available edition.

- Release the keys once you see a black screen with a spinning globe and this text: "Starting Internet Recovery. This may take a while."

- Your Mac will ask you to choose a network if you've connected via Wi-Fi. You might also need to provide your Mac password.

- Once your computer connects to the internet, you'll see your macOS starting Internet Recovery.

- Pick the desired macOS utility once the following screen appears, click Continue, and follow the on-screen instructions.

What To Do if Your Mac Won't Access Internet Recovery Mode
Here's what to do if you can't enter Internet Recovery Mode on your Mac.
- Check your macOS version - Mac OS X Snow Leopard and older editions don't have the Recovery partition.
- Troubleshoot your keyboard - Connect it to another computer to check if it works.
- Check your internet connection and network configuration - Don't use public Wi-Fi. Use the DHCP and set the WPA or WPA2 for Wi-Fi. Switch to an Ethernet connection to see if your Wi-Fi is causing the problem.
- Try Fallback Recovery Mode (Apple silicon) - Shut down your Mac, double-press the Power or Touch ID button, and release it once you see the loading startup screen. The subsequent steps are identical to accessing the standard Recovery Mode on Mac. The only difference is you'll boot your Mac from the fallback recoveryOS instead of the primary Recovery partition.
- Reset the NVRAM or PRAM (Intel-based processors) - Turn off your Mac, hit the Power button, and immediately long-press Command + Option + P + R. Release the keys after your computer reboots twice.
If you still can't boot your Mac in Internet Recovery, disk corruption might be at play. A professional repair service can help you diagnose and resolve the problem, but we highly recommend recovering data beforehand. Here's how.
Bonus Advice: How To Recover Data if Your Mac Can't Access Internet Recovery Mode
In situations where you can't start your Mac in Internet Recovery Mode, you may be faced with a corrupted or damaged startup disk, a missing or damaged recovery partition, or other hardware and software issues that prevent normal access to your important data. This can be a significant concern, especially if you have crucial files and documents stored on your Mac.
In such cases, it's essential to have a reliable data recovery solution to retrieve files. Recoverit data recovery for Mac is among the leading solutions for salvaging data from corrupted, malware-infected, or inaccessible drives.
Here's a video tutorial that demonstrates how to recover data from your Mac when it's unable to boot.
If your Mac is still functional and you've only lost some important data due to software-related issues, the data recovery process is simpler:
- Download, install, and launch Recoverit for Mac computers.
- Click on Hard Drives and Locations and select the drive where you lost your files.
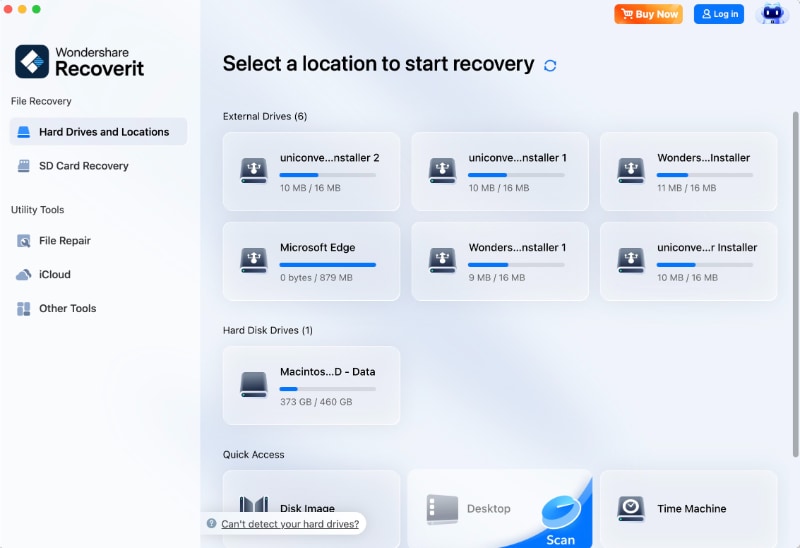
- Let the program scan for lost files. Leverage the search bar and filters like type, size, tag, modification time, and status for faster data retrieval. You can pause or stop the process anytime.

- Preview the retrievable images, videos, documents, presentations, emails, audio files, and other data, choose what to restore (or click Select All), and hit Recover.
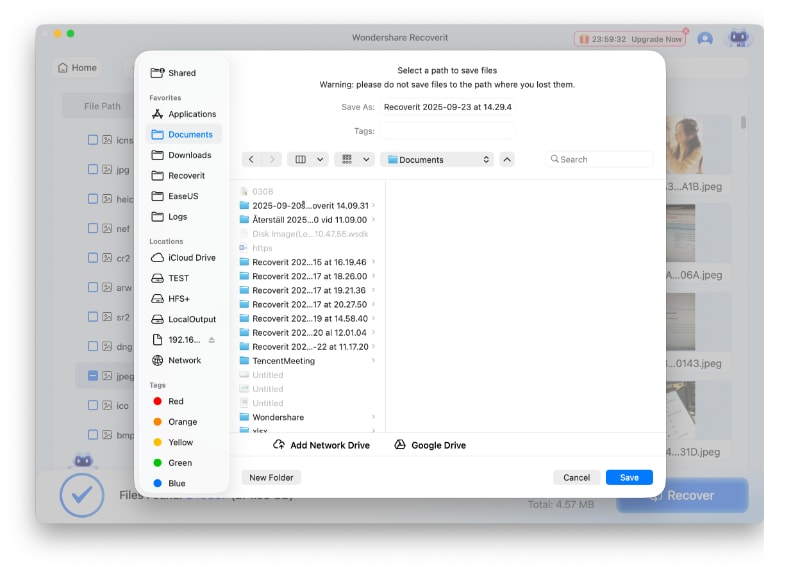
- Set the preferred destination (preferably different from the original path) and click Save.
Easily recover deleted or lost files from 2000+ storage devices like HDDs, SSDs, external drivs, USB drives, memory cards, and more. The software confidently retrieves all data types, regardless of how they went missing.
Conclusion
Internet Recovery Mode is an excellent macOS feature for restoring backed-up system files, modifying various settings and security policies, eliminating disk errors, and reinstalling macOS.
However, it has specific network requirements, so check them beforehand to ensure you can access it. If a problem like disk corruption prevents you from accessing macOS Internet Recovery, use trusted software like Wondershare Recoverit to retrieve files to a safe location.
FAQ
-
What should I do if MacOS Internet Recovery is not working?
If MacOS Internet Recovery fails, it often indicates a network connection failure. Try connecting your Mac directly to the router via an Ethernet cable or restart your modem to ensure a stable signal before retrying the recovery process. -
Does Internet Recovery erase my data?
Simply entering the mode does not delete files, but selecting "Reinstall macOS" or using Disk Utility to erase a drive will. Always perform a backup if possible to avoid data loss during the Mac network recovery process to fix system corruption. -
How do I start Internet Recovery on an Apple Silicon Mac?
Shut down your Mac, then press and hold the power button until "Loading startup options" appears. Click "Options" to access MacOS Internet Recovery. This differs from Intel models and is essential for fixing Mac boot issues. -
Can I use Internet Recovery without Wi-Fi?
No, MacOS Internet Recovery requires a live internet connection to download the system image from Apple's servers. If Wi-Fi is unavailable due to computer network faults, use a wired Ethernet connection to proceed with the restoration.

![How To Start a Mac in Internet Recovery Mode [2026]](https://images.wondershare.com/recoverit/article/how-to-start-mac-in-internet-recovery-mode-1.jpg)

 ChatGPT
ChatGPT
 Perplexity
Perplexity
 Google AI Mode
Google AI Mode
 Grok
Grok






















