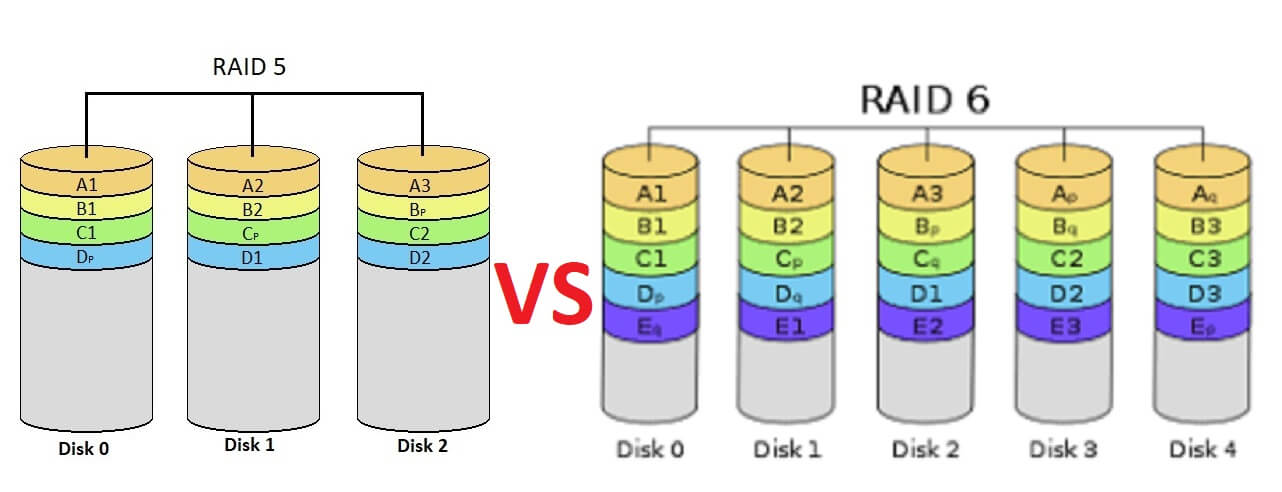
People often ask, what is RAID 5 and what is RAID 6? RAID stands for Redundant Array of Independent Disks. There are different levels of RAID, but the most popular are RAID 5 and RAID 6.
The primary difference between RAID 5 and RAID 6 is that a RAID 5 array can keep working after a single disk failure, but a RAID 6 array can continue to function despite losing two disks. RAID 6 arrays are also less prone to faults during the RAID rebuilding process.
Part 1. RAID 5 vs RAID 6 – The Comparison Chart
Here we will discuss the key differences between RAID 5 and RAID 6, as both RAID 5 and RAID 6 are data storage technologies that provide better security and performance by storing data across multiple disks.
Feature |
RAID 5 |
RAID 6 |
| Minimum Drives | 3 | 4 |
| Maximum drives | 32 | 32 |
| Software/Hardware RAID configuration | Both | Hardware only |
| Parity | Single | Double |
| Fault tolerance | Single-Drive Failure | Two-Drive Failure |
| Read Performance | Fast | Fast |
| Write Performance | Slow | Slower |
| Capacity Utilization | 67% to 94% | 50% to 88% |
| Common Applications | Data warehouses, web servers | Data Archives, backup disk, large capacity servers |
| Cost Analysis | Cheaper Than RAID 6 | Can be costly |
| Storage Ability | Stores limited information | Stores more data partial information |
Part 2. RAID 5 vs RAID 6: How They Work Compared
In a RAID 5 configuration, data is distributed across all of the drives in the array. This means that if one drive fails, the data is still accessible from the other drives. To ensure data integrity, parity information is also stored on each drive. This parity information allows the data to be reconstructed if a drive fails.

RAID 5 is a new RAID type that employs the RAID parity concept. This method uses parity data or bonus data to reconstruct any lost information. But if two of the drives are damaged or lost data, you won't be able to retrieve it through parity reconstruction. Learn more about RAID 5 Data Recovery.
RAID 6 employs two parity stripes across each disk, in contrast to RAID 5's single stripe per disk. In that way, RADI 6 allows for two disk failures within the RAID set before any data is lost.

Part 3. Difference between RAID 5 and RAID 6 in Features
Disk Requirement and Storage Capacity
When choosing between RAID 5 and RAID 6, one of the critical considerations is the number of disks required for each level of protection. With RAID 5, you need a minimum of three disks to implement the system. On the other hand, to create a RAID 6 array, you need at least four disks.
Software and Hardware RAID Configuration
Another important difference between RAID 5 and RAID 6 is how each level can be configured. RAID 5 requires special software or a hardware controller in order to function, whereas RAID 6 can be configured using standard hardware RAID controllers.
Cost of Implementation
When comparing the cost of implementation, RAID 5 is generally cheaper than RAID 6 because RAID 5 only requires a minimum of three disks, while RAID 6 needs four disks.
Read and Write Performance
RAID 5 offers excellent read and write performance. In contrast, due to the added parity information, RAID 6 does have a slightly lower write performance than RAID 5.
Real-world Applications
Both RAID 5 and RAID 6 are commonly used in enterprise storage systems. However, due to its lower cost and higher performance, RAID 5 is more famous for general-purpose storage applications.
RAID 5 is also a good choice for applications that require high availability, such as database servers because RAID 5 offers excellent read performance and can tolerate the failure of a single disk without data loss.
RAID 6, on the other hand, is typically used in applications where data integrity is critical, such as financial databases.
Recovery Ability from Failure
RAID 5 and RAID 6 both offer good recovery ability from disk failures. However, due to the extra parity information, RAID 6 is able to recover from two disk failures, while RAID 5 can only recover from one.
Rebuild Time
The array must be rebuilt when a disk fails in a RAID 5 or RAID 6 array. However, the rebuilding time for a RAID 5 array is typically shorter than that of a RAID 6 array due to the extra parity information that must be processed.
Part 4. RAID 5 vs RAID 6: Which One Should You Choose
The advantages & disadvantages of RAID 5 and RAID 6 are summarized below.
Advantages and Disadvantages - RAID 5
Pros
When a disk fails, the IOA automatically reassembles the missing data.
A failed disk unit can be removed without turning off the computer.
The server keeps running even after a single disk failure.
Compared to RAID 6 levels, RAID 5 is more cost-effective.
Efficient and fast data storage and access.
Cons
The read and write speeds are lower than those of single drives.
Single disk data storage is limited.
Advantages and Disadvantages - RAID 6
Pros
RAID 6 is more fault-tolerant.
Best to keep data for a long period of time.
High-capacity storage solution.
Disc capacity increases by adding a RAID 6 array.
Use only 25% of disk capacity.
Cons
A RAID 6 data striping array is formed by utilizing two pairs of parity bits for each parity set, which reduces write performance.
Expensive because of the extra disks.
Ultimately, the choice depends on various factors, such as data protection requirements, cost, performance, and capacity.
Regarding data protection, RAID 6 offers a higher level of protection than RAID 5. This is because RAID 6 uses a dual parity scheme, which means that two disks can fail before data is lost.
This makes RAID 6 more suitable for mission-critical applications where data availability is paramount.
Regarding cost, RAID 5 is typically cheaper than RAID 6 as it requires one less disk. However, the increased protection offered by RAID 6 may be worth the extra cost for some organizations.
In terms of performance, RAID 5 generally offers better performance than RAID 6 as it has a lower overhead. However, the increased protection offered by RAID 6 may come at the expense of some performance.
In terms of capacity, RAID 6 typically offers more capacity than RAID 5 as it uses less disk space for parity. However, the increased protection offered by RAID 6 may result in lower overall capacity.
Part 5. How to Convert RAID 5 to RAID 6
If you want more fault-tolerant or higher storage space, you can change the RAID 5 to RAID 6 on Windows PC and servers using storage manager. Here’s how you can do it with Synology.
- Open your Synology Storage Manager and go to "Storage Pool" to identify the drives and selection.

- Go to the “Action” menu from the top list and select the “RAID” type. It will open another window.

- As you can see, RAID 5 is already selected, meaning the drives are RAID 5. Now tick the RAID 6 and press next.

- Now it will confirm by showing you the list of selected drives. If there is any extra drive, you can repeat the process after deselecting it.

- Then press next and again confirm the details.

- Wait until it saves the changes and convert RAID 5 to RAID 6. After converting, confirm the type from the disk storage.

FAQ
Why is RAID 5 not recommended?
Due to several issues, including longer rebuilding time, half capacity availability during the rebuild, write hole and write performance, it is not recommended to use RAID 5.
Does RAID 6 rebuild faster than RAID 5?
No, RAID 6 does not rebuild faster than RAID 5. It is typically slower due to the additional parity information that must be written. However, the tradeoff is that RAID 6 can continue to operate even if two drives fail, whereas RAID 5 stops working.
Should you use RAID 6?
If you have work that needs high availability, like servers and customer data services, then the RAID 6 is the best choice for you. However, avoid RAID 6 for your personal small setup as it may cause performance issues.
How much space do you lose with RAID 6?
It takes about two disk spaces as it makes an extra protection layer. So, if you have four 1TB drives in your array, your total storage space would be 2TB. So no matter what is your entire disk space it always takes two disks.
Does RAID 5 slow down performance?
In the case of hardware RAID 5, it won't decrease your performance as it will provide some extra space. However, if one of the disks in the RAID 5 array fails, then the performance will be impacted as the data is reconstructed on a new disk.
Conclusion
RAID stands for Redundant Array of Independent Disks, a way to protect your data using multiple disks. The most popular types of RAID are 5 and 6. RAID 5 protects your data by striping the data across multiple disks, while RAID 6 does the same thing plus parity checks, which means that if one disk fails, you can still recover your data.

 ChatGPT
ChatGPT
 Perplexity
Perplexity
 Google AI Mode
Google AI Mode
 Grok
Grok






















