In the world of high-quality audio experiences, where audiophiles and cinephiles seek pristine sound enjoyment, purchasing top-rated media playback devices doesn't cut it. Reaching the heights of auditory experiences also involves proper device setup, and that's where audio formats play a pivotal role.
For example, choosing between PCM and RAW audio outputs is crucial and can massively impact the quality of your high-tech device's sound.
That's why today's guide will delve deep into the differences between these two sound outputs, examining how PCM and RAW work and where they're used the most and helping you choose which one to use for your specific audio needs.
In this article
PCM Audio Explained
Before we can show you the differences between PCM and RAW, we must first elaborate on how these audio formats function.
PCM, which stands for Pulse Code Modulation, is a conventional method for digitally representing analog audio signals. This analog-to-digital audio converter takes samples of analog signals, quantizes them, and creates a digital form of the perceived analog audio.

Common Uses of PCM Audio Format
PCM is often used in long-distance communication due to its high transmission efficiency and noise immunity. It's the default digital audio form in computers, CDs, and smartphones and has countless other digital audio applications.
RAW Audio Format Explained
The RAW file format isn't connected to just audio files. Instead, it's also a format for other data types like images and represents files that have been unaltered and uncompressed. This section will focus solely on RAW audio format, sometimes called bitstream.
Unlike PCM, the RAW file format doesn't compress the audio file. The original audio signal remains unprocessed, retaining its original quality, as no additional encoding and compression algorithms are employed by the RAW audio format.

Additional Processing and Lack of Compression in RAW
Due to how RAW audio format works, these files store audio in its purest form, and RAW audio is known for its unaltered, uncompressed, and high sound quality. There's no quantization or compression like with PCM, and audio signals are represented as sequential sample values, making such files perfect for any post-processing application.
When and Why Is RAW Used
Audio professionals and sound purists prefer RAW audio due to its preservation of original sound quality. The RAW format is often used in professional audio editing and numerous other scenarios requiring top-notch sound quality. Archiving sound is a prime example of an application where audio enthusiasts will use the RAW format.
Quick Check: RAW vs PCM
Now that we know more about PCM and RAW audio formats, we can look into their differentiating factors to help you choose. Below is a table comparing PCM's and RAW's compression, sound quality, and file size, outlining their fundamental differences.
| Audio Format | PCM | RAW (Bitstream) |
| Compression | PCM applies compression algorithms that slightly impact audio quality and file size | The RAW audio format doesn't use any compression algorithms |
| Audio Quality | High audio quality with some losses due to compression | Files retain original audio quality, and it's higher than PCM |
| Transfer Method | PCM audio signal must be transferred over a wire | It can work both wired and wirelessly |
| File Size | Small file size thanks to PCM's compression algorithms | Larger file size than PCM, as there's no compression |
| Decoding | Decoded by the receiver | Decoded by the player |
While PCM is an excellent audio format used in computers, smartphones, and other long-distance digital audio applications, RAW audio is often a better choice for audiophiles and enthusiasts looking for pure sound, thanks to its unaltered and uncompressed approach.
Differences in Details: Audio RAW vs PCM
The differences in compression, audio quality, and file size between PCM and RAW audio formats are only a part of the puzzle. These two digital formats also differ in other aspects, and this section will cover their differences in detail.

Compatibility and Conversion
On the one hand, you have PCM, a widely adopted audio standard used in computers, CDs, DVDs, smartphones, TVs, etc. As such, PCM is highly compatible across various audio playback platforms, but it still offers effortless conversions to other audio formats without significant audio quality losses.
Conversely, many audio playback devices don't support RAW audio files, resulting in limited compatibility. Consequently, RAW files will likely need to be converted to different audio formats to be enjoyed on typical playback devices.
Compression and File Size
PCM applies various compression algorithms to reduce the file size of audio files. Conversely, RAW audio files don't use any compression algorithms, and this format always creates larger audio files, which might not be ideal for users trying to be efficient with their storage space and store a lot of audio files on a particular device.

Sample Rate and Bit Depth
Regarding sample rates and bit depth, PCM offers excellent flexibility, as these two elements can be adjusted to your audio requirements. However, maintaining the characteristics of the original analog audio can be challenging and will likely involve some compromises during settings adjustments.
In comparison, the RAW audio format preserves the original analog audio signal's sample rate and bit depth, providing an exact digital representation of the analog audio.
Audio Quality and Fidelity
While the quality of PCM audio files isn't bad, the fact that there's compression means this format's fidelity will be lacking compared to RAW files. However, it's worth noting that today's advanced compression algorithms minimally affect PCM audio quality.

Bonus: How to Recover Deleted/Lost Audio Files
Trying out different sound configurations, copying and pasting your audio files to various storage devices, and converting audio formats are all instances that can negatively affect your audio file's quality or even lead to data loss.
While such experiences can be disheartening, these files are recoverable in most cases, and such actions are surprisingly effortless with today's advanced professional data recovery apps.
Among these, Wondershare Recoverit is a prime example of such an application, as this data recovery app supports 500+ data loss situations like accidental deletion, formatting, interrupted file transfers, system crashes, corruption, viruses, etc.
Using Wondershare Recoverit is remarkably easy, as the app's beginner-friendly user interface is effortless to navigate. We've included comprehensive step-by-step instructions with pictures, so here's what you'll need to do to recover deleted or lost audio with this app:
- Open the app on your computer, tap the Hard Drives and Locations option on the left sidebar, and select a disk drive whose files you want to scan.
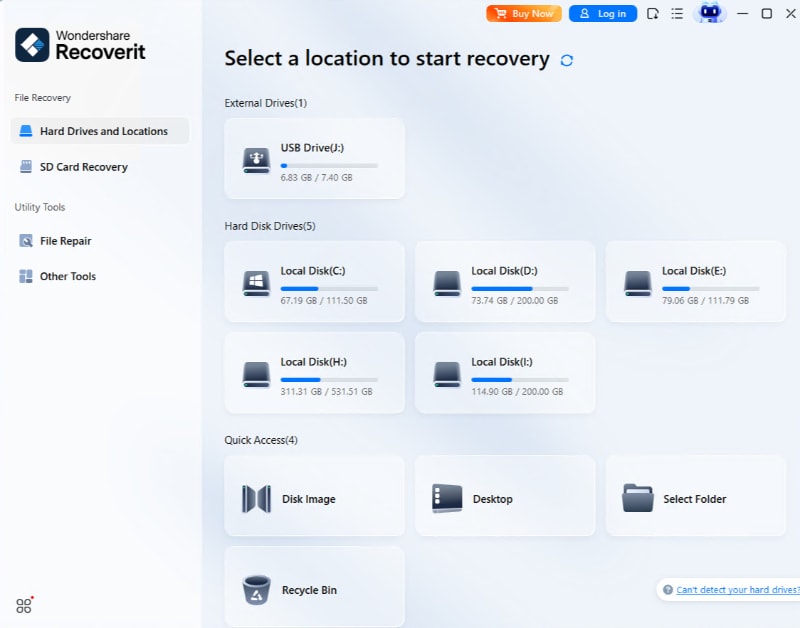
Alternatively, you can navigate your folders in Windows File Explorer, right-click a specific folder, and tap the "Scan for deleted files with Recoverit" option.
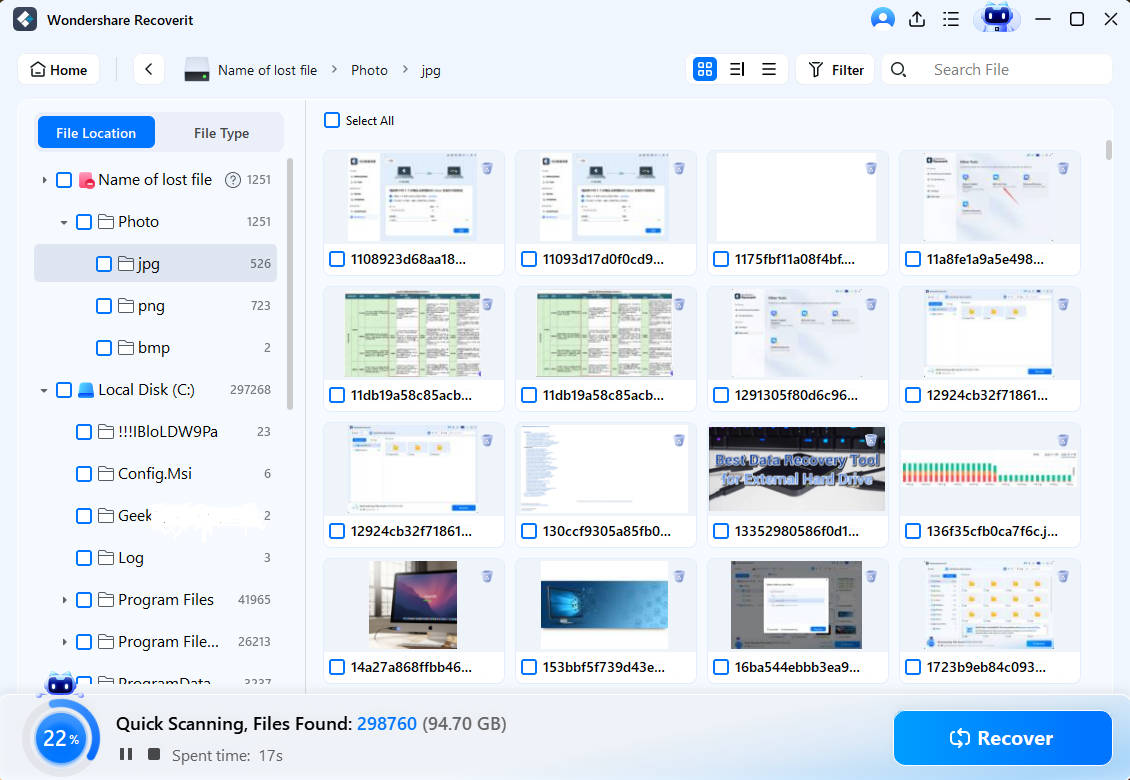
- The app automatically begins a deep scan of the selected folder or disk drive.
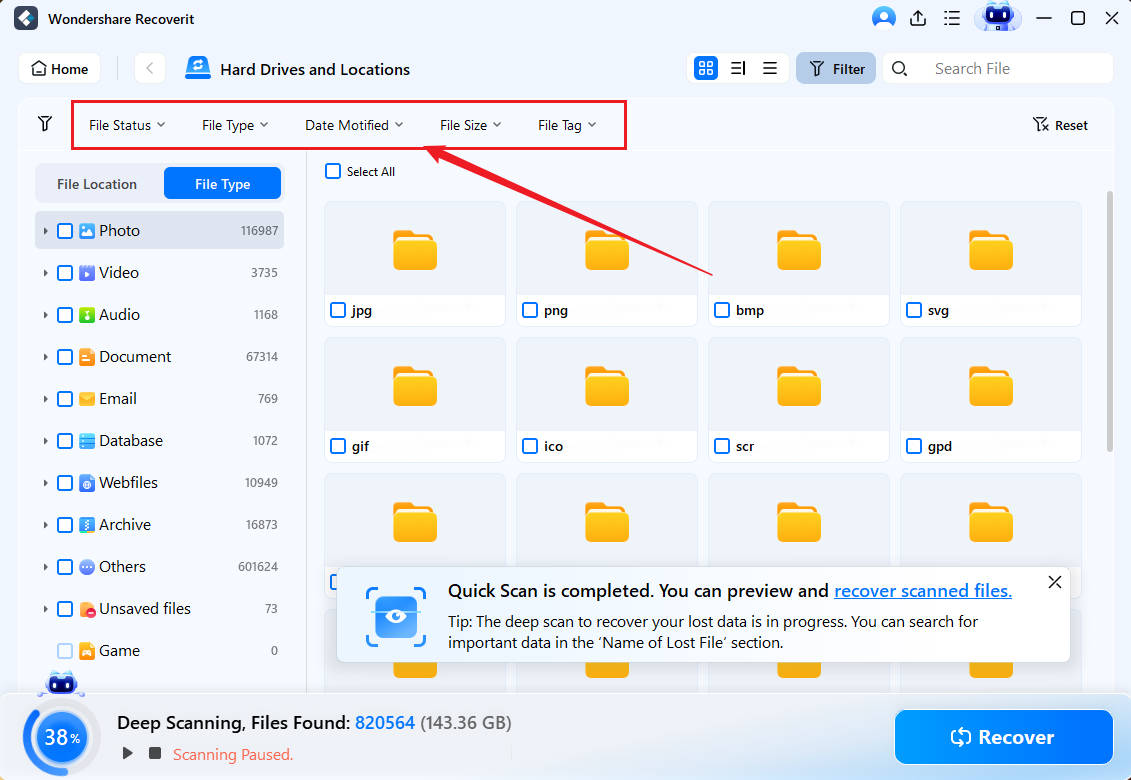
- You can modify various file filters to point the app's deep scan in the right direction.
- You can also use keywords to search for specific audio files.
- You can then preview the found audio files to verify their integrity before restoring them. If you're satisfied, you can immediately tap Recover.
- Once the app's scan finishes, you can select the audio items you were looking for and hit Recover to save them to your computer. Alternatively, you can pause or stop the scan at any moment if the app has already found the files you're looking for.
In just a few simple steps, your lost or deleted audio files will be restored to your computer, and you can enjoy your favorite music, podcasts, and recordings again.
Conclusion
Achieving a pristine sound experience requires setting up your playback devices and choosing between two widely used audio formats – PCM and RAW.
PCM is a method of digitally representing analog audio samples by converting their waveform into binary codes and applying compression. This conversion results in a highly compatible, decent audio quality and small file size format that works great on computers, smartphones, CDs, etc.
In contrast, RAW is a format that takes an unaltered and uncompressed approach, often resulting in higher file size and better sample rates, which makes RAW files the preferred format in digital audio applications where the highest fidelity is vital.
Experimenting with these audio formats and converting files can help you find a suitable format. However, it can also lead to data loss and file corruption, in which case, you'll need a professional data recovery tool like Wondershare Recoverit.
FAQ
Should digital audio out be set to PCM?
Setting digital audio out to PCM is only recommended if your external sound system isn't Dolby-compatible, which is often the case with older audio receivers. While Dolby Digital is derived from PCM, it's typically a better option than PCM and should be selected whenever you have the choice.What are SPDIF/RAW and SPDIF/PCM modes?
SPDIF stands for Sony/Philips Digital Interconnect Format and is a cable that transmits audio. In SPDIF/RAW mode, this cable goes from a TV or a DVD player into an audio receiver, transmitting unaltered or raw audio and letting the receiver decode it.Should I set my TV to PCM or RAW?
Choosing between PCM and RAW on a TV depends on your speakers. If your TV is the only sound source, or you have a soundbar or a stereo system, PCM is an excellent option and will provide fantastic audio quality. Still, you should remember that PCM only provides stereo audio when used over a coaxial or a digital optical cable, and it's not recommended for audio devices that support advanced audio formats.



 ChatGPT
ChatGPT
 Perplexity
Perplexity
 Google AI Mode
Google AI Mode
 Grok
Grok






















