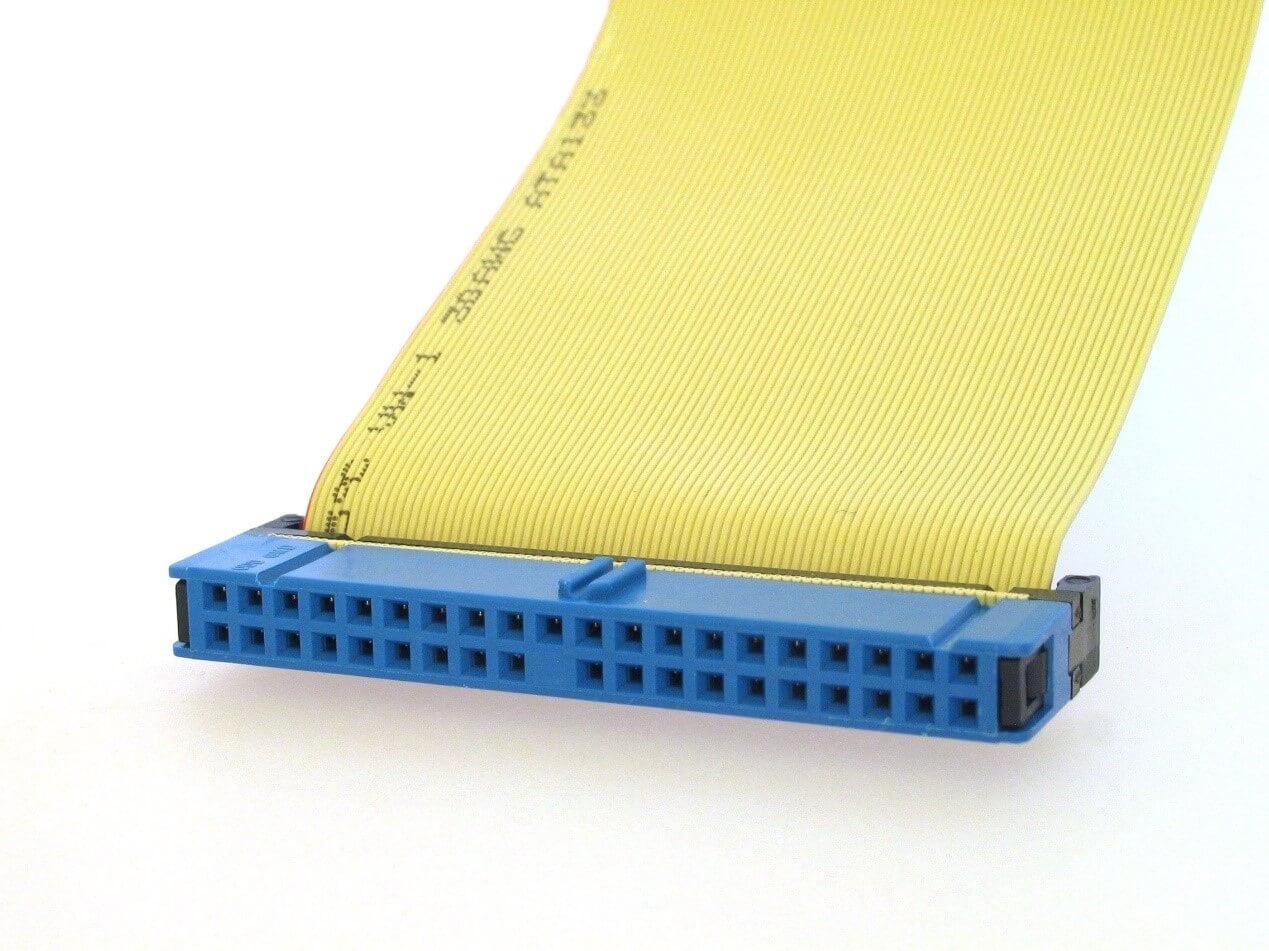
Although PATA drives are not recent, there's a chance that you will need to work on computers that have this kind of interface. PATA stands for Parallel AT attachment and is a callback for previous PC versions known as PC/AT. So if you're asking 'what is PATA?' there's a chance you've heard of PATA or simply ATA, and you're wondering what it is all about.
This article explores the meaning of PATA, how it came about, its features, and how it is different from SATA and IDE. You'll have all the information you need by the end of this article. So on that note, let's get right into it.
In this article
What Is PATA?
If you're asking 'what is PATA in the computer?' you're not alone. This section will provide you with clear insight into what it is. PATA is an acronym for Parallel Advanced Technology Attachment. It is an IDE standard for connecting storage devices like optical and hard drives to the motherboard. PATA is a term that generally refers to the cables and connections in line with this standard.
PATA used to be known as ATA, and it only became Parallel ATA when the new Serial ATA (SATA) came into existence.
Features of PATA
Some of the features of a PATA cable is that it is usually flat and features 40-pin connectors on each side. One of the ends of this plug goes into a port on the motherboard. Most times, it is labeled IDE. The other end of PATA goes into the back of the storage device; this could be a hard drive. Some cables come with more than one PATA connector midway through the cable. This additional connector aims to connect to another device like an optical disk drive.
Its main feature is connecting PCs to storage devices. It usually comes in 40 or 80 wire designs. However, new PATA storage devices require 80-wire cables to meet speed requirements efficiently. Both types of PATA cables typically come with 40 pins that look identical, making it difficult to tell them apart. Most connectors on the 80-wire cable are generally black, gray, or even blue. On the other hand, the 40-wire line only comes in black color.
History of PATA
To fully understand what PATA is, it is essential to know its history. This storage connection was created in 1999 by Western Digital. Initially, the company named it Integrated Drive Electronics (IDE). Today, you can see some updated versions of this storage connection standard as EIDE or Enhanced IDE.
The primary function of PATA is to connect to the 16-bit ISA directly. This standard was therefore conceived as an AT Bus Attachment. Officially, people knew it as AT accessory and abbreviated it to ATA.
Over the years, there were many PATA standards have been released. While some offered 16 megabytes each second, others could ensure 133 megabytes for each passing second. There was also an enhancement to PATA that allowed users to connect to more than just hard drives. People could now effectively connect to CD-ROM drives and many more storage devices.
However, when the company created SATA in 2013, the manufacturers modified the term ATA to Parallel ATA. The developer's goal was to make it easier to tell the difference between PATA and SATA connection. During this period, PATA began to phase out of existence as SATA became the standard component for PCs everywhere.
Types of PATA
There are different types of PATA available. Therefore, to fully answer the in-depth question 'what is PATA?' it's crucial also to have an idea of the different types of PATA. So, in this section, we'll explore the available types of PATA and their functions.
- ATA-1
This is the first type of PATA included in the DeskPro 386. It began the use of a master/slave configuration. ATA-1 is a type of PATA based on a subset of the standard 96-pin connecter, and it utilizes either 40 or 44-pin connectors and cables. For the 44-pin versions, those extra four pins helped supply power to a drive that didn't have a separate power connector.
In addition, ATA-1 provided signal timing for direct memory access and programmed input/output functions. This meant that the drive would send information directly to the memory, and the PIO facilitated the computer's CPU in managing the information transfer.
- ATA-2
ATA-2 was the second type of PATA released, and it increased the transfer rate from 4-16 megabytes each second to 16.67 megabytes per second. It was an upgrade from ATA-1, providing power management and removable device support. It is also called EIDE because it increased the hard drive support to 137.4 gigabytes.
- ATA/ATAPI-4
This type of PATA is also known as UDMA/33. This version of PATA added the ATA Packet Interface (ATAPI) to the standard. This way, it was now possible to support several other devices like CD-ROM, tape systems, etc. With ATA-4, the data transfer rate increased significantly to 33 megabytes per second. This PATA also provided support for 80-conductor, 40-pin ribbon cables.
Most people consider ATA-4 to be the best addition to the PATA standard. This is because, before this version, ATAPI was completely separate. Its addition is what improved the removal support of ATA.
- ATA/ATAPI-6
This version of PATA provided support for UDMA.100. Additionally, it increased the data transfer rate from 100 megabytes per second. As a result, most people refer to it as PATA/100 drives. ATA-6 also provided automatic acoustic management, allowing drives to adjust the access speed. This action also helped to reduce running noise.
PATA And SATA
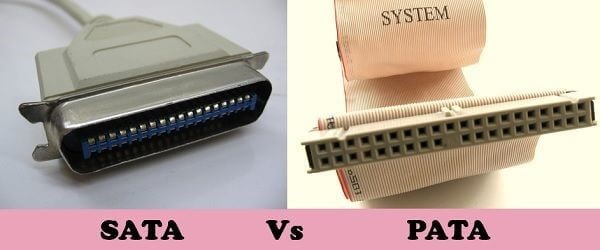
PATA and SATA are two different interface versions that people usually confuse for one another. However, they're pretty different in many ways. PATA was ubiquitous in the early days of the ATA interface when it was first introduced. Serial Advanced Technology Attachment (SATA) is an improved version of PATA, and while ATA-6 stopped at 100 megabytes per second, the highest speed of SATA is 16GB. Almost all computers today use SATA to transfer data and information. Below is a simplified breakdown of the differences between both interfaces.
- Transfer Speed
SATA offers a higher transfer speed than PATA hard drives. That is because PATA only transfers data in mb/s, while the SATA interface allows you to transfer data in gb/s. This is a considerable distinction from PATA. This increased speed is useful when you need to transfer large documents. Also, if you enjoy playing games, the high transfer speed from SATA ensures a smooth and seamless gaming session.
- Cable Length
This is another crucial difference between SATA and PATA. The maximum length of PATA is 18 inches, while SATA can extend up to a meter. In this way, SATA is more flexible for moving around your hard drive.
- Performance
Being an older version, PATA doesn't support hot-swapping. This means that you cannot change the part while using the computer. On the other hand, SATA fully supports hot-swapping. Additionally, although SATA cables are longer, they're quite small. This is to prevent the clogging of airflow in the computer. This way, SATA cables increase the life of a computer and ensure a faster performance daily.
- Compatibility
SATA cables are designed to support forward and backward compatibility. This means that even with future upgrades to the SATA standard, the system will still be able to accept input from future and past versions.
- Versatility
Although SATA is the most recent version, PATA tends to offer more versatility. This means it allows the connection of two devices to the cable simultaneously. One of the devices is recognized as device 0, the primary device, while the second is tagged device 1, making it the secondary device. On the other hand, SATA only offers two connection points; one to the motherboard and the other to the storage device.
IDE VS. PATA
PATA and IDE are two terms that confuse people even though they refer to the same hard drives. Although it looks like there should be some difference between the two, there's none. When you ask 'what is PATA hard disk?' you also refer to IDE. This is because they both refer to the same type of hard drive that utilizes flat, ribbon-like cables. These were commonly used before SATA's creation.
The confusion between the two terms came from the evolution of technology. Western Digital created the first IDE drive, which was quite different from older hard drives. Part of IDE's specification is the interface. It was previously known as ATA before Western Digital added P to make it easier to differentiate from SATA. So, to be clear, IDE is the term used to refer to the first hard drive generation that utilized the PATA interface.
Conclusion
Storage is a crucial part of a computer; some people have one or more storage devices. Before PATA, controllers and hard drives were separate. Western Digital created this interface to simplify the use of hard drives in the computer. PATA was an interface that allowed easy connection of your storage device to the computer. We touched on all the basics of PATA and how it differs from SATA and IDE. If you've been asking 'what is Parallel ATA?' we hope this article succinctly answers your question.

 ChatGPT
ChatGPT
 Perplexity
Perplexity
 Google AI Mode
Google AI Mode
 Grok
Grok






















