In this article
1. What Is a Disk Volume
A volume is the part of the disk that the user uses and/or can interact with easily. So, it is clear that despite partition, volume is not raw and without format. It is highly important to understand volume is formatted and has a specific file system. Not only does disk volume contain a file system, but also it has named a size specifically. In computer sciences, a formatted storage device is called a volume which can be divided into several logical partitions.

The volume appears in your file browser when you mount a storage device and see its icon. Operating systems keep track of which volumes are stored on which drives by storing multiple volumes on the same disk. Furthermore, defining a volume is the equivalent of naming an area of storage that users and applications can access.
In another word, there is a logical area called a volume on a physical disk. This type of file system provides a structure for accessing information and acts as a container for data. It is believed that there are both physical and logical volumes. Physical volumes can only be accessed when based on underlying hard disks. There is no such limitation for logical volumes. On the other hand, it may be possible to confine a logical volume to a section of a single disk, much like a partition.

2. Partition vs Volume: What's the Difference
You may get confused by partition and volume in the first phase. So, in this part, the differences between partition and volume are going to be explained in detail. You can learn more about partition in our article What is a partition.
As you know, every smartphone, server, and pc has storage. This storage is divided into partition and volume. An operating system mounts volumes as mass storage containers by combining one or more partitions. It means that volumes are logical assemblies of partitions that are mounted as mass storage containers by the operating system. Storage volumes can contain multiple partitions as one of their key characteristics. The name and size of a volume are provided by the file system. You can also attach your USB flash drive as a volume when you plug it in.
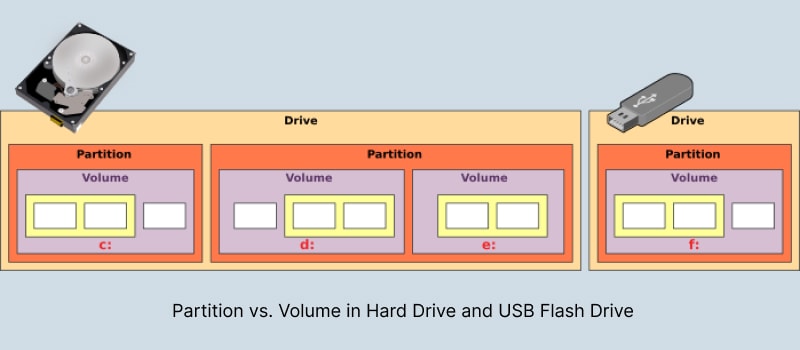
On the other hand, the partition is a logical portion of the volume and it is not usually formatted. To make the partition more sensible, it can be said that it doesn't contain a file system like volume, but it has an allocated size and you can format the disk and rewrite the partition to change its size. It is noticeable that to separate operations in an operating system, a partition has been created.
- Volume vs Partition in Types
One of the main differences between partition and volume can be mentioned in their different types. There are five volume types: simple volume, mirrored volume, striped volume, spanned volume, and RAID-5 volume, while there are three partition types: primary partition, logical partition, and extended partition.
- Volume vs Partition in Maximum Size
The maximum partition size is the size of the hard drive since the same area can be divided into one. As opposed to simple volumes, complex volumes generally have a larger maximum size. Creating other four types of volumes on two or more disks can combine them into a large volume, so volume sizes are larger than partition sizes because they combine disks.
- Volume vs Partition in Limit to the Numbers
In addition, there is a limit to the number of volumes and partitions on a hard drive. There is no restriction on the number of dynamic volumes. You can create regardless of whether a system's disks are partitioned in MBR or GPT. There is no limit to the number of partitions that can be used on a basic disk, but the style of partitions the disk uses determines the maximum. With the MBR style partitioning, you can create four primary partitions, three primary partitions, and a single extended partition that can contain several logical partitions. There can be up to 128 primary partitions when the disk uses GPT partitioning.
Remember that when multiple OS editions are being used on the same physical volume, this might require dividing it into two partitions. Because partitions are simple to create, virtual machines mostly use them. A virtual machine must recognize and use partitions. Among the different types of storage, volumes are hard drives, solid-state drives, DVDs, and CDs. Physical volumes are not the only kinds, though there are also logical ones. Partitions have the advantage over volumes when it comes to flexibility. As your needs change, they can be closed or expanded.
3. Volume Types Explained

What Is Simple Volume?
The concept of a simple volume refers to a single volume on a dynamic disk. From unallocated space on a dynamic disk, you can create a simple volume. In contrast to a partition, a simple volume doesn't have size restrictions, nor are there any limits on how many volumes can be created on a single disk. Simple volumes are not extendable if they are part of the system or boot volume. Physical disks contain simple volumes. Each of them functions independently. It is good to know that in Windows NT 4.0 and earlier versions, a simple volume acts as a primary partition. Simple volumes can only be created when a single dynamic disk is present.
What Is Spanned Volume?
As the name implies, a spanned volume combines disk space from multiple physical disks. You can use spanned volumes to unite unallocated disk space of multiple physical drives to utilize multiple disks to the fullest extent possible. There is a limit of 32 disks per spanned volume.
Note: Fault tolerance is not available with spanned volumes. All data on a spanned volume is inaccessible if one of the disks containing the spanned volume fails.
What Is Stripped Volume?
Striped volumes are built by configuring two or more disks to combine free areas into a single logical volume. Data is arranged into blocks across all the disks of the volume and distributed in a fixed order. A striped volume is similar to a spanned volume in that data is written to several disks simultaneously. But striping adds data to each disk at the same rate by spreading files over all disks. Stripped volumes typically contain 256 disks. All disk management strategies perform better with striped volumes.
What Is Mirrored Volume?
Hard disks or other storage devices that mirror data from another volume can be classified as mirrored volumes. Mirrored volumes serve as backup devices in case the primary device fails, which helps ensure fault tolerance. Data on mirror volumes are protected against disk failure. As duplicate sets of data are provided, mirroring reduces the chances of an unrecoverable error. However, it increases the number of disks required for data storage and increases input/output (I/O) operations when writing data to the disk. The I/O load balancing of requests between the plexes is, however, responsible for some performance gains in reading data. In read operations, mirrored volumes are comparable to RAID-5 volumes, but write operations are faster.
4. How to Create a Volume?
How to Create a Simple Volume?
- Step 1: Open disk management. Press the shortcut "Windows + R" to call out the "Run" box, and type "diskmgmt. MSC".

- Step 2: Click on the "New Simple Volume" button when you have right clicked on the unallocated space. Following that, you will see the "New Simple Volume Wizard," which instructs you to analyze volume size, assign a driver letter, choose file system, assign unit size, and name volume label.

- Step 3: After you are satisfied with the settings, all you need is to click on the "Finish" button to create a simple volume,.
How to Create a spanned Volume?
- Step 1: By opening Disk Management, the process would be started. After clicking on the free space, choose "New Volume".
- Step 2: Following that, in the New Volume Wizard, click "Next", choose "Spanned", and then click "Next".
- Step 3: Select the dynamic disks you want and specify their sizes, click Next, and then follow the instructions displayed on your screen.

How to Create a Striped Volume?
- Step 1: You have to open up Disk Management and right-click one of the free spaces. Now, you have to click on click New Striped Volume.
- Step 2: Click Add to add the disks to the striped volume. Setting the amount of space to use on the disks for the striped volume is the thing that you should do in this stage.
- Step 3: On the Path page, when creating a new volume, the default is to assign it the next available drive letter. You can also mount a volume on an empty NFS folder on an existing volume using the NFS command.
- Step 4: When formatting a new volume, select the formatting options from the Format Volume page of the New Striped Volume Wizard.
How to Create a Mirrored Volume?
- Step 1: Open Disk Management and right click one of the empty drives, and select New Mirrored Volume.
- Step 2: After Selecting the available drive from the left, choose Add button. Specify the size of the mirrored volume.
- Step 3: Select Format this volume with the following settings option making sure the file system is set to NTFS. set the allocation unit size to default, and then enter a name for the new volume.
- Step 4: After checking the Perform a quick format option, the process of creating mirrored volume would be finished.
Accidentally deleted or lost an important volume?
No worries. Wondershare Recoverit can get back your lost data within 3 steps. The ultimate and professional data recovery software is totally reliable and 100% safe.
People Also Ask
Does volume formatted and has allocated size?
Volume is not raw and without format. It is highly important to understand volume is formatted and has a specific file system. Not only does volume contain a file system, but also it has named a size specifically.
What does the main role of volume in an operating system?
There is a logical area called a volume on a physical disk. This type of file system provides a structure for accessing information and acts as a container for data.
Which one has a bigger size? Partition or volume?
volume sizes are larger than partition sizes because they combine disks.
Conclusion
In this article, you have understood that volume is related to the storage and it has divided into four parts: simple volume, striped volume, spanned volume, and mirrored volume. As usual through disk management and some simple steps you can create any volume you desire. In addition, it is mentioned that Volumes on a single disk can also be created multiple times, much like partitions.

 ChatGPT
ChatGPT
 Perplexity
Perplexity
 Google AI Mode
Google AI Mode
 Grok
Grok






















