RAID (redundant array of independent disks) is a fussing disk technology with the ability to combine multiple disk drives into one single logical unit. With this feature, all disks behave as one, with different RAID levels (RAID 0, RAID 1, RAID 5, etc.).
Among these levels, RAID 1 can be considered a simple and secure one, working based on the mirroring principle. To be precise, disks are organized in pairs; each pair have the same data simultaneously, an absolute redundancy that comes in handy when you face disk failure on one end.
Part 1. What Is RAID 1 (Disk Mirroring)?
RAID 1 is a redundancy technique through mirroring, meaning data is written identically to two drives. Therefore, unlike RAID 0, which uses striping and offers zero redundancy and data protection, RAID 1 is much safer.
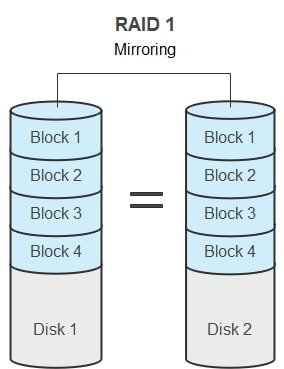
RAID 1 Features
- Performance: It has good read speed yet adequate write speed equivalent to a single drive.
- Safety: With mirroring, redundancy, and fault tolerance, this is relatively safe, and data loss in one disk can be restored.
- Space: Compared to RAID 0, half of the space in the disks is lost because of mirroring.
Advantages and Disadvantages of RAID 1
Advantages
It has excellent performance while being somehow slower compared to RAID 0.
With the mirroring aspect comes fault tolerance and easy recovery. If a disk fails, you copy the contents of its duplicate.
It is best used when you can’t afford to lose data like an archive.
Disadvantages
It has a slower writing performance than RAID 0.
With two copies, storage space is practically half of the actual volume.
The recovery process needs powering down, so data is not accessible during the recovery.
Video Tutorial on What is A RAID 1? How to Set Up RAID 1?
For Windows XP/Vista/7/8/10/11
For macOS X 10.10 or later
Part 2. How to Set Up a RAID 1?
- Before setting up a RAID 1, remember you require at least two hard disks for the RAID 1 configuration to work. Besides, it is best to apply disks with the same brand, type, and sizes when opting for RAID 1.
- Also, before starting the configuration, always have a backup of your data because hard disks will be erased during the RAID setup.
- To set up a RAID 1 array in Windows, you first need to know what this feature is called; then, the actual operation is easy to follow. Microsoft uses "Storage Spaces" instead of the common name "RAID," but it works in the same capacity.
The following is the step-by-step instruction on how to set up a RAID 1:
- Step 1: Press the shortcut Win+S or click the search icon to find and launch "Storage spaces".
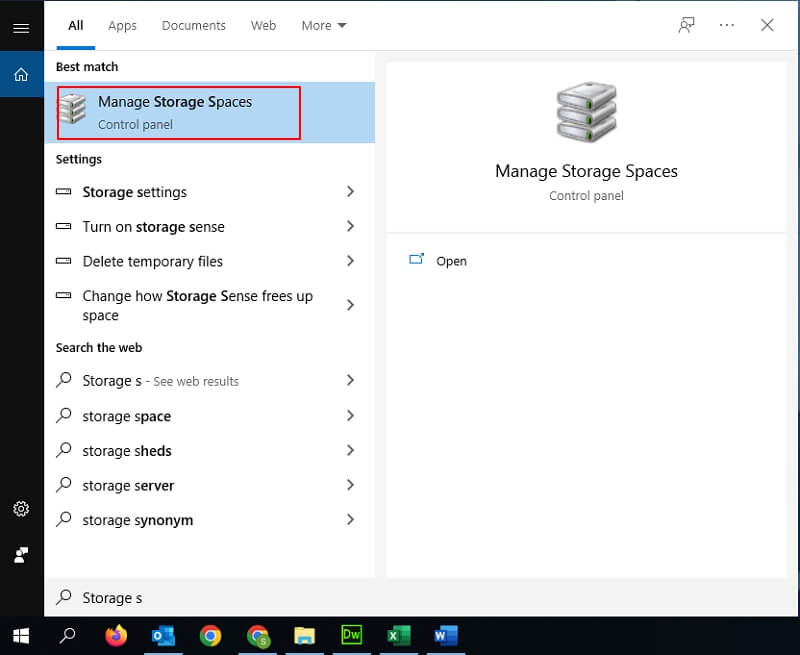
- Step 2: Click"Create a new pool and storage space." For the process to continue further, you’ll need administrator access.
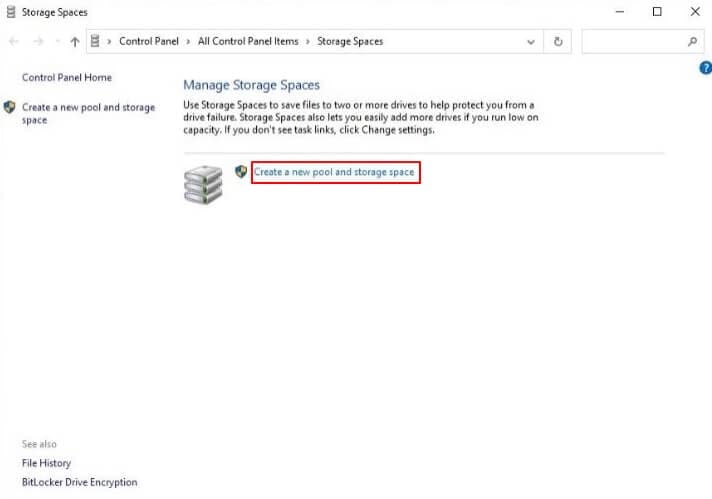
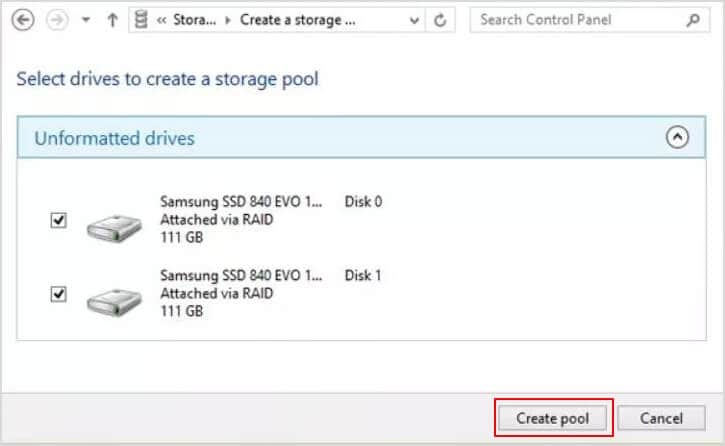
- Step 3: A new screen opens, showing you all the unformatted disks you can use for the RAID 1 configuration. Select all the disks you want in the array and click on “Create pool."
- Step 4: Here, you should name it and determine the drive letter and file system. The name you gave will appear as the drive label. Pick NTFS as the file system, and for the Resiliency type, select“Two-way mirror," equivalent to RAID 1. Finally, click“Create storage space”to proceed.
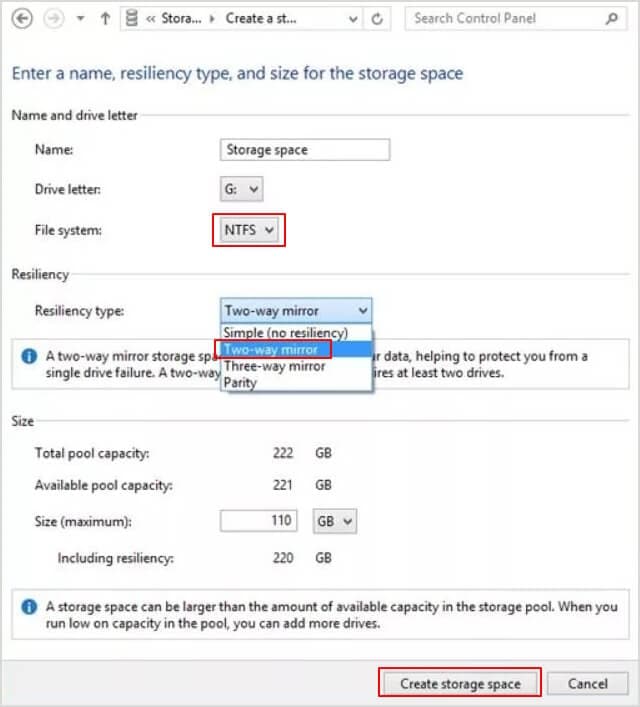
With RAID 1, you practically can only use half of your storage space, but in the end, it is more secure, and the other half works as a backup.
Part 3. How to Rebuild RAID 1 without Losing Data?
When a drive fails in a RAID 1 configuration, its files are not lost, considering being copied on a mirrored disk. So, you can replace a failed RAID 1 to continue working without data loss. However, if more than one drive fails at a time, it will cause trouble and needs more serious work to remedy the situation.
The only indication of a hard drive failure can be displayed during boot in the form of a RAID volume status, which can be seen as "Failed," "Degraded," or "Rebuild" status. You can press CTRL-I to enter the Configuration Utility to correct the condition, but it is not recommended because you may accidentally destroy the fine disk. Therefore the better option is to boot Windows and uses the “Intel® Rapid Storage Technology Manager” to rebuild a failed disk.
To rebuild RAID 1 without data loss, proceed as below:
- Step 1:First, Replace the defective disk.
- Step 2: Run the Intel® Rapid Storage Technology Manager. For that, go to Start > All Programs, and in "Intel," run "Intel® Rapid Storage Technology."
- Step 3: You can find the failed disk on the Status screen, Then select “Rebuild to another disk.”
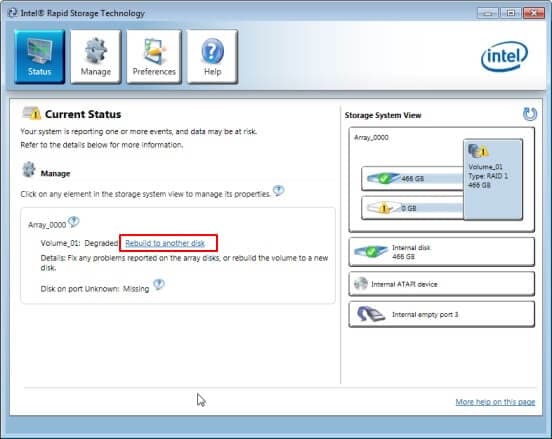
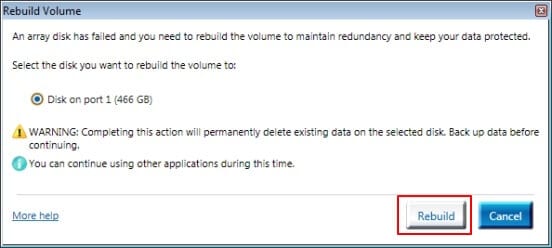
- Step 4: Press “Rebuild”to confirm the operation.
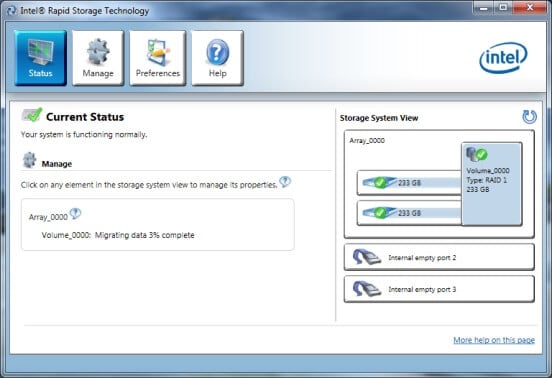
- Step 5: You can watch the status of the disk rebuild and how the operation is in progress. RAID 1 reconstruction takes 1 - 3 hours to complete.
Part 4. How to Transfer a RAID 1 Drive to a New Computer?
So what happens if you need to move a RAID 1 drive to another computer? Is it possible, and how?
You can transfer a RAID 1 array drive from one PC to another with no impact on data in case you need to recover the RAID1:
Firstly you should ensure that the new machine is equipped with the required hardware, such as a compatible RAID driver and the same type of RAID volume.
These are the steps to transfer a RAID 1 drive to a new system:
- Step 1: Back up your data to an external source, if you can. Better safe than sorry.
- Step 2: Undo the RAID pair.
- Step 3: Insert the disks into your new system.
- Step 4: Set up a new RAID array.
- Step 5: Finally, move data back from the backup if necessary.
Part 5. How to Recover Data from RAID 1?
Easy Recovery: Among RAID levels, RAID 1 is the easiest to recover data. As previously mentioned, mirroring in RAID 1 lowers the chances of RAID 1 failure to the minimum because one drive failure can be fixed by copying data from the mirror drive.
Undetected Drive Failure: Even if both RAID 1 drives don't fail simultaneously, one hidden drive failure results in your RAID 1 no longer providing data redundancy.
Drive With the Same Age: Keep in mind that hard drives in RAID 1 are often manufactured at the same time, which means they are likely to fail together.
That said, the best method to recover data from a RAID 1 drive is working with RAID data recovery software, preferably a reliable and user-friendly one. Wondershare Recoverit is a professional recovery program that you can work with to restore many types of lost data, videos, images, documents, etc., from different internal and external drives. A practical and inexpensive solution to aid recover data from your RAID 1 drives.

Wondershare Recoverit – The Best RAID 1 Data Recovery Software
5,481,435 people have downloaded it.
With Recoverit, users can quickly bring back data from all types of RAIDs, including RAID 0 (the hardest), RAID 1 (the easiest), RAID 5, RAID 6, RAID 10, etc.
Recover files lost due to disk failure, accidental deletion, system corruption, or any other causes.
Recover lost or formatted RAID logical volumes.
Supports storage media & RAID arrays having FAT, exFAT, & NTFS file system.
Free version to try and paid version to enjoy more.
For RAID 1 Data Recovery with Recoverit data recovery software, follow the steps below:
Step1Select the RAID 1 Hard Drive
After installing Recoverit recovery software, select the RAID 1 hard drive under the "Hard Drives and Locations," then click "Start" to begin scanning.
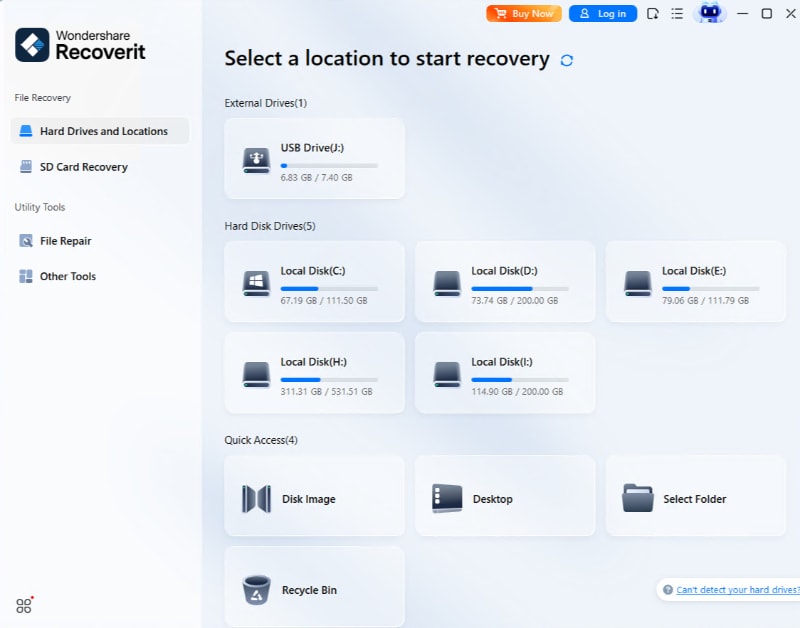
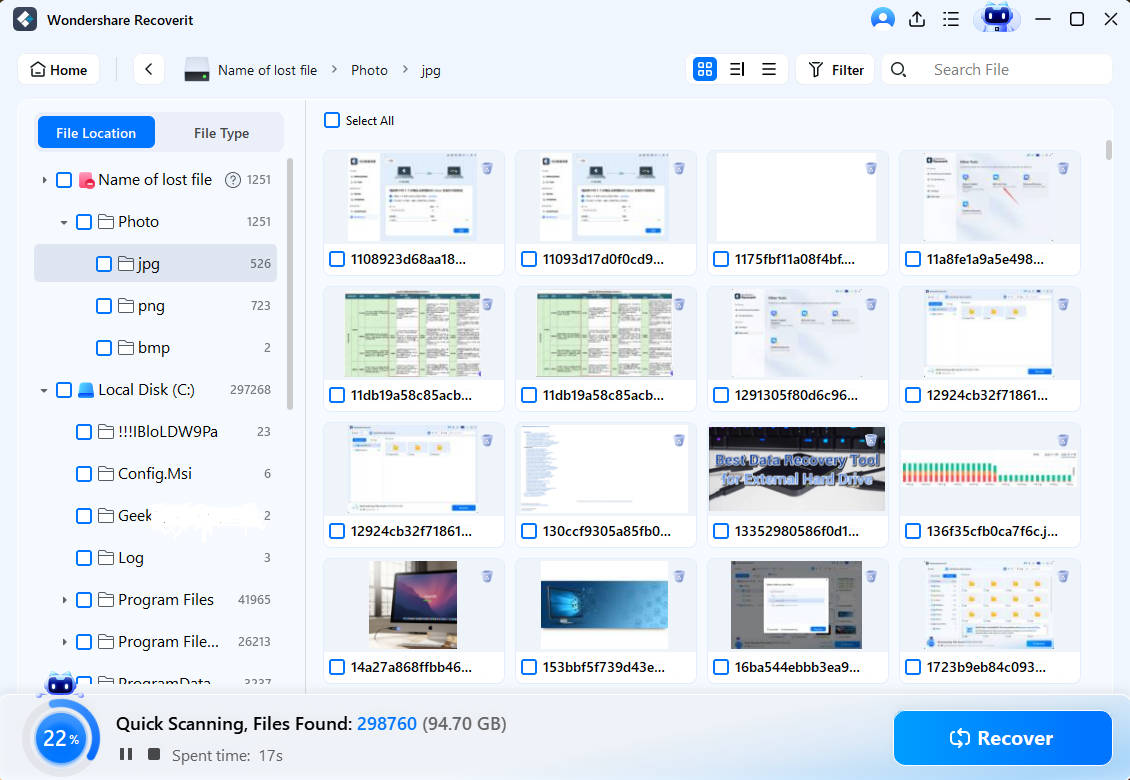
Step2Scan the Selected Drive
Recoverit begins scanning the selected drive for recovery to go underway. The scanning process may take some time, depending on the files' size. You can stop scanning anytime by clicking on the "Pause" button at the top.
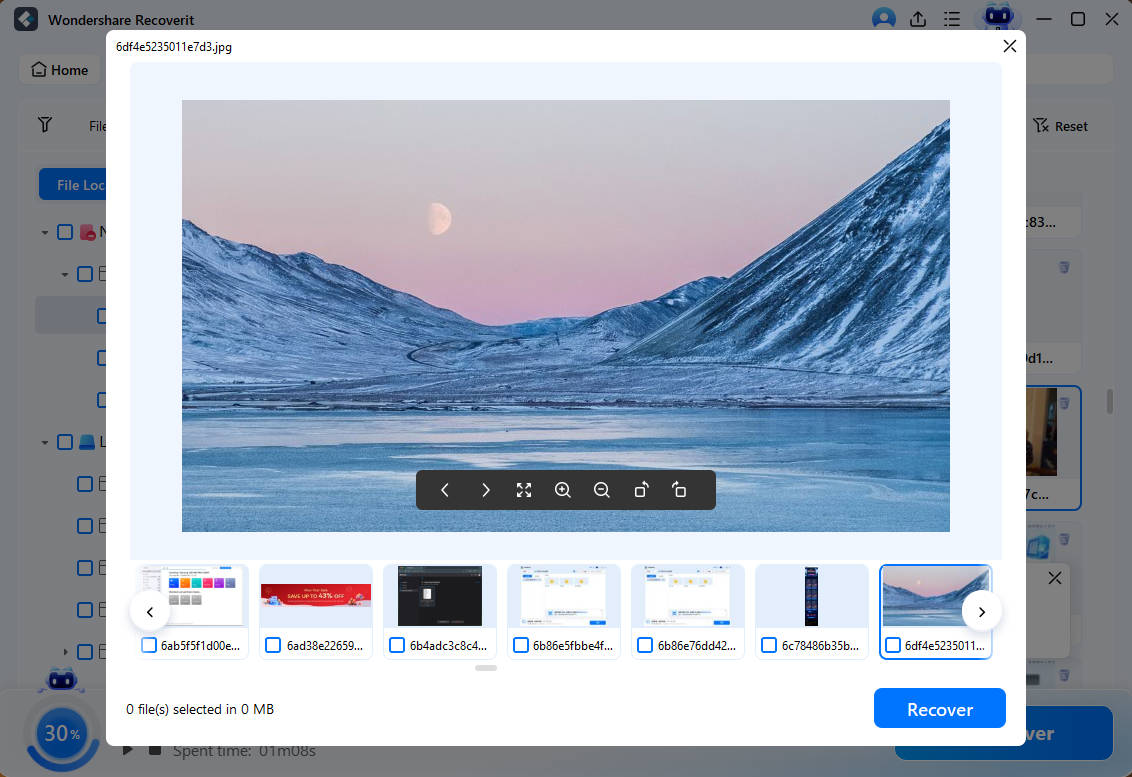
Step3Preview Your Desired Files
When the scan is complete, you can click on a file to see a “preview” of your files before retrieving them. You can restore all files or select them individually. Nevertheless, watching the preview of RAID 1 before data restoration in the Recoverit program is a convenient feature.
Step4Recover
Finally, click "Recover" to retrieve lost data.
For Windows XP/Vista/7/8/10/11
For macOS X 10.10 or later
Part 6. RAID 1 vs. RAID 10, RAID 5, RAID 0, and SHR
1. RAID 1 vs. RAID 10: What's the Difference
RAID 10: Also called "stripe of mirrors," this expensive advanced technology utilizes data striping and disk mirroring to obtain data redundancy with a high degree of fault tolerance.
RAID 10 and RAID 1 are mirroring technologies; however, the big difference is the number of drives they can use in a RAID group.
Raid Level |
RAID 10 |
RAID 1 |
| Process | Mirroring + striping | Disk Mirroring |
| Redundancy | Excellent | Excellent |
| performance | Excellent | Good ( no striping. no parity ) |
| Fault Tolerance | Fault-Tolerant | Fault-Tolerant |
| Minimum Storage Disks | 4 | 2 |
| Price | Very expensiveVery expensive | Moderate cost |
2. RAID 1 vs. RAID 5: What's the Difference
RAID 5: As the most common RAID configuration, it utilizes data striping and parity, and unlike RAID 0 and RAID 1, it requires at least three disks to function.
Raid Level |
RAID 5 |
RAID 1 |
| Process | Striping + parity | Disk Mirroring |
| Redundancy | Good (distributed parity) | Excellent |
| performance | Good (as blocks are striped) | Good ( no striping. no parity ) |
| Fault Tolerance | Fault-Tolerant | Fault-Tolerant |
| Minimum Storage Disks | 3 | 2 |
| Price | Best cost-effective option | Moderate cost |
Read More: RAID 5 vs. RAID 1: Which One is Better?
3. SHR vs. RAID 1: What's the Difference
Synology Hybrid RAID (SHR): Synology's automated RAID management system allows users to create a flexible storage solution with optimized capacity and performance.
Here we render a comparison of SHR vs. RAID 1 based on pros and cons:
Synology Hybrid RAID (SHR) |
RAID 1 |
|
| Advantages |
|
|
| Disadvantages |
|
|
4. RAID 1 vs. RAID 0: What's the Difference
RAID 0: It fusses two or more hard drives together in a way that they work as one logical drive to create fast performance, but not a very secure option for vital data.
Raid Level |
RAID 0 |
RAID 1 |
| Striping | Yes | No |
| Redundancy | No | Yes |
| Mirroring | No | Yes |
| Parity Disk | No | No |
| performance | In theory, it offers faster read and write speeds. | It offers slower write speeds but could the same read performance as RAID 0 |
| Fault Tolerance | No | Yes |
| Minimum Storage Disks | 2 | 2 |
| Application | Used where data reliability is less concerned and speed matters like broadcasting | It is used for vital data like data archival |
Read More: RAID 1 vs. RAID 0: Which One is Better?
Conclusion
Among RAID levels, RAID 1 is considered simple and secure, offering redundancy through mirroring. A fast and secure technology with an easy recovery process. This article discussed setting up, rebuilding, transferring, and recovering RAID 1. Then we compared the RAID 1 vs. RAID 10, RAID 5, RAID 0, and SHR.

 ChatGPT
ChatGPT
 Perplexity
Perplexity
 Google AI Mode
Google AI Mode
 Grok
Grok






















