RAID 0 technique aims to improve performance for reading and writing data by combining multiple physical disk drive components into one. RAID 0 associates at least two hard disks in a striping aggregation, leading to writing data to distribute over assembled physical disks and accelerate the process successfully. In other words, managing a body of organs and creating a proper blood flow that connects all the organs and moves the whole body in harmony.
With the number of hard drives mounted together, performance enhances but using the proper RAID controller is the key.
Part 1. What Is RAID 0 (Disk Striping)?
A RAID (Redundant Array of Independent Disks) combines at least two storage media to form a single logical drive. It is primarily done for a more advanced throughput rate and a more secure system which the latter is debatable regarding RAID 0.
RAID 0 is a permanent feature among expected RAID levels, but technically it is not even a Redundant Array of Independent Disks. In a RAID 0 network, a single logical drive is created from at least two near or entirely identical storage media to optimize performance. The main difference with other RAID levels is that it renders no extra security.
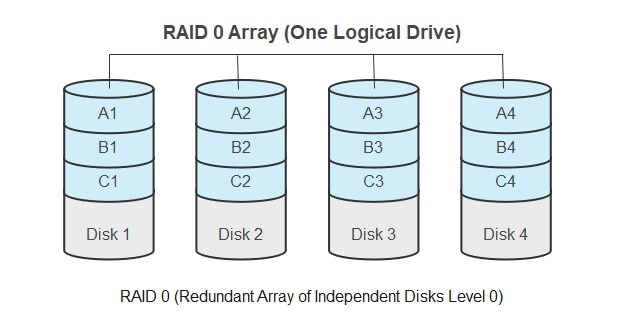
In standardized RAID 0, combining two or more hard drives, data are equally into blocks on a participating storage media known as "stripes ." This process is called "striping ." The size of the individual blocks is usually 64 kilobytes (kB) and can be referred to as "chunk size" or "individual blocks."

What Is RAID 0 Used for?
RAID 0 speeds up data processing, and many hardcore gamers use this technology to create faster and more efficient environments. It can also benefit multimedia developers, so the hard disk is a frequent bottleneck in processing gigabytes.
However, not being the safest, this method is not recommended for data storage, sensitive and precious material, or being used as web hosting and database servers.
How Does RAID 0 Work?
There are various standard levels of RAID (RAID 0, RAID 1, RAID 2, and so on), with many variations evolving over time. RAID 0 consists of striping but no mirroring or parity.
In RAID 0, striping is a way of maximizing the read and write access. Compared to non-RAID drives, the RAID 0 has the sum of the drives' capacities in the set. But remember, it is a very delicate procedure, and as much as it is beneficial, it becomes vulnerable. Because striping distributes the contents of each file among all drives, the failure of any drive causes the entire RAID 0 to collapse. Therefore, if a hard drive fails, the data gets lost, considering intact hard drives only have their respective stripes stored on them.
Advantages and Disadvantages of RAID 0
The primary advantage of RAID 0 array over only one hard drive is parallelized data access which offers high speed and maximizes performance. In addition, with such an efficient network, you are provided with more bandwidth, and consequently, the number of input and output operations per second (aka IOPS) increases.
However, RAID 0 can not be set up in more current storage devices considering that using SSDs in a RAID array comes at the expense of performance. Nonetheless, compared to other RAID levels, with RAID 0, the technology has more compatibility with HDD hard disks.
The most significant disadvantage of this "house of cards" compared to only using one hard disk is the risk of failure and the higher possibility of data loss. Any problem, whether software or hardware related, can threaten the whole network and cause a system failure.
Therefore, with one part crumbling, all the structure collapses. More so, with more linked data carriers, the possibility of breakdown is higher. Compared with other RAIDs, RAID 0 doesn't offer any redundancy. Therefore, any single defect not only immediately leads to total system failure but also loses most of your stored data in drives.
What makes this a significant loss is when you fail to have a separate backup, and hence, all your data from all hard disks are deleted because of one single damage in just a corner.
RAID 0 Advantages
Greater bandwidth than single drives.
Compared to single drives, the probability of system failure is higher.
RAID 0 Disadvantages
Compared to single drives, you can experience a higher number of input and output operations per (Speeding up performance).
There is a lack of redundancy, which means data may be lost without proper backup in the event of a defective disk.
Read more: RAID 0 Data Recovery
How to Set Up RAID 0 on Windows 10/11?
A minimum of two disks are required to apply RAID 0. While software and hardware RAID support RAID 0, like most controllers, no-fault tolerance is the downside.
RAID 0 configuration, designed to “stripe” data between multiple drives, produce one virtual drive under the “This PC” section of File Explorer, automaticallycutting down on all the clutter.
In higher Windows like Windows 10, the system doesn't call "RAID 0" by its familiar name, yet you can find the option to create a RAID 0 array under a search term called "Storage Spaces."
In this section, we provide instructions on how successfully set up RAID 0 on Windows 10/11, step by step:
- Step 1: First, you need confirmation about the drive brands and make sure their model and speed are matched before unifying the hard drives. Using the same firmware brands is practically essential, although it is possible to link different drives in a RAID 0 arrangement. However, it could be a waste considering the final fussed system will assume the speed of the lesser drive.
- Step 2: After ensuring the brand’s solidarity, having a backup of your data is necessary. Every piece of data on the drives in question requires a backup before forging a RAID 0 array.
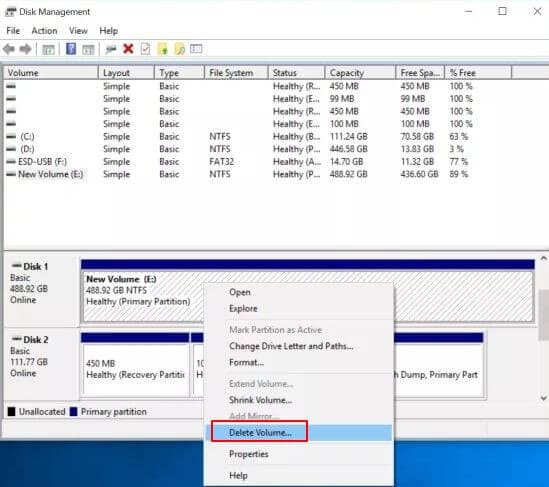
- Step 3: In the Cortana search bar at the bottom left-hand side of your screen, key in "Disk Management."It will bring the option "Create and format hard disk partitions." Click on that, locating the drives you want to combine in the lower half of the recently opened window.
Then to delete the already existing drives, right-clicking each volume followed by the “Delete volume” command.
- Step 4: Now you have no recognizable drives, you can go for RAID 0 creation. To proceed in Windows 10, search for a search term called “Storage Spaces" by typing that in the search bar next to the Start button.
- Step 5: The newly opened window is headlined "Manage Storage Spaces."
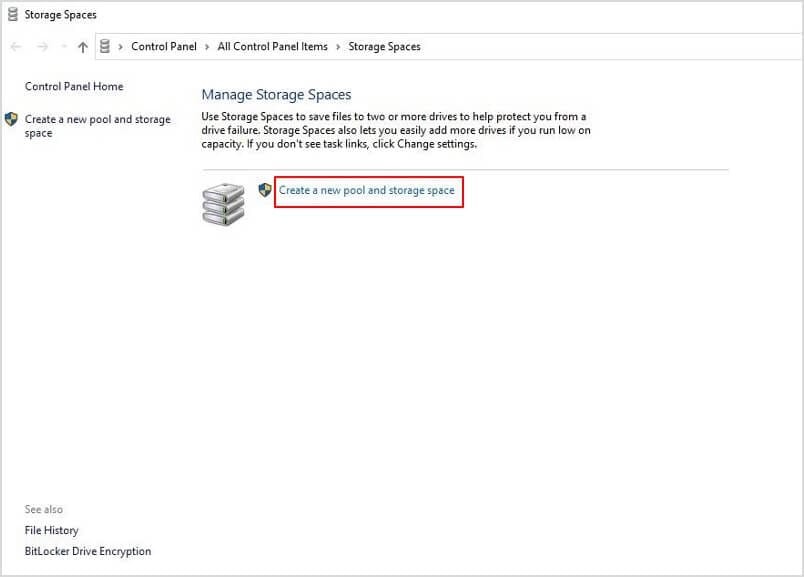
- Step 6: Go for "Create a new pool and storage space," which is a sensitive procedure; therefore, Microsoft will ask for administrative verification; after approval, you can carry out the RAID 0 array.
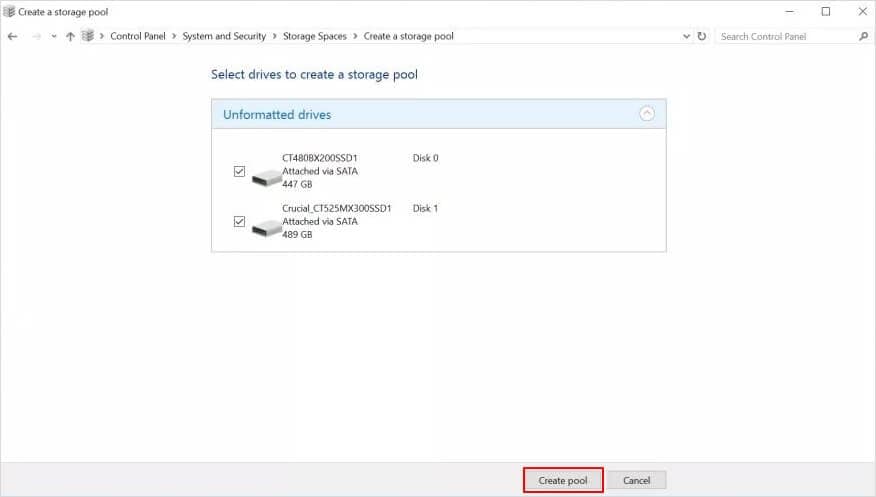
- Step 7: Then verify that the unformatted drives listed are the ones you want to merge and press “Create pool ."This part takes a few minutes to finalize, and Windows take a while to prepare your drives to initiate their impending RAID 0.
- Step 8:Then, you'll be asked to choose a name, "resiliency type," and size for your array.
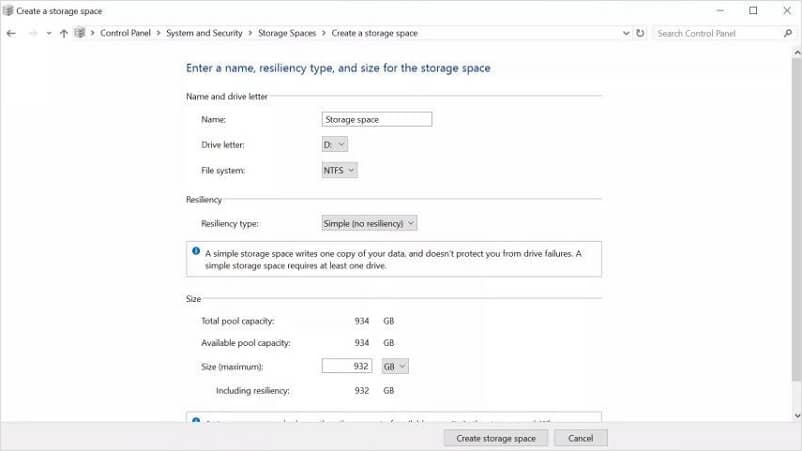
To put it simply, resiliency type means the level of security for your data. Storage Spaces provides you with four Resiliency Types: For example, “Simple” (no resiliency) writes one copy of your data and doesn't protect you from drive failures.
The drive letter and name are personally important for identification and order. It is up to you to assign any name you desire and fill these empty boxes, but it’s suggested that the file system stay as NTFS.
- Step 9: Now, you established the first RAID 0 array on a Windows 10, which allows you to store twice the number of files and applications on the "same" device if your new system has two identical drives. The last task is to use your backup to restore your deleted data and put them back into newly created storage space.
Disk Striping vs. Disk Mirroring
Disk Mirroring (aka RAID 1) is the replica of data to two or more disks. This technique is suitable when our applications need high performance and availability, for example, transactional applications, email, and operating systems. Learn more about what RAID 1 is.
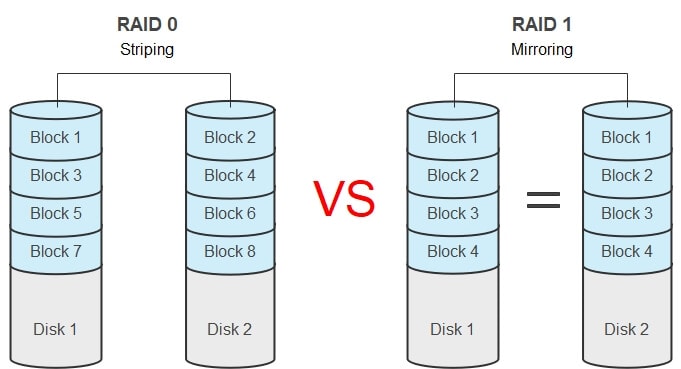
RAID 1 and RAID 0 are both the earlier levels of RAID, and the main difference between them is the usage of striping vs. mirroring. As we mentioned, in RAID 0 technology, "disk stripping" is used; on the other hand, RAID 1 technology has "disk mirroring."
Disk Striping |
Disk Mirroring |
| Disk stripping is used. A lower-cost technology. It has no written penalty. Its Relative storage efficiency is 100%. The write performance of RAID 0 is better and works well in reading performance. It emphasizes data accessing speed. It has no protection available. |
Disk mirroring is used. A more expensive technology. It has a written penalty. Its relative storage efficiency is 50%. The write performance of RAID 1 is slower and works moderately in Reading performance. It emphasizes data availability. It has mirror protection. |
Dig deeper into RAID 0 vs. RAID 1.
RAID 0 vs. RAID 5, JBOD, and SSD
1. RAID 0 vs. RAID 5
RAID 5 is a type of RAID that uses disk striping with parity, and because of evenly divided data across all of the disks, no single disk is a bottleneck. Also, Striping allows users to reconstruct data in case of a disk failure. With RAID 5, you can have the best of all worlds, which means combining outstanding performance plus safety at an affordable price. Learn more about what RAID 5 is.
With RAID 0, you only need two drives; however, RAID 5 requires using at least three drives. With RAID 5, a "parity" is distributed across the drives, so if a single drive failure happens, you can restore the data using the parity information stored on the other drives. There are downsides and upsides for both systems.
RAID 0 |
RAID 5 |
|
| Performance (Read and Write) | It has a high “read and write” performance | It comes with a low “read and write” performance |
| Speed | Very fast (on both read and write) | Read speed is very fast, although write speed is somewhat slower because of the parity that has to be calculated. |
| Fault tolerance | Not very secure and has non-fault tolerance | It has a single-drive failure function |
| Capacity utilization | It has 100 capacity utilization | It has almost 67% – 94% capacity utilization |
| Minimum number of drives | 2 | 3 |
| Cost | It is not very expensive | Likewise, it is less costly than many RAIDs |
2. RAID 0 vs. JBOD
JBOD stands for "just a bunch of disks" or "Just a bunch of drives." It is a multilevel storage architecture consisting of numerous disk drives inside a single storage enclosure. It is not referred to as RAID but could be and has similar functioning.
Structure: Unlike RAID0, JBOD is a non-RAID category with none of the various features found in RAID levels. It doesn't provide data redundancy, parity check, or striping and just integrates several storage disks into a single disk. In technical language, this integration of disks is known as spanning.
Speed: RAID 0 is superior to JBOD when it comes to speed (data reading and writing).
Fault tolerance: Although JBOD doesn’t offer any advantage in terms of high speeds, unlike RAID 0, one tiny failure of a single disk doesn’t mean the entire system fails and loses all data.
If you want speedy data retrieval, go for RAID 0, but if you only look for disk integration, then opt for JBOD.
3. RAID 0 vs. SSD
SSD is an abbreviation for “solid-state drive” or “solid-state storage device” that uses integrated circuit assemblies to store data, using flash memory, and functioning as secondary storage. Learn more about what an SSD is.
Speed: When it comes to speed, an SSD will always win out against a RAID 0 hard drive setup.
Performance: Practically, a single SSD will always beat a pair of mechanical drives, so in the case of pure performance, it's superior
Cost: Even with less expensive SSDs recently, they are still costly and much more expensive than mechanical drives.
Endurance: SSDs wear out when they've been written too much. However, write endurance is far beyond what most users will ever need for modern drives.
Storage: SSDs unattractive as redundant mass storage, and HDD RAID is still best for mass storage.
FAQs
When Should I Use RAID 0?
In general, when you need the performance over data redundancy, like when you're handling mission-critical data, then RAID 0 is your choice.
Is RAID 0 or RAID 5?
RAID 0 performs better than RAID 5, while RAID 5 gives redundancy by spreading parity data across the different drives.
How Fast Is RAID 0 Compared to SSD?
In nature, a single SSD is always the winner against a RAID 0 regarding speed.
Is RAID 0 Good for SSD?
RAID 0 is for big/fast scratch disks only, and you should be careful using that with vital data storage.
Is Raid 0 Faster than Raid 10?
RAID 10 can provide the speed of RAID 0 with the redundancy of RAID 1.
Conclusion
What is RAID 0? In this brief, first, we offered information on RAID 0, its features, pros, and cons, and its attributes against other technologies like RAID 5, JBOD, and SSD. Further, we provided instructions on how to set up RAID 0 on Windows 10/11.

 ChatGPT
ChatGPT
 Perplexity
Perplexity
 Google AI Mode
Google AI Mode
 Grok
Grok






















