The unmountable boot volume error is a common issue faced by many Windows users. Whether you are using Windows 11, Windows 10, or even the older Windows 7, encountering this error can be frustrating.This error usually shows up as a blue screen with the message "stop code unmountable boot volume."
When your computer's boot partition cannot be accessed, Windows cannot start properly, leading to a significant disruption in your workflow or daily activities. In this article, we will explore what an unmountable boot volume is, what causes this error, and how to fix it.
Dealing with a blue screen error is never pleasant, especially when it involves an unmountable boot volume. This error can be intimidating because it prevents your computer from booting up normally. However, it's important to remember that this issue can be resolved with the right steps. By the end of this guide, you'll be equipped with the knowledge to fix the unmountable boot volume error and get your system up and running again. With patience and careful execution of the steps outlined in this article, you can overcome this error and restore your computer to its normal functioning state.
In this article
Part 1: What is an Unmountable Boot Volume?
An unmountable boot volume Windows 11 refers to a situation where your computer's boot partition cannot be accessed. This means that the system is unable to read or write data on the partition that contains the operating system, preventing Windows from starting up properly. The unmountable boot volume error is often accompanied by a blue screen, signaling a critical issue that needs to be addressed.
The boot partition is crucial for the proper functioning of your computer. It contains the essential files and data required for the operating system to load. When this partition becomes unmountable, it can be due to several reasons, such as file system corruption, physical damage to the hard drive, or issues with the BIOS settings. Understanding these underlying causes can help you take the necessary steps to fix the error and prevent it from occurring in the future.
Part 2: What Causes the Blue Screen to Have an Unmountable Boot Volume Error?
Encountering a blue screen with an unmountable boot volume error Windows 11 can be both alarming and frustrating. This error often signifies deeper issues within your system that need to be addressed promptly to restore normal functionality. The causes for this error can vary widely, ranging from software-related problems like corrupted system files and outdated drivers to hardware issues such as a damaged hard drive or faulty components.
Understanding these potential triggers is essential for effectively troubleshooting and fixing the unmountable boot volume error, ensuring your system runs smoothly and reliably.
- Corrupted system files: When essential system files become corrupted, the operating system cannot access the boot partition, leading to the unmountable boot volume error.
- Damaged hard drive or SSD: Physical damage to the storage device can prevent data from being read or written correctly, causing this error.
- Incorrect BIOS settings: Improperly configured BIOS settings can interfere with the boot process, resulting in the system being unable to access the boot volume.
- Faulty hardware components: Defective components, such as RAM or motherboard issues, can disrupt the normal functioning of the computer, triggering the error.
- Sudden power outages: Abrupt power loss can corrupt system files or damage the hard drive, leading to boot issues.
- Virus or malware infections: Malicious software can corrupt critical system files, making the boot partition unmountable.
- Outdated or corrupted drivers: Drivers that are not up-to-date or are corrupted can cause conflicts that result in the unmountable boot volume error.
- Incomplete Windows updates: If a Windows update is interrupted or not installed correctly, it can lead to system instability and boot errors.
Part 3: How to Fix the Unmountable Boot Volume Error?
Fixing the blue screen unmountable boot volume error requires a systematic approach to identify and resolve the underlying issues. This error can be caused by various factors, so it's essential to try different solutions to see which one works for your specific situation.
In this section, we'll explore several fixes, from using Windows Automatic Repair and running commands in the Command Prompt to repairing the Master Boot Record and checking for hardware issues. Each method is designed to address common problems that can lead to the unmountable boot volume error, helping you get your system back to normal as quickly as possible.
Fix 1: Use Windows Automatic Repair
Windows Automatic Repair is an integrated tool that automatically addresses common startup issues. It identifies problems that stop Windows from booting and tries to fix them. This approach is easy to use and can frequently solve the blue screen unmountable boot volume error without needing advanced technical skills.
- Restart your PC. Press the F8 key. Enter Advanced Boot Options. Select Repair Your Computer.

- Choose Automatic Repair and follow the instructions.
Fix 2: Run the CHKDSK Command
The chkdsk command is a powerful utility that checks the integrity of your disks and repairs errors it finds. Running this command can help fix issues related to corrupted files or bad sectors on the hard drive, which might be causing the unmountable boot volume error.
- Boot from a Windows installation media. Open Command Prompt.

- Type chkdsk /f/r/x and press Enter.
Fix 3: Repair the Master Boot Record (MBR)
The Master Boot Record (MBR) is a crucial part of your computer's boot process. If the MBR is corrupted, it can cause the unmountable boot volume error. Repairing the MBR can restore the boot partition and allow Windows to start correctly.
- Boot from the installation media. Open Command Prompt.

- Type bootrec /fixmbr and press Enter.
Fix 4: Run the System File Checker (SFC) Scan
The System File Checker (SFC) scan is a tool that scans for and repairs corrupted system files. Running an SFC scan can help resolve the unmountable boot volume error if it's caused by missing or damaged system files.
- Boot from the installation media. Open Command Prompt.

- Type sfc /scannow and press Enter.
Fix 5: Check for Hardware Issues/Run Diagnostics Tool
Hardware issues can also cause the unmountable boot volume error. Checking your hardware for faults using built-in diagnostics tools can help identify and resolve issues with components such as the hard drive or RAM.
- Restart your PC. Enter BIOS/UEFI settings.

- Run the built-in diagnostics tool to check hardware integrity.
Part 4: Lost Data Due to Stop Code Unmountable Boot Volume Error?
Losing data due to the unmountable boot volume error can be distressing. However, with the right data recovery tool, you can recover lost files and documents. Recoverit is a reliable data recovery software that can help you retrieve lost data quickly and efficiently.
Recoverit works by scanning your hard drive for lost or deleted files. It supports a wide range of file formats and can recover data from various storage devices.
Whether you have lost important documents, photos, or videos, Recoverit can help you get them back.
Steps to Use Recoverit:
- First, download Recoverit and install it on your computer. Open Recoverit and select the drive or location from where you want to recover data.
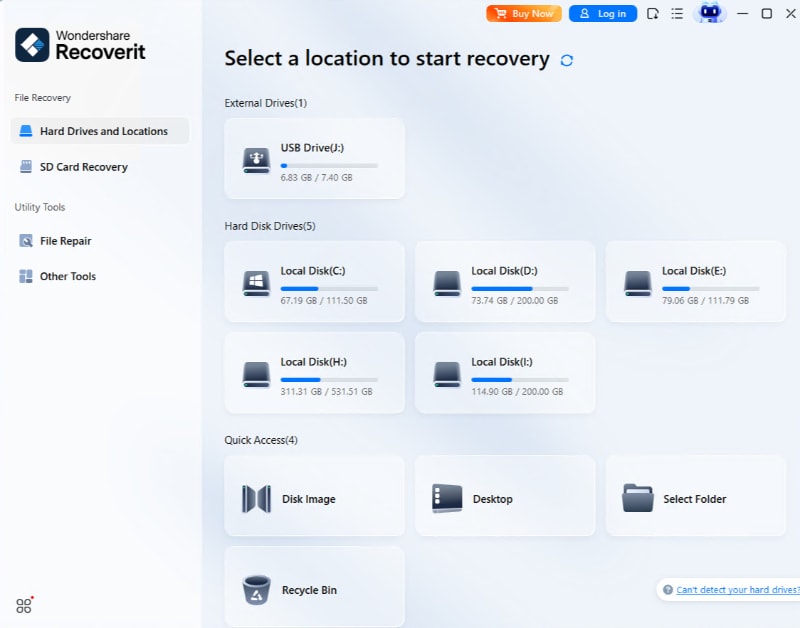
- Start the Recovery Process: Start scanning for lost files.
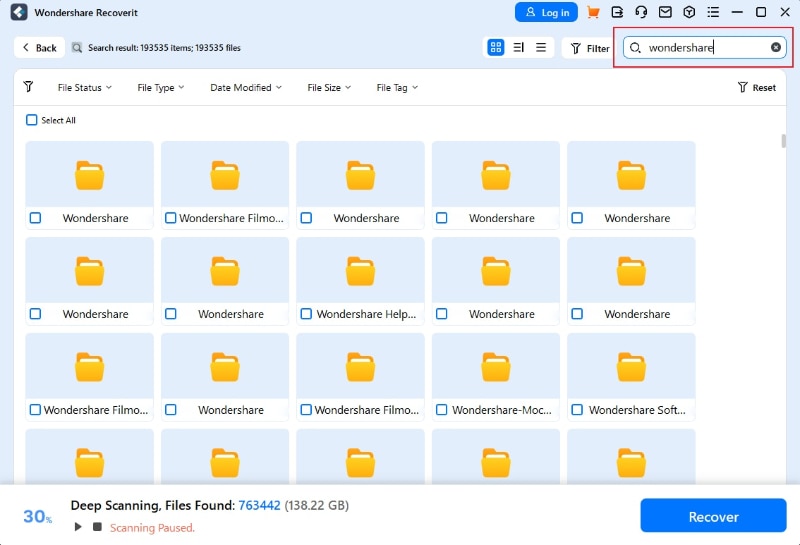
- Once the scan is complete, preview the files and select the ones you want to recover.
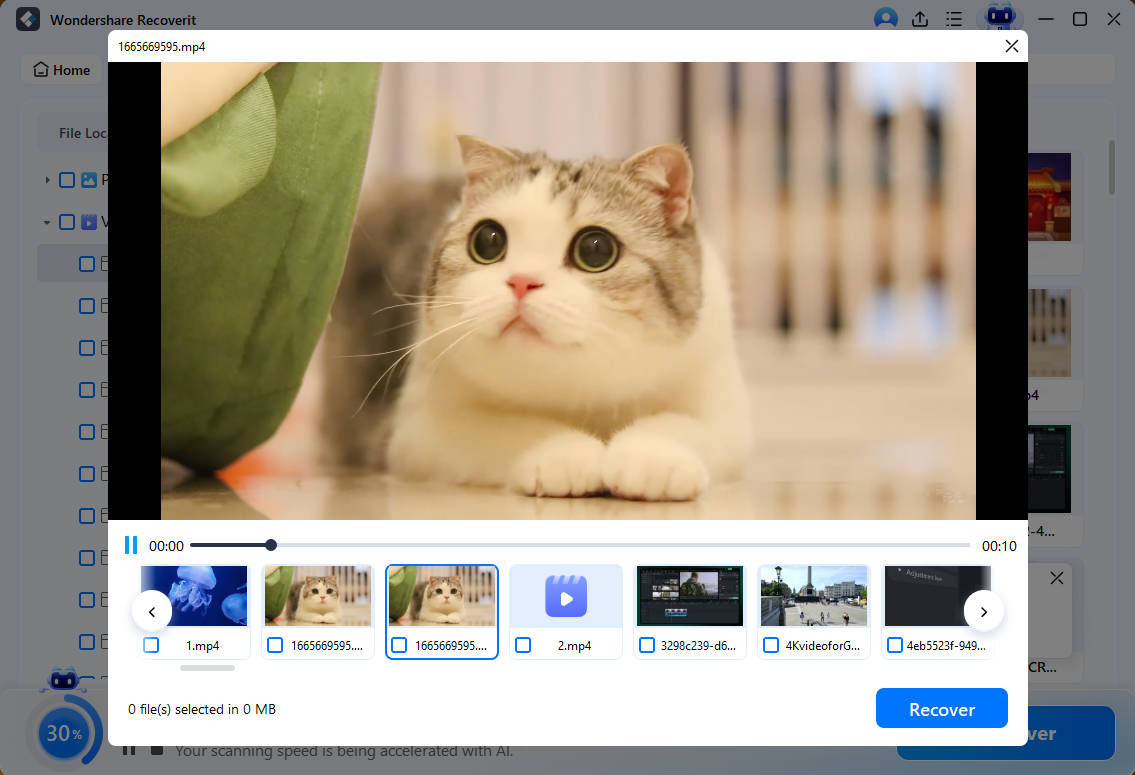
This simplified process should help you recover your lost data efficiently.
Video tutorial: Partition Data Recovery
Part 5: Tips to Fix Unmountable Boot Volume Issue
Dealing with an unmountable boot volume error can be a hassle, but there are several proactive steps you can take to minimize the risk of encountering this issue again:
- Regularly Back Up Your Data: Always ensure you have a current backup of your important files. This way, if something goes wrong, you won’t lose critical data.
- Keep Your System Updated: Regularly install Windows updates and driver updates to ensure your system is protected against known issues and vulnerabilities.
- Use Reliable Antivirus Software: Protect your system from malware and viruses by using trusted antivirus software. Regularly scan your computer to detect and remove any potential threats.
- Check Disk Health Periodically: Use built-in tools or third-party software to monitor the health of your hard drive. This can help you detect and address potential issues before they cause serious problems.
- Avoid Sudden Shutdowns: Always shut down your computer properly to prevent file corruption and potential hard drive damage.
- Maintain Proper Ventilation: Ensure your computer has adequate cooling and is free from dust and debris. Overheating can cause hardware failures.
- Run Diagnostic Tools: Use hardware diagnostic tools to regularly check the integrity of your components. This helps in early detection of hardware issues.
- Create a System Restore Point: Before making significant changes to your system, create a restore point. This allows you to revert to a previous state if something goes wrong.
By following these tips, you can keep your system running smoothly and reduce the chances of encountering an unmountable boot volume error. Regular maintenance and proactive measures are key to a stable and reliable computer.
Conclusion
The unmountable boot volume error in Windows 11, Windows 10, and Windows 7 can be a frustrating issue, but it is not insurmountable. By understanding what causes this error and following the steps outlined in this guide, you can effectively troubleshoot and fix the unmountable boot volume error. Regular system maintenance and data backups can help prevent such issues in the future. Remember, if you lose data due to this error, tools like Recoverit can assist in recovering your lost files.
Encountering a blue screen error can be alarming, but with the right approach, you can resolve it and get your system back to normal. Taking proactive measures to maintain your system's health and performance is crucial. Keep your software and drivers updated, perform regular scans for malware, and back up your data frequently to ensure that you can recover quickly from any unexpected errors.
By following the tips and solutions provided in this guide, you can minimize the chances of encountering the unmountable boot volume error and keep your system running smoothly. Don't let this error disrupt your productivity. Take the necessary steps to fix it and prevent it from happening again.
Try Recoverit to Recover Partition
Security Verified. Over 7,302,189 people have downloaded it.
FAQ
-
Q1: What is an unmountable boot volume?
An unmountable boot volume means that your computer's boot partition cannot be accessed. This error prevents the operating system from starting up correctly, often resulting in a blue screen. The boot partition contains critical system files needed to load the OS. If it becomes unmountable due to corruption, hardware failure, or incorrect settings, Windows cannot initiate its boot sequence. -
Q2: How do I fix the unmountable boot volume in Windows 11?
To fix the unmountable boot volume error in Windows 11, you can use several methods. Start with Windows Automatic Repair, which can diagnose and fix startup issues automatically. If that doesn't work, try running the Chkdsk command to repair disk errors, repair the Master Boot Record (MBR), run a System File Checker (SFC) scan to fix corrupted system files, or check for hardware issues using built-in diagnostics tools. Each of these steps targets common causes of the unmountable boot volume error and can help restore normal operation. -
Q3: Why does the unmountable boot volume error occur?
The unmountable boot volume error can occur due to several reasons. Common causes include corrupted system files, a damaged hard drive, incorrect BIOS settings, faulty hardware components, sudden power outages, virus or malware infections, outdated or corrupted drivers, and incomplete Windows updates. Identifying the specific cause is crucial for effectively resolving the error and preventing future occurrences. Regular system maintenance and updates can help mitigate these risks.



 ChatGPT
ChatGPT
 Perplexity
Perplexity
 Google AI Mode
Google AI Mode
 Grok
Grok






















