Part 1: What Is BitLocker?
BitLocker Drive Encryption, or simply BitLocker, is an encryption software that Microsoft introduced to protect user data. It seamlessly integrates with the operating system and prevents hackers and cybercriminals from stealing or viewing data stored on the drive.

With BitLocker, you can choose to use AES 128-bit or 256-bit encryption keys. It also combines on-disk encryption technology with unique key management features.
Video Tutorial on What Is A BitLocker?
For Windows 7/8/8.1/10/11
For macOS X 10.10 - macOS 12
Supported OS – Windows
Windows first released BitLocker for Windows Vista in 2007. It received a significant update for Windows 10 that included improvements to the encryption technology, removable data drives, updated the group policy settings, and more. The updates were applied to Windows 10, 11, and Server 2016 and higher.
BitLocker is compatible with:
- Windows Vista and Windows 7: Ultimate and Enterprise Editions
- Windows 8 and 8.1: Pro and Enterprise Editions
- Windows 10 and 11: Pro, Enterprise, and Educational Editions
System Requirements
In addition to the proper version and edition of Windows, you need the following system requirements to run BitLocker:
- TPM 1.2 or later: If your computer doesn't have the Trusted Platform Module 1.2 or higher, you will need to save the startup key on a flash drive or removable hard drive.
- BIOS or UEFI Firmware: The computer needs one of these Trusted Computing Group (TGC) compliant firmware to ensure a reliable chain of trust when the system boots up. If the computer doesn't have a TPM and you're using a flash or external hard drive, it doesn't need to be BIOS or UEFI compliant
- Multiple partitions on the hard drive: You must have a minimum of two drives available on the hard drive. One of them is an NTFS file system that stores the OS and supports files. The second drive is where the files necessary to load Windows are located. BitLocker won't run on this drive, must not be encrypted, and requires FAT32 formatting for UEFI devices or NTFS for computers with IOS firmware. After BitLocker is installed, the system drive should be at least 350 MB with 250 MB in free space.
How to Use BitLocker?
BitLocker is an easy-to-use software that is integrated with Windows Vista and higher. You can access it through the Control Panel > System and Security > and then click on the Mange BitLocker option.
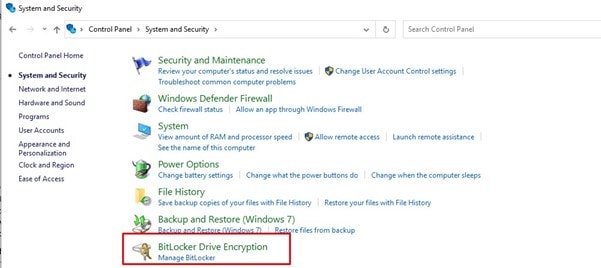
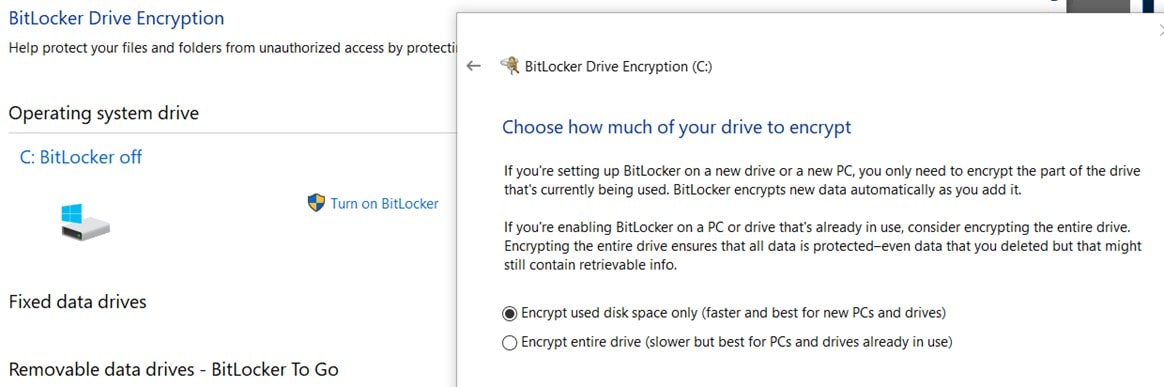
The BitLocker window will open, press the “Turn on BitLocker” link to begin, you will need admin rights on the computer to proceed. The system will run a scan of your computer to ensure that its compatible, and then give you two options for encrypting your data:
- Used Disk Space Only: This is a faster option and ideally suited for new computers or hard drives.
- Completed Disk Space: This option encrypts the entire drive. While it takes a little longer to complete, it's the best option for computers and hard drives that aren't new.
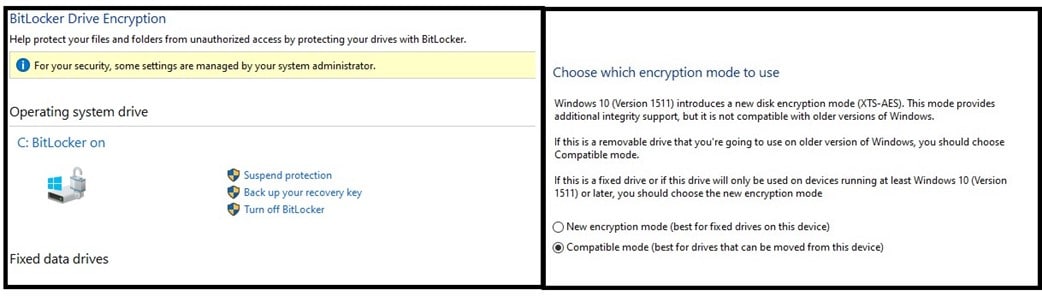
Once the encryption is complete, the data on the system and any data that is stored in the future will be protected. The BitLocker decryption key is stored on the device, allowing you to boot your computer as you normally would, although there is the option to require a password during the pre-boot.
BitLocker has a feature called BitLocker to Go, which you can use to encrypt external hard drives and USB drives.
BitLocker FAQs
- Why is there a two-partition requirement when using BitLocker?
BitLocker needs certain components on separate drives to encrypt and secure the device's data successfully. The boot drive has the operating system and support files and must format it with an NTFS file system. The second drive can't be encrypted but contains crucial components, such as the files needed to load Windows. Not only must it be different from the boot drive, but it also needs to be formatted with FAT32 or NTFS, depending on the firmware.
- Which Trusted Platform Modules (TPMs) does BitLocker support?
Your computer needs to have a TPM 1.2 or later to run BitLocker. Additionally, if you have a compatible TPM, you will also need a Trusted Computing Group (TGC) firmware, such as BIOS or UEFI.
- How to check if my computer has TPM?
Step 1: For Windows 10 and higher, open the Windows Security app, and click on the Device Security box.
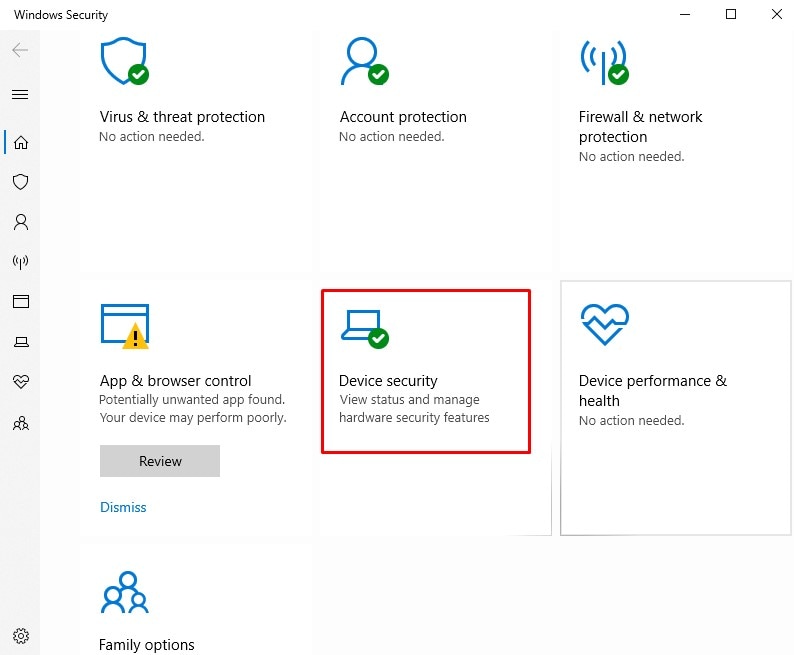
Step 2: If you have a TPM, it will be listed in the Security Processor section. Click on the Security Processor Details link to see the TPM version number.
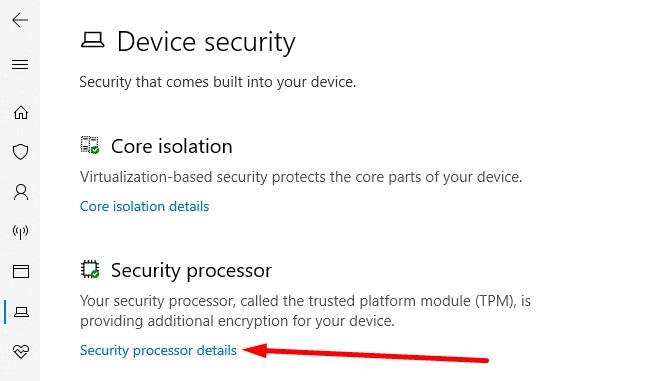
Step 3: Here you'll see the specs for your TPM. If it's 1.2 or higher, you can run BitLocker without any trouble.
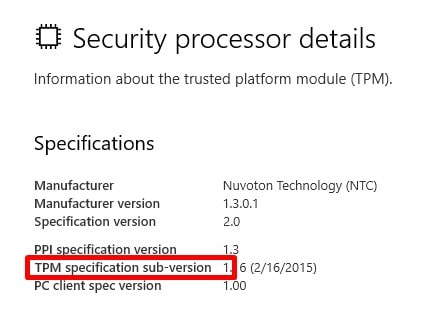
For older versions of Windows, open the TPM MMC tool (tpm.msc), and you'll see the TPM status in the Status section. Another option is to run PowerShell and run a search for Get-TPM. This will show you the specs of your TPM. Note that you need admin permission to run the PowerShell search.
- Will BitLocker run on an operating system that doesn't have a TPM?
Yes, if your PC doesn't have a TPM, you can still enable BitLocker through a USB flash drive, provided you have a startup key. The computer will still need IOS or UEFI firmware, as they are needed to activate the boot environment from the USB.
Sometimes, you may need to remove the BitLocker encryption.
- How do I obtain BIOS support for the TPM on my computer?
You will need to contact the manufacturer if your PC doesn't have BIOS firmware. Make a request for a Trusted Computing Group (TCG)-compliant BIOS or UEFI boot firmware that meets the minimum requirements to work with BitLocker.
- What access level is required to use BitLocker?
You need network or system admin access to turn on, off, or change the config settings for BitLocker on an operating system. If you're using BitLocker to Go on a removable drive, any standard user has access to turn it on, off, and change the config settings.
- What is the optimal boot order for computers that have BitLocker encryption?
When configuring the startup order for your PC, you should ensure that the hard disk drive is the first component to start. After that, you can allow the other drives, such as external or removable hard drives to run, and then the regular software and programs.
Part 2: How Does BitLocker Work?
BitLocker works with the TPM (Trusted Platform Module) to secure the data of an operating system or on a removable hard drive with powerful encryption. It creates a unique and unhackable recovery key for your hard drive. Without the key and its specific PIN, you won't be able to access the data. You can also create a recovery key as a backup in case you lose or forget your password. It's recommended that you store that key in a safe place and not on your computer.
Encryption Modes
BitLocker has three different encryption modes to choose from:
- Transparent Operation Mode: BitLocker connects with the TPM hardware to create a transparent user experience. Once it's installed, you can boot up your computer without doing anything special. The encryption key is stored in the TPM and will only decrypt the operating system and the loader code if there are no modifications to the early boot files. This all takes place in the background and doesn't require that you do anything.
- USB Key Mode: The USB drive stores the encryptions key. The operating system won't boot up if you don't connect the USB drive to the computer.
- User authentication mode: Before the computer boots, you must enter your authentication credentials, such as a PIN or password, to decrypt the OS and access your data.
Multiple Encryption Algorithms
Your data is encrypted with Advanced Encryption Standard (AES). You have the option of using 128-bit or 256-bit, which determines the length of the encryption key. Both options are incredibly powerful and secure and nearly impossible to hack.
If you're using BitLocker on Windows 10 or higher, you can choose an even more advanced encryption known as the XTS-AES encryption algorithm.
BitLocker Key Protectors
It doesn't matter how many bits the encryption is if the key isn't protected. BitLocker uses the following safety measures to secure the recovery key.
- TPM: The TPM secures a root of trust while protecting the BitLocker recovery key.
- PIN: Create a secure numeric PIN code that must be entered during pre-boot. This works together with the TPM.
- Enhanced PIN: The user has to enter an alphanumeric Pin to unlock the key. This works together with the TPM.
- Startup Key: Upload the encryption key on a removable hard drive or USB flash drive. The startup key doesn't need a TPM to work.
- Recovery Password: Generate a 48-digit code to access your data when the computer is in recovery mode. If your numeric keypad isn't working in recovery mode, you can enter the recovery password using the F1 – F10 function keys.
- Recovery Key: Upload the recovery key to an external or removable drive. You can use it to recover your encrypted data from any BitLocker volume. There are a few ways to find the recovery key, such as on your Microsoft account, on a USB flash drive, and with your system admin.
Read more: What is BitLocker PIN/Password and How to Change It?
Part 3: Difference between BitLocker and Encrypting File System (EFS)
Both BitLocker and the Encrypting File System (EFS) are secure tools developed by Microsoft for encrypting and securing data that is stored on your computer. While both programs use secure encryption, they operate very differently.
EFS requires that you go through your files and folders and add them to the encryption queue one at a time. It's helpful if you only want to protect specific files, although you have to adjust the advanced settings for each file.

BitLocker is a full drive encryption software allowing you to create a BitLocker drive. It will automatically encrypt the entire hard drive or operating system, and you can just let it run in the background. If you need to remove the encryption, there is the option to format the BitLocker encrypted drive, which isn't an option with EFS.
Another major difference is that BitLocker works with the TPM while EFS doesn't need any special hardware, making it more accessible for older computers.
BitLocker is integrated with Windows, making it incredibly easy to set up and use. It. The EFS is more of a feature of the NTFS file system and takes more configuration to set it up properly.
The two encryption programs can work together, which gives you an incredibly secure data protection solution.
Part 4: BitLocker Data Security - Is BitLocker Safe?
The burning question is, can a skilled hacker or cybercriminal still gain access to your data even with AES 128- or 256-bit encryption, security keys, TPMs, and safeguards against anyone accessing your data?

According to a source at Microsoft, there is no designed backdoor vulnerability in BitLocker. This means that government agencies or law enforcement have no way to force or compel Microsoft or a systems admin to give them access to user data.
Noted Security Concerns
While there is no official backdoor vulnerability, no system is 100% secure. Early in 2008, a team of online security researchers published a report of a "cold boot attack." It's a method for hackers to bypass full-disk encryption, which is what BitLocker provides, by booting the OS on a removable disk drive connected to a different computer and operating system. Then, they were able to dump the contents of the pre-boot memory on the new drive and access the data.
A Princeton University professor published a paper with two recommendations for protecting your data.
- Shut down the computer if you do not have physical control over it. This is a full shutdown and not just putting the device in sleep mode.
- Always configure the encryption software to only boot up with a password that the device owner manually enters.
Microsoft released an update in November 2015 to close a major vulnerability. Some hackers discovered a way to bypass the encryption key authentication process by using a malicious Kerberos key distribution center. For this attack to work, the hacker needed physical access to the computer, it had to be part of a network domain, and it didn't have PIN or USB flash drive protection.
Data Loss

One of the main problems you might have with BitLocker is your data being unintentionally deleted or lost. The most common cause of BitLocker data loss is accidentally formatting the hard drive, USB drive, or other external drives. You have to find a way to recover files from BitLocker encrypted drives, or the data stored in the encrypted environment is essentially lost to you. Another form of data loss is if you lose your password and recovery key. There are some methods that you use to unlock BitLocker without a password or recovery key.
The Bottom Line
If you are looking for an easy-to-use and secure solution to protect the data on your hard drive, BitLocker is for you. The full disk encryption software is integrated with Windows Vista and newer, as long as there is a TPM 1.2+. There are multiple safeguards put in place, including a 48-digit recovery code, to ensure that no unauthorized users can access your data without permission.

 ChatGPT
ChatGPT
 Perplexity
Perplexity
 Google AI Mode
Google AI Mode
 Grok
Grok






















