As digital technology advances, there are several computing concepts that you don't need to fiddle around. With every new update keeping the function as smoothly as possible, you can perform the required actions without going into the more intricate details.
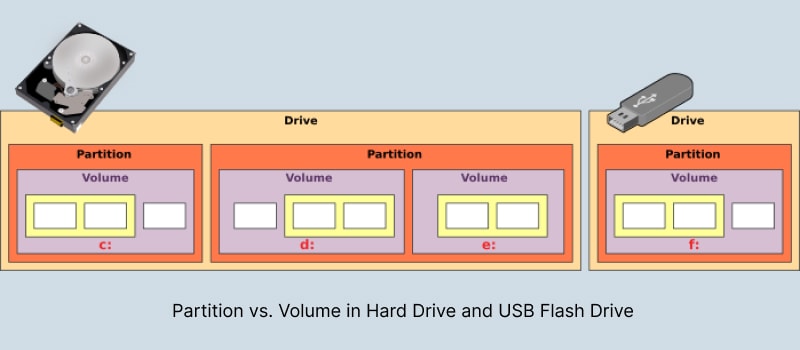
However, that also leaves you out of the loop for several integral system functions. One of them is the difference between partition and volume, which has become less apparent with more advanced storage solutions. So, if you wish to gain detailed insights into partition vs. volume, this is just the guide for you.
Part 1. What Is a Volume and Partition in Windows Computer?
Despite what your system configuration might let you believe at first glance, volumes and partitions are two separate entities. You can learn a quick definition between the two from the following points.
What Is a Volume?
A disk volume is referred to as a storage area that can be accessed using a single file system (such as FAT32, exFAT, or NTFS) that your computer recognizes. The term is often used in the context of operating systems. In addition, storage devices like flash drives, memory cards, and some partitions of the hard drives can be considered volumes.
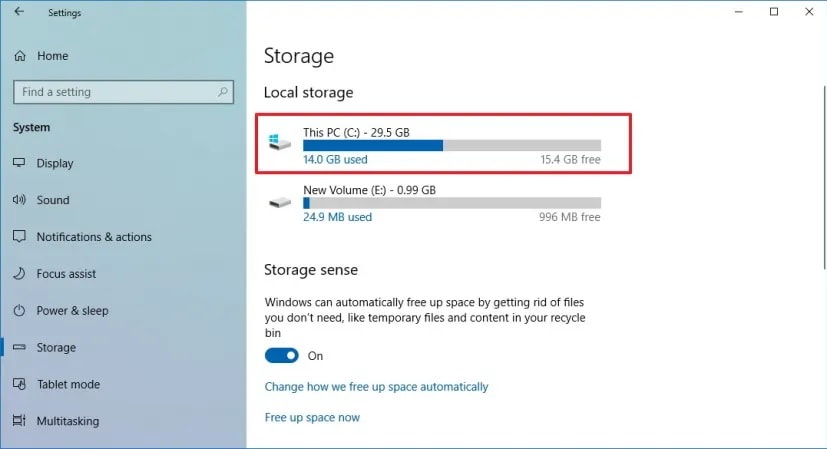
The data within the volume can only be accessed once the system identifies it. You can quickly move data within a volume with an appropriate file system. It doesn't require any physical modifications. However, doing the same among different volumes can prove more challenging, especially when both of them run with separate file systems.
What Is a Partition?
A disk drive can be divided into several storage units called partitions, whether an HDD or SSD. Each partition can hold multiple volumes, depending on its type. You can create three partition types in a hard disk drive: primary, extended, and logical. Furthermore, A disk drive can contain a maximum of four primary partitions. Of those, three can be primary partitions and one as a single extended partition. You'll learn more about the types of partitions later in this article.
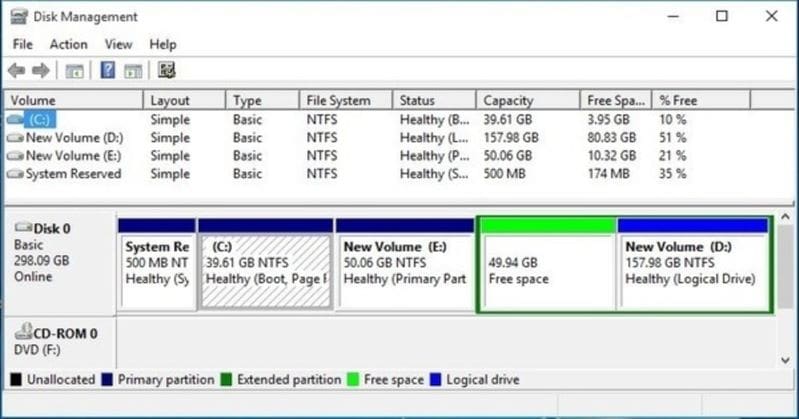
A single partition requires one file system. When there are multiple primary partitions in a hard disk, only a single partition can be active at any given time. The other partitions will remain hidden. It is essential for a bootable drive to contain a primary partition that contains all the necessary files for the OS.
Information about the partitions in a computer is included in the Partition table, which is located in the Master Boot Record (MBR) or GUID Partition Table (GPT). The extended partition in a hard disk drive could be subdivided into several partitions called logical partitions. The extended partitions act as containers for logical partitions.
One or more data tables, the Extended Boot Records (EBR), define the structure of all logical partitions within a drive. As you create more partitions, you can store more files, even belonging to different file systems, on those partitions. Additionally, you can create multiple primary partitions containing MBRs to operate multiple OSs on the same system.
Part 2. What Is the Difference Between Partition and Volume?
Now that you know the basic idea behind partitions and volumes, let's take a closer look at their differences in a direct side-by-side comparison.
Partition vs. Volume in Types
You can configure a volume on your PC to be any of the following types:
Volume Types |
Explanation |
| Simple Volume | It is a physical disk that functions like an independent unit with a single file system. It usually contains the operating system and any additional files simultaneously. |
| Mirrored Volume | A mirrored volume uses two copies on different physical disks to duplicate data. When new data is written to the mirrored volume, it shall be converted into two copies. If one of the physical disks fails, the data on the disk becomes unavailable. Still, the mirrored volume is a fault-tolerant volume, which means the data on the other physical disk is used instead. |
| Striped Volume | This volume is created by combining areas of free space on two or more disks into one logical volume. A striped volume does not provide fault tolerance, which means the entire volume will fail even as one of the disks containing a striped volume fails. |
| Spanned Volume | A spanned volume combines areas of unallocated space from multiple disks into one logical volume. When new data is written into a spanned volume, data will first fill up the free space on the first disk, then fill up that on the next disk, and so on. It increases the storage efficiency of data and makes it quicker to access. |
| RAID Volume | RAID stands for Redundant Array of Independent Disks. It is a volume with data and its parity striped intermittently across multiple physical disks. As a fault-tolerant volume, it allows you to recreate the data should the disk become damaged or corrupted. It is constructed from the parity and the remaining data on the disks. It has several configurations, with RAID 5, RAID 6, and RAID 10 being the most popular. |
On the other hand, partitions can be of the following types:
Partition Types |
Explanation |
| Primary Partition | A primary disk partition is identified by a drive letter and is used for storing operating systems and other essential data. The C: drive is often a primary partition. Although, you can create more primary partitions to install other operating systems. A single drive can typically support up to four primary partitions. |
| Logical Partition | A logical partition is a subset of a computer’s hardware resources. A PC can have as many logical partitions as the number of OSs, even allowing you to virtualize various sessions on the same system. |
| Extended Partition | Additional logical partitions facilitate the storage of any excess data that may be configured for a separate file system. |
Partition vs. Volume in Max.Size
The size of a volume on a PC is limited by the type of file system in action. For example, operating a drive configured for a FAT32 file system can create a single volume with a maximum of 4 GB storage. But, an NTFS file system can support volumes as large as 8 petabytes.
In the case of partitions, only the primary partition containing the Master Boot Record (MBR) is limited in size. On Windows 10/11, you can create a primary partition no more than 2.199 TB in size.
Partition vs. Volume in Max. Number of Disks
The maximum number of volumes that can be allocated to a single system depends upon the operating system it's running. For example, for Windows 10, you can create up to 26 volumes at a time, as each one corresponds to a specific letter of the English alphabet.
In the case of partitions, a disk can have a maximum of four primary partitions, provided it runs through an MBR. If you can convert MBR to GPT, you can create up to 128 primary partitions. There is no limit to how many extended partitions you can create, regardless of the number of primary partitions on the drive.
Partition vs Volume in Creation
While you can create a volume or partition using the same Disk Management tool in Windows, there are limitations as to how you can allocate space to either of them. Moreover, if your drive is not configured correctly, you might have to format partitions to create a new volume.
You can create a new volume by going to Disk Management and initializing the New Simple Volume Wizard, provided the disk is a dynamic disk. If it is a basic variant, you best format a new partition.
Partition vs Volume in Security
A volume has much higher security than a partition, as it allows for dynamic data allocation. You can also use File Explorer to encrypt specific volumes on your system. As far as partitions are concerned, all users with access to your system can access the data on any partition they desire.
Part 3. How to Create a Volume or Partition?
You can utilize the Disk Management utility in Windows to create a volume or partition out of any unallocated disk space within a drive.
Create a Volume
You need a dynamic disk installed on your system to create a volume. Then, follow the steps below to create a volume on Windows 10.
Step 1. Launch the Disk Management utility from the Start menu or using the Search function in the taskbar.
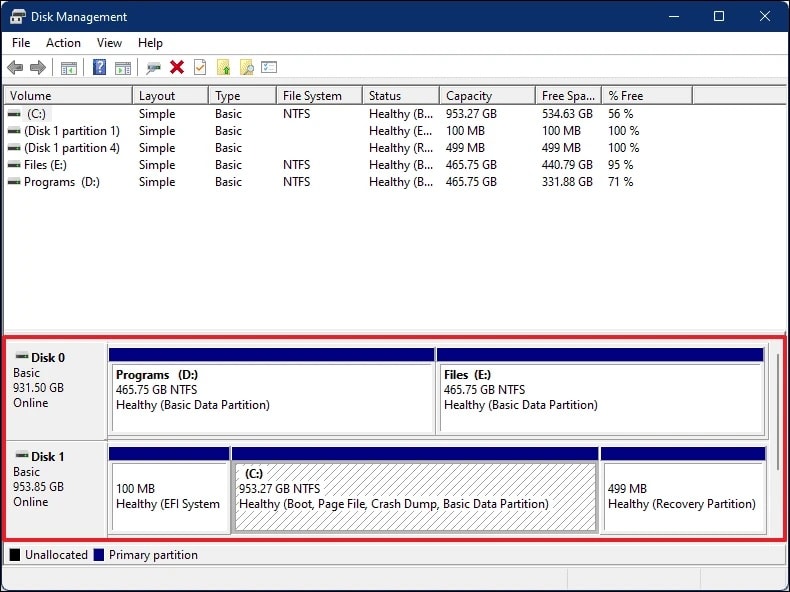
Step 2. You can select a dynamic disk from the available list of disks to initialize the New Simple Volume Wizard. In case the disk is a basic disk, you can convert the basic disk to dynamic.
Step 3. Once you have selected the required disk, right-click on the unallocated region and choose New Simple Volume from the drop-down menu.
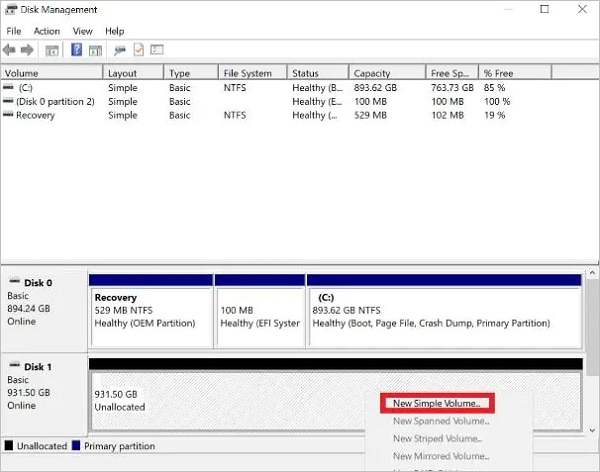
Step 4. Enter the desired size of the disk and click Next.
Step 5. Now, you need to assign a letter to your volume. Choose the one you want and click the Next button.
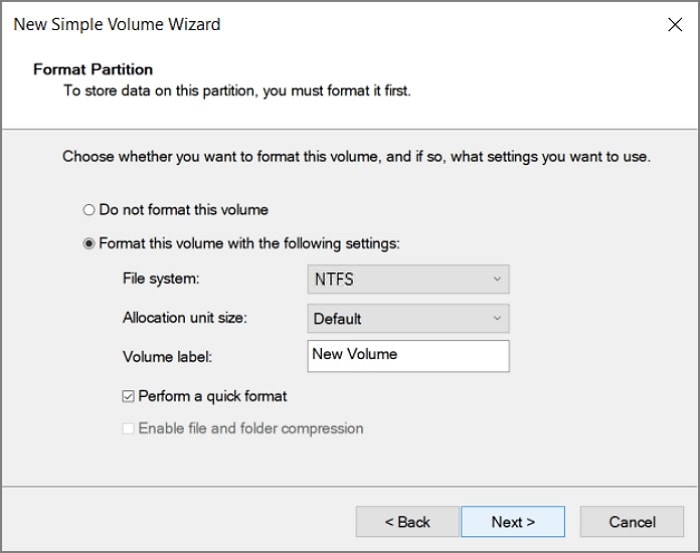
Step 6. Format the volume or the entire partition as per your preference and click Next to proceed. Remember that formatting the partition will erase all the data on it.
Step 7. Review your settings and click the Finish button.
You can also check the video below to learn how to create a volume on Windows 11.
Create a Partition
In order to create a new partition, you need to format the space according to an appropriate file system compatible with your OS. Visit the page about creating a new partition to get the step-by-step guide.
Part 4. How to Delete a Volume or Partition?
Deleting a volume or partition is pretty straightforward. First, you must access Disk Management and right-click on the volume/partition you wish to remove. Next, select the 'Delete Volume' or 'Remove Partition' button and confirm your choice.
You can look over the video guide on Youtube for a thorough walkthrough.
Part 5. How to Recover a Deleted Volume or Partition?
When deleting a volume or reformatting a partition, you lose access to all the data you had stored on it beforehand. Thus, if you don’t have a backup, you may have to rely on data retrieval software that can help you get it back. One of the most reliable choices you can go for is Wondershare Recoverit.

Wondershare Recoverit – Leader in Data Recovery
5,481,435 people have downloaded it.
Recover data from 500+ data loss scenarios, including unexpected deletion, formatting, hard disk corruption, virus attacks, computer crashes, etc.
Recover lost or deleted photos, videos, music, emails, and other 1000+ file types effectively, safely, and completely.
Retrieve data from almost any storage devices, including computers/laptops, USB drives, SD cards, external hard disks, digital cameras, etc.
95% recovery success rate. The user-friendly interface lets you preview the files before recovery.
You can download Wondershare Recoverit for your preferred Windows or macOS computer. Once installed, follow the below-mentioned steps to get any essential data back from a volume or partition.
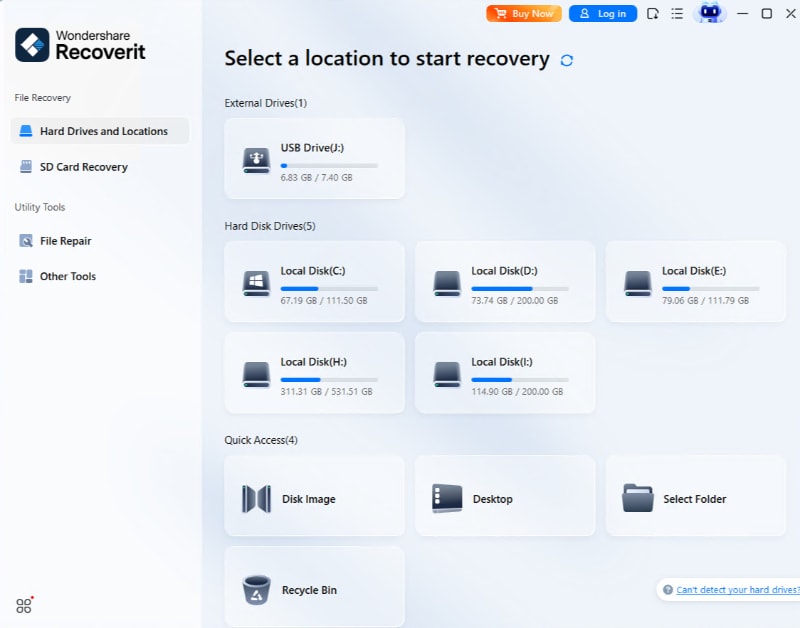
Step 1. Select the Volume or Partition
Launch Recoverit data recovery and select a location from where you want to recover the files.
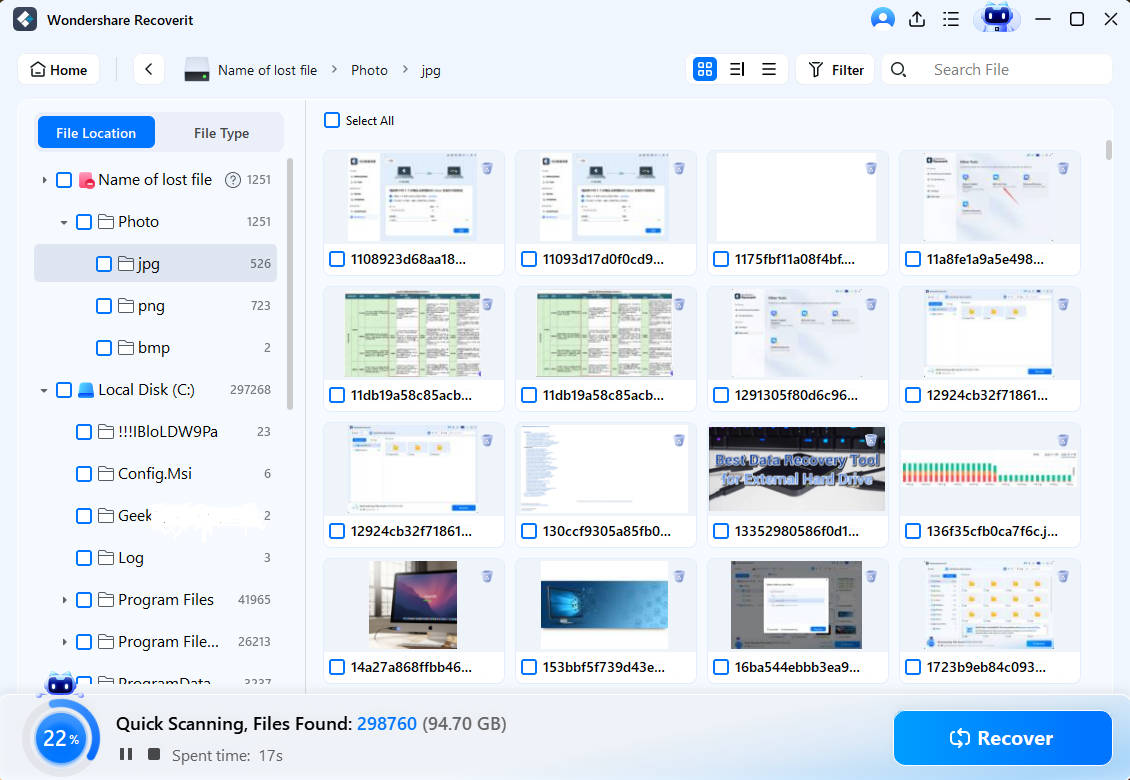
Step 2. Scan for Lost Data
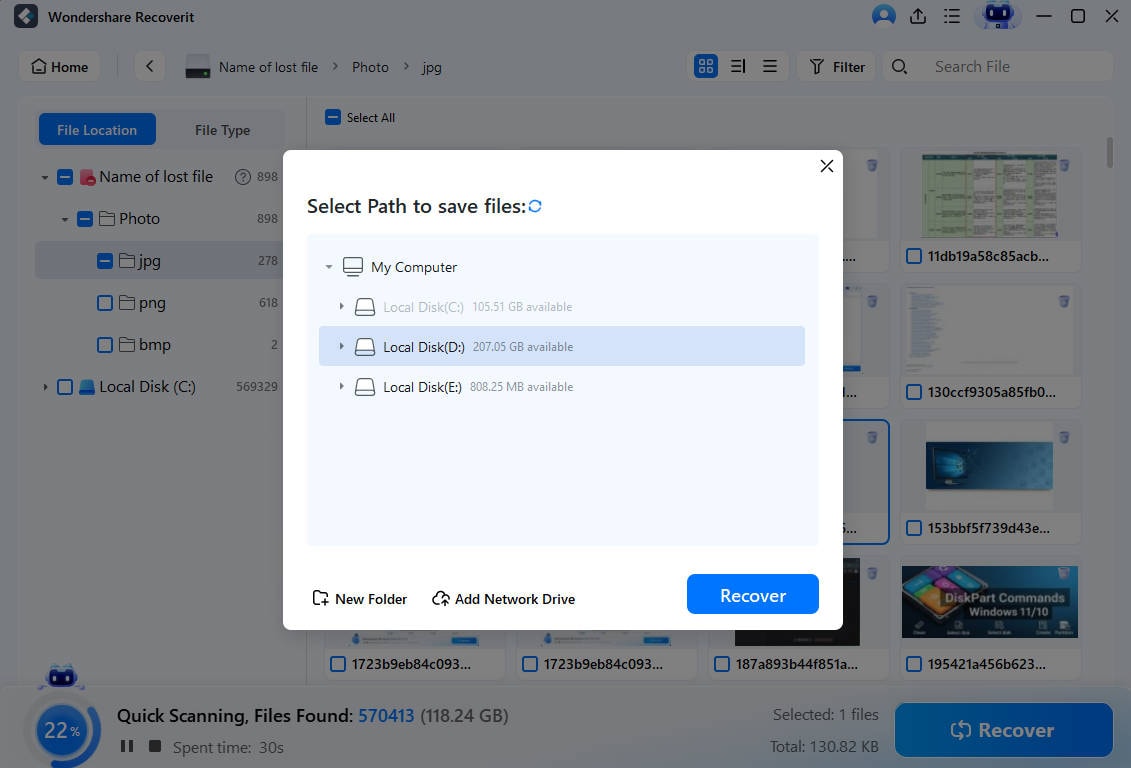
Recoverit will start scanning deleted partitions or volumes automatically. During the scanning, you can choose the type of files you are looking for or type in the filename in the search bar to find the desired files quickly.
Step 3. Preview and Recover
You can use the Preview button to verify the files you wish to retrieve. Once done, select the relevant files and click on Recover to restore the files to a safe location.
For Windows XP/Vista/7/8/10/11
For macOS X 10.10 or later
When the process concludes, all the selected files will appear at the selected location. Depending on the size of the disk and your computer’s hardware, it can take some time to recover all the files. So, it is best to work on any other disk in the meantime or leave your system idle with a consistent power supply.
FAQs About Partition and Volume
Is a partition the same as a volume?
No. Although most people use the two terms interchangeably, partition and volume are separate entities. Each partition can hold multiple volumes, depending on its type.
What makes a volume different than a partition?
A partition is part of the disk allocated for a specific file system, whereas a volume is that allocation divided into various segments for more convenient data management.
Should I add volume or partition on Mac?
If you desire to allocate data, it is best to add a partition to your Mac computer first. That can help you determine the adequate file system for your needs and create the space for an operating system, should you require it.
Once you’ve done adding partitions, you can use volumes to segment it further and make the data management within that partition much more straightforward.
How many partitions are best for a 1 TB drive?
If you have a 1 TB HDD or SSD, it is best to have at least three partitions on the disk. One of them can be used as a primary partition to install the OS and all the necessary files to run your system. The other two can contain data or software that you need in your daily routine. Most people would prefer work data on one partition and entertainment on the other.
Do partitions improve performance?
Yes. If you segment your partitions appropriately, you can massively improve the performance of your system. You can utilize either of the two methods mentioned as follows:
● Partition Pruning: It is the arrangement of data in a partition using a viable parameter, such as date of creation or data type. If you have specific data stored in the partition, it can help the system quickly scan the drive with the most relevant match instead of the entire system.
● Partition-wise Joins: If you know your way around partition tables, you can join two or more together to create an integrated database with access to multiple partitions. That way, scanning the entire system is quicker, and you can locate the files you want much faster.
Summing Up
It can be confusing for the casual user to learn the difference between partition and volume. We hope this guide helped you understand it by granting you new insights and valuable tools you can use. If you have any other queries, feel free to share your thoughts in the comments below.

 ChatGPT
ChatGPT
 Perplexity
Perplexity
 Google AI Mode
Google AI Mode
 Grok
Grok






















